* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Prothrombin complex concentrate Octaplex
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
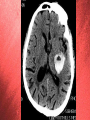
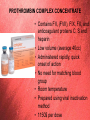
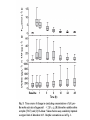
Prothrombin complex concentrate Octaplex Maude Latulippe, CCFP-EM res Grand Rounds, FMC CASE • 73 year old male • Hx CVA in 2007 and A fib on Coumadin • Brought in by EMS for right sided weakness and aphasia. • Pt unable to walk • Pt speaks limited English and follows a few commands. No family is present. On exam: • Vitals 37.2, 100, 16, 167/98, 98% RA • Glucometer 6.8 • Eyes open spontaneously. He has a right lower face, arm and leg hemiparesis. He is agitated. • EKG: a fib • Remainder of physical exam is noncontributory. PMHX: • Ischemic CVA in 2007 secondary to A fib and subtherapeutic INR. Was left MCA symptomatology • A fib • CHF • Remote MI • HTN • PVD • Chronic venous insufficiency • Dyslipidemia Meds: • Warfarin • Lipitor • Micardis • Ramipril • Lasix Post CT the patient deteriorates: GCS drops to 7 (E2 M4 V1) Breathing becomes more shallow and appears less effective. Eyes deviate to the left. CBC, lytes, creat unremarkable INR 3.6 PTT N Management: • Should vitamin K be given? • How long does FFP take to work? • What are the other disadvantages of FFP? • What new blood product is the best treatment for this patient? • What are the other indications for Octaplex- prothrombin complex concentrate? Objectives • What is Prothrombin Complex Concentrate (PCC)? • Potential risk • Advantages: PCC vs Vit K PCC vs FFP • How to use it? Indications/Protocol PROTHROMBIN COMPLEX CONCENTRATE • Contains FII, (FVII), FIX, FX, and anticoagulant proteins C, S and heparin • Low volume (average 40cc) • Administered rapidly, quick onset of action • No need for matching blood group • Room temperature • Prepared using viral inactivation method • 1150$ per dose Octaplex: Contains FII, FVII, FIX, FX in the ratio of approx. 1:1:1:1 Role of prothrombin complex concentrates in reversing warfarin anticoagulation: A review of the literature, Cindy A. Leissinger, Am. J. Hematol. 83:137–143, 2008 • Review of 14 studies involving urgent warfarin reversal with PCCs • 460 patients • 7 thrombotic complications = 1.5% • … in patient with a pre prothrombotic co-morbidity Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 2008 Single-arm prospective study was from Oct 05 to Nov 06 at 15 centers in Austria, Germany, Hungary, Israel, Lithuania, the Netherlands, Poland, andSwitzerland. 43 patients with INR > 2 : 26 requiring interventional procedures 17 acute bleeding Method: • Vit K given prior to PCC infusion (88% pt) • Dose Beriplex by INR INR Dose IU/kg 2-3.9 4-6 >6 25 35 50 • Concomitant tx with blood, plasma hold for 30 min Primary end point: - INR at 30 min 40/43 INR<1.3 3/43 INR=1.4 Plasma levels of coagulation factors and clotting inhibitors following administration of Beriplex® P/N. F, factor. Adverse events • Adverse events in 25 pt (58%) • Serious : 6 patients – 3 died 1 death possibly related to treatment • All other serious/non-serious AE not related to treatment New generation PCC Thromboembolism risk Better balance pro/anticoag factor No active phospholipid No activated factor (FVIIa, FIXa) Often only 1 dose required Viral transmission 4 cases Parvovirus B19 seroconversions Allergic reaction Treatment options for reversal of oral anticoagulants Vitamin K Application of vitamin K: oral: slow decrease of INR, start within 12-24 h i.v. : slow decrease of INR, start within 6-8 h FIX and FX takes longer Warfarin resistance for 1 week Studies comparing PCC with Vit K Treatment, time and INR Fresh frozen plasma (FFP) • • • • • • • • 15 ml/kg – 1050 ml in 70 kg patient 30-45 min from demand to start infusion Blood group specific Thawed 1-3h for reversal Longer time to infuse TRALI, infection, allergic reaction 200$/unit Studies comparing PCC and FFP Hematoma Growth and Outcome in Treated Neurocritical Care Patients With Intracerebral Hemorrhage Related to Oral Anticoagulant Therapy Comparison of Acute Treatment Strategies Using Vitamin K, Fresh Frozen Plasma, and Prothrombin Complex Concentrates. Huttner Stroke 2006 • Retrospective review 55 pts ICH -Group 1 (31pts): PCC +- FFP +- VitK -Group 2 (18pts): FFP +- VitK -Group 3 (6pts) VitK • Outcomes -Reversal of INR -Hematoma growth (CT or MRI>33%) -Neurological outcome (1 year) • INR reversal (<2h) -84% vs 39% vs 0% (p<0.01) • Frequency of hematoma growth -19.3% vs 33.3% vs 50% (p<0.01) • Extent of hematoma growth -44% vs 54% vs 59% (NS) • Incidence of growth PCC vs No PCC -19.3% vs 37.5% (p<0.01) • No difference in outcome PCC vs FFP Favouring PCC Rapid No thawing No blood group testing and matching No volume limitation fast application Highly predictable effect (Antagonism of OAC) No acute lung injury (TRALI) Is INR a good test? • Sensitive to FII, FVII and X (but not FIX) • Thromboelastography a better test? Profile of clot formation in whole blood Guidelines controversies Indications for use (AHR) 1) For Warfarin reversal only in cases of Urgent surgical procedure required or Massive bleeding – CNS, GI 2) INR >1.5 CONTRAINDICATION: A. History HIT Not recommended for* A. Elective reversal of OAT pre-invasive procedure B. Tx of elevated INRs without bleed or need for surgical intervention C. Massive transfusion D. Coagulopathy associated with liver dysfonction E. Recent Hx thrombosis, MI, recent ischemic stroke or DIC Special population: Pregnant/lactating women, pediatric, congenital factor II and X deficient patients *Evaluation case-by-case basis possible with hematologist/transfusion medicine physician on call PCC Dosage (Regional guidelines): (less than the manufacturer’s recommended dose) 40mL (1000IU Factor IX activity) and Vit K 10mg IV (Higher dose may be needed in extremes of INR or weight) - Max 120mL (3000 IU) Administration: Initial rate 1mL/min x 10 min max rate 3 mL/min F-U: PT/INR 15 min post dose Availability • Octaplex available at FMC, PLC and RGH • Any physicians who follow the protocol can order Octaplex. • An Octaplex request form must be completed and faxed to the transfusion Medicine department. • Octaplex available very rapidly Progress of case: • FFP is ordered. 10mg IV Vitamin K given. • Transfusion medicine is called to release Octaplex from the blood bank. • Octaplex 40cc (2 vials) given • INR is reversed from 3.8 to 1.3 within 15 minutes of administration of Octaplex. • The patient does not appear to worsen clinically and does not require intubation. • He is admitted to the Stroke Team. A CT scan the next day unfortunately shows significant progression of the bleed. The patient has very poor neurological function. Goals of care are changed to comfort measures and he dies on the 10th day after admission. Take home point • Octaplex is a Prothrombin Complex Concentrate available in Calgary through blood bank • Contains FII, FVII, FIX, FX, protein C, protein S and heparin • Use if INR>1.5 + Massive bleeding (GI/ICH) or Urgent surgical procedure needed • C-I: HIT • Give 2 vials (40cc) + vit K 10 mg IV • Should be effective in less then 30 min, recheck INR • Very sick patients with poor outcomes, mortality/morbidity benefit still unproven Special thanks • Thanks to Dr Carey, Dr Dorrington, Dr Shelagh Coutts (neuro) and Dr Rad (hemato) • Thanks to Carolyn Jursa, Octapharma representant and to the department of blood product FMC • • • • • • • • Prothrombin complex concentrate (Beriplex P/N) in severe bleeding: experience in a large tertiary hospital, David Bruce,Tim JC Nokes, Department of Haematology, Derriford Hospital, UK, critical care,2008 Prothrombin complex concentrate (Beriplex P/N) for emergency anticoagulation reversal: a prospective multinational clinical trial., PABINGER, B. BRENNER J, Thromb Haemost 2008, Warfarin-reversal: results of a phase III study with pasteurised, nanofiltrated prothrombin complex concentrate, Ingrid Pabinger-Fasching , Medical University of Vienna, Austria Role of prothrombin complex concentrates in reversing warfarin anticoagulation: A review of the literature, Cindy A. Leissinger, Philip M. Blatt, American Journal of Hematology, 2008 Current Practices and Unresolved Questions Intracerebral Hemorrhage Associated With Oral Anticoagulant Therapy, Steiner, Stroke 2006 Hematoma Growth and Outcome in Treated Neurocritical Care Patients With Intracerebral Hemorrhage Related to Oral Anticoagulant Therapy Comparison of Acute Treatment Strategies Using Vitamin K, Fresh Frozen Plasma, and Prothrombin Complex Concentrates, Huttner, Stroke 2006 The use of PCC in Intensive Care Medicine, symposium Oct 2009, UK Up to date