* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Practice of Statistics
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
Name: ______________________
Chapter 6: Probability and Simulation: The Study of Randomness
Section
6.1 & 6.2
6.2
6.3
Topics
Page #
Assignment
Simulation
Trials
Independent Intro
Probability
Random
Probability model
Sample space
Event
Tree diagram
Multiplication principle
Sampling with or without
replacement
397-398
1, 3, 5
402-404
7, 9, 11, 13
416-417
29, 32, 33, 36
Probability rules
Union
Intersection
Empty
Venn diagram
Probability of a finite sample
space
Multiplication rule for
independent events
Disjoint vs. independent
423-425
37, 38, 40, 44
430-435
45-47, 49, 50, 61, 62, 64
440-441
65-70
446-447
74, 78
453-455
86, 87, 93, 94
Rules of Probability
Joint
Joint event
Addition Rule: joint
Complement
Multiplication rule: joint
Conditional probability
Intersection
Tree diagram
Independence test
Ch 6 Review
411
WS
23, 24
Probability Worksheet
Practice Exam
Chapter 6: Probability
Key Vocabulary:
trial
random
probability
independence
random phenomenon
sample space
S = {H, T}
tree diagram
6.1
replacement
event
P(A)
Complement AC
disjoint
Venn Diagram
union (or)
intersection (and)
Simulation
1. In statistics, what is meant by the term simulation?
2. What are the steps to perform a simulation?
3. How do you use RandInt on the calculator?
4. In statistics, what is meant by an independent trial?
joint event
joint probability
conditional probability
6.2
Probability Models
1. In statistics, what is a sample space?
2. In statistics, what is an event?
3. Explain why the probability of any event is a number between 0 and 1.
4. What is the sum of the probabilities of all possible outcomes?
5. What is meant by the complement of an event?
6. When are two events considered disjoint?
7. Explain the difference between disjoint and independent.
8. What is the Multiplication Rule for independent events?
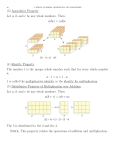
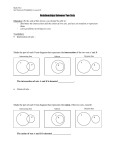
9. Draw a Venn diagram that shows the union of two events. Then draw one that shows the
intersection.
6.3
General Probability Rules
1. State the addition rule for joint events.
2. What is meant by joint probability?
3. What is meant by conditional probability?
4. State the general multiplication rule.
5. How is the general multiplication rule different than the multiplication rule for independent
events?
6. State the formula for finding conditional probability.
7. State the formula used to determine if two events are independent.
8. Explain how to use a tree diagram to find the probability of something.