* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Geography (ppt)
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
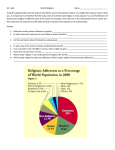
Unit 2 Human Geography World Population Population Growth The increase in the world’s population Growth Rate How fast the population of a country is growing. Birth Rate How many people are born in a country each year. Death Rate How many people die in a country each year. Natural Increase When population grows at such a rate that resources can keep up. Doubling Time How long it takes for the population of a region to double. Population Distribution Population Distribution is uneven. Many things affect this including environmental issues and human issues. Factors that in distribution • Natural resources (oil, arable land, water) • Climate (hot/cold; wet/dry) • Economic development • Government policy • Rural/urban settlement • Capital resources (transportation, technology) • Conflicts (refugees) Migration The movement of people Push Factors Things that make people want to leave an area such as conflict, lack of jobs, persecution, etc. . . Pull Factors Opposite of Push Factors. Things that make people want to go to an area such as lack of conflict, economic opportunity, freedoms, family ties, etc . . . Urbanization People leaving rural (country) areas to go to urban (city) areas. Global Cultures Culture: The way of life of a group of people Elements of Culture Language Latin America Spanish and Portuguese speaking world Francophone world French Speaking Religion Muslim World Found mostly in North Africa and the Middle East (SW Asia). Also found in parts of SE Asia. Cultural Change Culture Hearths A place of great cultural significance to a particular area. Cultural Contact (Cultural Diffusion) The spreading of culture from one area to another. Industrial and Information Revolutions Great changes in the way that people work and communicate that have influenced the world. Types of Religion • Ethnic Religions o Usually involves one ethnic group and usually does not spread to other cultures. o Examples: Hinduism (India), Confucianism and Taoism (China), Shintoism (Japan), and Judaism (Israel) • Animist Religions o Belief in the presence of spirits and the forces of nature o Polytheism: Belief in many gods o Examples: Native American Religions, Hinduism • Universalizing Religions o Seek followers all over the world by using missionaries o Monotheism: Belief in one God o Examples: Christianity, Islam, and Judaism Buddhism Originated in India, but no is found mostly in East and SE Asia Hinduism Found mostly in India Christianity Began in the Holy Land. Now is dominant religion of Europe, Latin America, and some other areas. Judaism The Jews have been scattered throughout the world because of the Diaspora. There are large concentrations in the United States and Israel. Levels of Economic Activity Primary Economic activities that deal directly with natural resources. Mining, forestry, drilling for oil, agriculture, etc. . . Secondary Manufacturing Tertiary Service industries Retail Economic Systems Traditional Economy Things are done the way they have always been done. Market Economy (Capitalism): Producers and consumers decide what is made. Producers: Make goods or provide services Consumers: Consume goods and services Supply and Demand: The balance between what is available and what people want. Mixed Economy: A blending of different economic systems. Command Economy The Government decides what is produced Socialism: Everything is jointly owned by everyone Communism: The government owns everything. There is no private property. Resources, Trade, and the Environment Resources: What nations have to produce the things they need Natural Resources: Resources that come from the earth Renewable: Natural resources we can get more of. Ex: Soil, Forests Non-Renewable: Natural resources we can not get more of Ex: Fossil Fuels Capital Resources Plants and Equipment: Infrastructure Money for Investment Human Resources Things that people can provide Education: The higher the education of an individual, the more they can usually contribute to the economy. Entrepreneurial Ability: The ability to start a new business. Developed Countries Developed countries have a higher standard of living. They make most of their income from Secondary and Tertiary economic activities. They have a low birth rate They have a low death rate They have a long life expectancy They have a small percentage of the population under 15 They have a high literacy rate Low infant mortality High per capita GDP Developing Countries These are countries with a lower standard of living. They make most income from primary economic activities They have low per capita GDP They have high birthrate Low literacy rates High infant mortality Low life expectancy High percentage of the population under the age of 15 High death rate ██ High human development ██ Medium human development ██ Low human development ██ Unavailable Political and Economic Systems Levels of Government Unitary System All power is held by the central government Federal System Power is divided between the State and National Government. Types of Government Autocracy (Totalitarianism) Single ruler holds all power Ex: Dictatorship Absolute Monarchy Constitutional Monarchy Oligarchy Rule by a small group Aristocracy Rule by rich land-owners Democracy Government where people vote and elect leaders Direct: People vote directly on issues Representative: People elect others to make decisions for them. World Trade Uneven Distribution of Resources Not every country has everything it needs to survive and continue to develop. Comparative Advantage Countries will make what they can sell for profit and import what they can not make themselves. Interdependence Countries need to trade with each other Multinational Corporations Businesses that operate in more than one nation. Ex: McDonalds, Nike, etc . . . Trade Organizations/Economic Organizations EU: European Union NAFTA: North American Free-Trade Agreement ASEAN: Association of SE Asian Nations OPEC: Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries Barriers to Trade Tariff: A tax against imports Embargo: To block an import completely Quota: To limit the amount of an import