* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Random Sampling
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
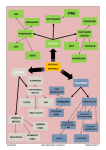
TYPES OF DATA – YEAR 7 Qualitative Data Data where you can’t have ‘in-between’ values e.g. How many children you have. Quantitative Data Data with numbers in it e.g. time, height, shoe size, age. Can be discrete or continuous. Continuous Data Not a number, often descriptive e.g. colour or make of car. Discrete Data Data you have collected yourself e.g. through questionnaires etc. Bivariate Data Data that can take on any value e.g. time and height. Primary Data Takes information that somebody else has already found. Secondary Data Combination of two variables (values) e.g. you might have age and weight. Categorical Data Name of data that has been put into groups e.g. things put into solid, liquids and gases. TYPES OF DATA – YEAR 7 1. List the following in your books under the headings Emma works in a charity shop. She sorts the clothes by SIZE The time it takes to cook a chicken kiev. The FLAVOUR of a packet of crisps. The time taken to run a marathon. The number of seagulls on a beach. The score you get on your next exam. The average speed a cyclist travels on his way to work. The weight of a bag of sugar. The weight of a bag of sugar. The colour of a jumper. Town Number of bedrooms. Cost of a mobile phone call. Time spent on a mobile phone call. qualitative data and quantitative data 2. Now pick two different colours. Colour all the discrete data in one colour and all the continuous data in another colour.