* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download KS3 Bio 7B Reproduction 116marks 4Teachers
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
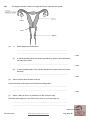
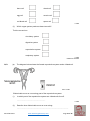
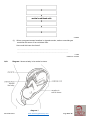
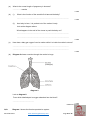
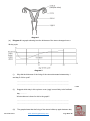
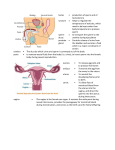
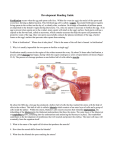
Name KS3 Bio 7B Reproduction 116marks 4Teachers Q1. The drawing shows a baby inside its mother’s uterus. Some substances pass from the mother’s blood to the baby’s blood. Other substances pass from the baby’s blood to the mother’s blood. Which way, if any, do the substances in the table pass? Tick one box in each row. 4 marks Patrick Brannac www.SmashingChemistry.com Page 1 of 35 The diagram shows a baby developing inside its mother’s body. Q2. (Adapted from Introduction to Biology, D.G.Makean; published by John Murray 1971) (a) Eggs are produced in organ X. What is the name of organ X? .................................................................................................................... 1 mark (b) The baby grows in a bag of amniotic fluid which is inside organ Y. What is the name of organ Y? .................................................................................................................... 1 mark (c) (i) Through which part, labelled in the diagram, is food passed from the mother to the baby? ............................................................................................................. 1 mark (ii) Name one useful substance, other than food, which passes from the mother to the unborn baby. ............................................................................................................. 1 mark (d) The diagram shows an organ system of the mother’s body. What is the name of this organ system? .................................................................................................................... 1 mark Maximum 5 marks Patrick Brannac www.SmashingChemistry.com Page 2 of 35 Q3. The diagrams below show the male and female human reproductive systems. not to scale (a) The table below contains descriptions of parts of the human reproductive system. Complete the table to give the name of each part. name of part description the tube that carries an egg to the uterus the organ that produces sperm he organ that produces the egg 3 marks (b) The diagram below shows an unborn baby. Patrick Brannac www.SmashingChemistry.com Page 3 of 35 Complete the sentences below by filling in the gaps. In humans, normal pregnancy lasts for .................. months. When the foetus is ready to be born, muscles in the uterus wall start to ............................................. . 2 marks After the baby is born, the .......................................................... connecting the foetus to the mother is cut. 1 marks maximum 6 marks Q4. The diagram shows a woman’s reproductive system just before fertilisation takes place. An egg cell, a ciliated cell and a sperm cell are drawn in more detail. not to scale (a) An egg cell is fertilised by a sperm cell in the oviduct. Describe one way in which a sperm cell is adapted to its function. ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... 1 mark (b) What is the function of the ciliated cells in the lining of the oviduct? ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... 1 mark Patrick Brannac www.SmashingChemistry.com Page 4 of 35 (c) A hen’s egg contains yolk which is a food store for the developing chick. A human egg cell does not contain yolk. Describe the way a human foetus gets its food. ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... 3 marks Maximum 5 marks ## (a) This question is about the menstrual cycle. Choose words from the list to complete the sentences. a daily the uterus the beginning the middle a monthly an ovary the end a weekly the vagina Menstruation is part of ......................................................... cycle. The cycle begins when the lining of ...................................... breaks away. An ovum (egg) is released from .......................................... at about .............................................. of each cycle. 4 marks (b) During adolescence, boys’ bodies change. Describe two of the changes. ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... 2 marks Maximum 6 marks Patrick Brannac www.SmashingChemistry.com Page 5 of 35 Q6. The drawing shows a flower. Six parts are labelled P, Q, R, S, T and U. (a) The names of three of these parts are given in the table. Write the letter of each part next to its name in the table. 3 marks (b) Which two letters on the drawing show parts of the stamen? ................................ and .................................. 1 mark Maximum 4 marks Patrick Brannac www.SmashingChemistry.com Page 6 of 35 Q7. (a) The graph below shows how the mass of a human foetus increases during the 40 weeks of pregnancy. In which five-week period on the graph does the mass of the foetus increase most rapidly? ...................................................................................................................... 1 mark The foetus is surrounded by a liquid called amniotic fluid. (b) Give one function of the amniotic fluid. ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... 1 mark Patrick Brannac www.SmashingChemistry.com Page 7 of 35 (c) The foetus needs oxygen but cannot breathe while it is in the uterus. Describe how oxygen gets from the air to the cells of the foetus. ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... 3 marks Maximum 5 marks Q8. (a) (i) The diagram shows a human sperm cell. What is the function of the nucleus of a sperm? ............................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................. 1 mark (ii) Sperm use their tails to swim to the egg so that fertilisation can take place. Give one other way in which a sperm is adapted for fertilisation. Explain your answer. ............................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................. 1 mark (b) The diagram shows the human male reproductive system. Patrick Brannac www.SmashingChemistry.com Page 8 of 35 The testes are outside the main part of the body. Suggest the relationship between temperature and sperm production. ..................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................... 1 mark (c) A chemical called a hormone, which changes a boy’s body, is produced from adolescence onwards. (i) Where is this hormone produced? ........................................... 1 mark (ii) Describe one change caused by this hormone. ............................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................. 1 mark (d) (i) During sexual intercourse about 250 million sperm are released at a time into the body of a woman. Why is it necessary to release so many sperm at a time? ............................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................. 1 mark (ii) Before being released from the body, sperm are mixed with a fluid. The fluid contains sugar. Explain how and why a sperm makes use of the sugar. ............................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................. 2 marks Maximum 8 marks Patrick Brannac www.SmashingChemistry.com Page 9 of 35 Q9. The diagram shows a section through the female reproductive system. (a) (i) What happens at fertilisation? ............................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................. 1 mark (ii) In which labelled part of the female reproductive system does fertilisation normally take place? ............................................................................................................. 1 mark (iii) In which labelled part of the female reproductive system does the foetus develop? ............................................................................................................. 1 mark (b) Some women have blocked oviducts. How do blocked oviducts prevent fertilisation taking place? ..................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................... 1 mark (c) When a baby is born it is pushed out of the mother's body. Describe what happens in the wall of the uterus to push the baby out. ..................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................... 1 mark Maximum 5 marks Patrick Brannac www.SmashingChemistry.com Page 10 of 35 Q10. The diagrams below show a human ovum (egg) and a human sperm. (a) What are eggs and sperm? Tick the correct box. animals cells organs 1 mark (b) Which part does a sperm use to swim towards an egg? ...................................................... 1 mark (c) Give the name of the male reproductive organ where sperm are made. ....................................................... 1 mark (d) The diagram below shows a sperm joining with an egg. What is this process called? Tick the correct box. fertilisation growth nutrition respiration 1 mark Maximum 4 marks Q11. The diagram shows a section through the human female reproductive system. Patrick Brannac www.SmashingChemistry.com Page 11 of 35 (a) (i) How often are eggs normally released in the female reproductive system? ............................................................................................................. 1 mark (ii) In which labelled part is an egg normally fertilised by a sperm? .......................................... 1 mark (b) Fill the two gaps in the sentences below. A fertilised egg divides into a tiny ball of cells called an embryo. The embryo attaches to the lining of the uterus. Here the embryo grows to become an unborn baby, called a ...................................... . It takes about ...................................... months for a baby to develop inside its mother. 2 marks (c) The diagram below shows a baby growing in its mother’s uterus. Patrick Brannac www.SmashingChemistry.com Page 12 of 35 (i) What is the function of the amniotic fluid? ............................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................. 1 mark (ii) Through which part can harmful substances, such as nicotine, pass from the mother’s blood to the baby’s blood? ................................................. 1 mark (iii) Give one other harmful substance which may be passed from the mother’s blood to the baby’s blood. ............................................ 1 mark (d) When the baby is born it is pushed out of the mother’s body. What happens in the wall of the uterus to push the baby out? ..................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................... 1 mark Maximum 8 marks Q12. The diagram shows two families. Some of the people in the diagram have freckles. family A Patrick Brannac www.SmashingChemistry.com family B Page 13 of 35 (a) (i) Which children are most likely to have freckles? Tick the correct boxes. Richard Simon Katie Penny Becca 1 mark (ii) How did you decide? ............................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................. 1 mark (iii) Suggest why Bill does not have freckles. ............................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................. 1 mark (b) (i) Which two cells pass on information from parents to their children? Tick the two correct boxes. Patrick Brannac www.SmashingChemistry.com Page 14 of 35 bone cell cheek cell egg cell muscle cell red blood cell sperm cell 1 mark (ii) Which organ system produces these two cells? Tick the correct box. circulatory system digestive system reproductive system respiratory system 1 mark maximum 5 marks Q13. (a) The diagram below shows the female reproductive system and a ciliated cell. not to scale Ciliated cells move an ovum along part of the reproductive system. (i) In which part of the reproductive system are ciliated cells found? ............................................................. 1 mark (ii) Describe how ciliated cells move an ovum along. ............................................................................................................... Patrick Brannac www.SmashingChemistry.com Page 15 of 35 ............................................................................................................... 1 mark (b) The diagrams below represent what happens at fertilisation and after fertilisation has taken place. not to scale (i) Some women find it difficult to become pregnant. Doctors have developed a technique in which an ovum is fertilised in a test-tube. An embryo is then implanted into the woman’s reproductive system. Which stage in part (b) shows an embryo and which stage shows a foetus? embryo ........................................................... foetus ............................................................. 1 mark (ii) Into which part of the woman’s reproductive system is the embryo implanted? ............................................................. 1 mark (c) (i) Explain why a child can look like both parents but is not identical to either of the parents. ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... 2 marks (ii) In the table below, tick one box by each human characteristic to show whether it is: Patrick Brannac www.SmashingChemistry.com Page 16 of 35 • inherited only • inherited and affected by environmental conditions. human characteristic inherited only inherited and affected by environmental conditions eye colour skin colour weight 1 mark maximum 7 marks Q14. (a) When fertilisation takes place, the nucleus of a sperm joins with the nucleus of an ovum (egg). In which part of the reproductive system does fertilisation normally take place in humans? Tick the correct box. cervix ovary oviduct uterus 1 mark (b) The table below gives information about fertilisation in three animals. animal Does fertilisation take place inside or outside the body? Number of eggs released at a time human inside 1 bird inside 4 frog outside 3000 Frogs release their eggs and sperm into water. The eggs are fertilised in the water. Why is it an advantage for frogs to release large numbers of eggs and sperm? ...................................................................................................................... Patrick Brannac www.SmashingChemistry.com Page 17 of 35 ...................................................................................................................... 1 mark (c) The diagram shows a section through a fertilised egg of a bird. (i) The shell of a bird’s egg is porous. This means it has microscopic holes in it. Why does it need to be porous? ............................................................................................................. 1 mark (ii) Give one other function of the egg shell. ............................................................................................................. 1 mark (d) A bird’s egg contains yolk which is a food store for the developing chick. A human egg does not contain yolk. Why does a human egg not need to contain a food store for the embryo? ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... 1 mark maximum 5 marks Q15. During pregnancy a woman's body increases in mass. The table shows the average increase in mass in some parts of the body during pregnancy. part increase in mass during pregnancy (kg) foetus 3.6 uterus 0.9 Patrick Brannac www.SmashingChemistry.com Page 18 of 35 placenta 0.7 red blood cells 0.2 amniotic fluid 0.9 breast tissue 0.4 fat 3.9 (a) Explain why the mass of the placenta increases as the foetus develops. ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ 2 marks (b) Pregnant women need to make sure they have plenty of iron in their diet. Use information in the table to explain why they need extra iron. ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ 1 mark (c) The foetus is not part of a woman’s body before she becomes pregnant. Which two other parts from the table are not present in her body before she becomes pregnant? ........................................................ and ........................................................ 1 mark (d) (i) The diagram shows the blood supply in the placenta and umbilical cord. not to scale When the mother breathes, oxygen and other gases pass to the foetus. Complete the flow diagram below to show how oxygen passes from the mother to the foetus. Use all the words from the list below. Patrick Brannac www.SmashingChemistry.com Page 19 of 35 lungs umbilical cord blood of foetus windpipe placenta 2 marks (ii) When a pregnant woman breathes in cigarette smoke, carbon monoxide gas combines with some of her red blood cells. How could this harm the foetus? ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... 1 mark maximum 7 marks Q16. Choose words from the box below to answer all the questions. cell division intestine digestion ovary fertilisation ovum (egg) foetus sperm testis genes uterus (a) A (i) What is the name of cell A? ............................................................. 1 mark (ii) Where is cell A produced? ............................................................. 1 mark Patrick Brannac www.SmashingChemistry.com Page 20 of 35 (b) B (i) What is the name of cell B? ............................................................. 1 mark (ii) Where is cell B produced? ............................................................. 1 mark (c) C not to scale What process is shown in C? Choose your answer from the box above. ............................................................. 1 mark (d) The diagram shows a baby developing inside its mother. Patrick Brannac www.SmashingChemistry.com Page 21 of 35 (i) Which word means an unborn baby? Choose your answer from the box above. ............................................................. 1 mark (ii) Where does the unborn baby develop? Choose your answer from the box above. ............................................................. 1 mark maximumm 7 marks Q17. During pregnancy a woman's body increases in mass. The table shows the average increase in mass in some parts of the body during pregnancy. part increase in mass during pregnancy (kg) foetus 3.6 uterus 0.9 placenta 0.7 red blood cells 0.2 amniotic fluid 0.9 breast tissue 0.4 fat 3.9 (a) Explain why the mass of the placenta increases as the foetus develops. Patrick Brannac www.SmashingChemistry.com Page 22 of 35 ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ 2 marks (b) Pregnant women need to make sure they have plenty of iron in their diet. Use information in the table to explain why they need extra iron. ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ 1 mark (c) The foetus is not part of a woman’s body before she becomes pregnant. Which two other parts from the table are not present in her body before she becomes pregnant? ........................................................ and ........................................................ 1 mark (d) (i) The diagram shows the blood supply in the placenta and umbilical cord. not to scale When the mother breathes, oxygen and other gases pass to the foetus. Complete the flow diagram below to show how oxygen passes from the mother to the foetus. Use all the words from the list below. lungs umbilical cord Patrick Brannac blood of foetus windpipe www.SmashingChemistry.com placenta Page 23 of 35 2 marks (ii) When a pregnant woman breathes in cigarette smoke, carbon monoxide gas combines with some of her red blood cells. How could this harm the foetus? ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... 1 mark maximum 7 marks Q18. Diagram 1 shows a baby in its mother’s uterus. diagram 1 Patrick Brannac www.SmashingChemistry.com Page 24 of 35 (a) What is the normal length of pregnancy in humans? .................. months 1 mark (b) (i) What is the function of the amniotic fluid around the baby? ................................................................................................................ 1 mark (ii) As a baby is born, it is pushed out of the mother’s body. Look at the diagram above. What happens in the wall of the uterus to push the baby out? ................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................ 1 mark (c) How does a baby get oxygen from its mother while it is inside its mother’s uterus? ......................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................... 1 mark (d) Diagram 2 shows a section through the mother’s lungs. diagram 2 Look at diagram 2. From which labelled part is oxygen absorbed into the blood? .............................................. 1 mark maximum 5 marks Q19. Diagram 1 shows the female reproductive system. Patrick Brannac www.SmashingChemistry.com Page 25 of 35 diagram 1 (a) Diagram 2 is a graph showing how the thickness of the uterus changed over a 28-day cycle. diagram 2 (i) Why did the thickness of the lining of the uterus decrease between day 1 and day 5 of this cycle? ................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................ 1 mark (ii) Suggest which day in this cycle an ovum (egg) is most likely to be fertilised. day .............. What evidence is there for this in the graph? ................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................ 1 mark (iii) Patrick Brannac The graph shows that the lining of the uterus builds up again between day www.SmashingChemistry.com Page 26 of 35 5 and day 14. Why is this necessary? ................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................ 1 mark (b) (i) Continue the line on the graph to show what would happen to the thickness of the lining of the uterus after 28 days if an ovum was fertilised. 1 mark (ii) Explain your answer. ................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................ 1 mark maximum 5 marks Q20.The diagram shows the reproductive parts of a flower. (a) Draw one line from each function to the correct structure. Function Structure anthers where female gametes are formed ovules where pollen grains are produced stigma Patrick Brannac www.SmashingChemistry.com Page 27 of 35 where pollen grains land during pollination style (3) (b) Suggest one way in which flowers attract pollinating insects. ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ (1) (c) The pollen grains land on the female part of the flower. Describe the next stages in the process which results in seed formation. ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ (4) (Total 8 marks) Patrick Brannac www.SmashingChemistry.com Page 28 of 35 Mark Scheme M1. substance passes from the passes from the mother’s blood to baby’s blood to the baby’s blood the mother’s blood poisons from cigarette smoke oxygen digested food carbon dioxide 1 (L6) (c) any three from • from the mother’s intestine accept ‘through the mother’s gut’ • carried in the mother’s blood • through the placenta • into the blood of the foetus • along the umbilical cord 1 (L7) 1 (L6) (ii) any one from • oxygen • antibodies • water do not accept ‘air’ or ‘blood’ or ‘liquid or ‘food’ or any type of nutrient 3 (L7) [5] 1 (L6) (d) reproductive system accept ‘reproductive’ or ‘reproduction’ do not accept ‘sex organs’ M5. (a) • a monthly 1 (L6) 1 (L6) [5] (a) • the uterus accept ‘uterus’ 1 (L6) • an ovary accept ‘ovary’ 1 (L6) description • the middle 1 (L6) accept ‘fallopian (tube)’ for oviduct ‘egg tube’ is insufficient accept ‘testis’ or ‘testicle(s)’ for testes do not accept ‘ovules’ for ovary accept only the technical terms given 3 (L5) (b) • 9 accept ‘9 ½’ accept a number in the range of 37– 42 only if the unit is changed to ‘weeks’ 1 (L5) Patrick Brannac [6] 1 (L7) (b) cilia move or push the egg accept ‘to waft the egg along’ (c) (i) placenta do not accept ‘umbilical cord’ • contract accept ‘contractions’ ‘tense’ is insufficient accept ‘contract and relax’ ‘squeeze’ is insufficient accept ‘(muscles) get shorter’ 1 (L5) M4. (a) • has tail or • it is streamlined accept ‘it has a pointed head’ accept ‘it only contains half the number of chromosomes’ 1 (L6) (b) uterus accept ‘womb’ • • • 1 (L5) 1 1 any one from flagellum 1 (L3) M2. (a) ovary accept ‘ovaries’ do not accept ‘ovum’ part oviduct testes ovary between the mother’s blood • umbilical cord and the‘cord’ baby’s accept or ‘umbilical’ blood ‘tube’ is insufficient 1 [4] M3. ‘get smaller’ is insufficient as the volume of the does notdoes pass not change muscles (b) any two from • voice becomes deeper • increase in facial hair • increase in body hair accept ‘voice breaks or changes’ accept ‘grows a beard’ accept ‘growth of pubic hair or hairy chest or hair in armpits’ • growth of penis • growth of testes or testicles • start to produce sperm • growth spurt accept ‘rapid growth’ do not accept ‘growth’ or ‘gets taller’ accept ‘development of more adult body shape’ or a description of a more adult body shape, such as ‘wider shoulders’ accept ‘sweats more’ 2 (L5) [6] www.SmashingChemistry.com Page 29 of 35 • very little cytoplasm so it swims faster ## (a) name of part anther style stigma 1 (L7) (b) the best temperature for making sperm is lower than body temperature accept ‘a lower temperature is needed for producing sperm’ accept ‘at higher temperatures sperm might be defective’ letter of part (*)T (*)P (*)U 1 (L7) 3 (L4) (c) (b) T and S letters may be in either order both letters are required for the mark (i) in the testes or testis 1 (L7) 1 (L4) [4] M7. (a) 35 to 40 weeks accept ‘35 and 40’ or ‘the last five weeks’ 1 (b) any one from • it allows the foetus to move accept ‘it allows the foetus to grow’ • it protects or cushions the foetus • it supports the foetus 1 (c) any three from • taken in by mother’s lung accept ‘breathed in’ • diffusion into the mother’s blood • transported in mother’s blood • through the placenta accept ‘diffusion from the mother’s blood to the baby’s blood’ • through the umbilical cord • in blood of foetus accept ‘in baby’s blood’ • diffusion into the cells of the foetus accept ‘in the blood’ as an alternative to either ‘transported in mother’s blood’ or ‘in blood of foetus’, but not to both (ii) any one from • body hair or pubic hair or hairy armpits do not accept ‘acne or spots’ • facial hair or beard • breaking or lowering of the voice • growth of the penis or testes do not accept ‘the testes drop’ • body becomes more muscular accept ‘shoulders broaden’ or ‘muscles develop’ • sperm production begins • growth spurt do not accept ‘grows taller’ 1 (L6) (d) (i) any one from • to increase the chance of one reaching the egg or the oviduct accept ‘to make sure an egg is fertilised’ • most sperm die before reaching the egg or oviduct accept ‘most do not reach the egg’ ‘most sperm die’ is insufficient 1 (L7) (ii) for respiration accept ‘for energy’ do not accept ‘for food’ 1 (L7) for movement or for swimming accept ‘to reach the egg’ 3 1 (L7) [5] [8] M8. (a) (i) any one from • it controls the activities of the sperm or cell • it carries or passes on genetic information accept ‘passes on information’ • it contains the genes accept ‘it contains chromosomes’ do not accept ‘it carries all the genetic information of the baby’ • fertilisation 1 (L6) M9. (a) (i) the nucleus of the egg and the nucleus of the sperm join or fuse accept ‘the sperm and the egg join’ accept ‘a sperm fertilises an egg’ ‘a sperm meets an egg’is insufficient 1 (L5) (ii) the oviduct or fallopian tube 1 (L5) (iii) uterus accept womb 1 (L5) (ii) Both the adaptation and the reason (b) any one from are required for the mark. • the egg cannot pass down the oviduct any one from • the sperm and egg cannot meet • streamlined or has a pointed head to help it • sperm cannot get through swim do not accept ‘the egg cannot reach the or penetrate the egg uterus’ • it produces a chemical to help it penetrate 1 (L6) the egg Patrick Brannac www.SmashingChemistry.com Page 30 of 35 (c) any one from • muscles contract • contractions 1 (L6) [5] M10. (a) cells if more than one box is ticked, award no mark 1 (L3) (b) tail 1 (L3) (c) testis or testicle accept plurals 1 (L4) (d) fertilisation if more than one box is ticked, award no mark 1 (L3) [4] 1 (L4) (iii) his parents or Bob and Emily do not have freckles accept ‘his family does not have freckles’ accept ‘his grandparents do not have freckles’ accept ‘he is not in family B’ if the answer for (ii) is ‘only family B has freckles’ 1 (L4) M11. (a) (i) any one from • every month or once a month • every four weeks • every 28 days accept answers from 26 days to 30 days 1 (L5) (ii) • their father or David has freckles • their parents have freckles • their grandmother or Mary has freckles • only family B has freckles accept ‘Rachel and Bill do not have freckles’ accept ‘a grandparent has freckles’ accept ‘their family or the family on the right has freckles’ accept ‘freckles run in the family’ accept ‘family A does not have freckles’ oviduct or fallopian tube (b) (i) egg cell sperm cell both answers are required for the mark if more than two boxes are ticked, deduct one mark for each incorrect tick minimum mark zero 1 (L4) 1 (L6) (b) foetus 1 (L5) 9 answers must be in the correct order 1 (L4) [5] 1 (L5) (c) (i) any one from • it cushions the baby • it protects the baby against shocks or bumps accept ‘it protects the baby’ • it absorbs shocks do not accept ‘keeps it warm’ or ‘keeps it moist’ (i) oviduct or fallopian tube 1 (L7) 1 (L5) (iii) alcohol accept ‘drugs’ or a named drug accept a named toxin accept ‘viruses’ or a named virus or a named viral disease 1 (L5) (d) muscles contract accept ‘contractions’ 1 (L6) [8] M12. (a) (i) Katie Becca both answers are required for the mark if more than two boxes are ticked, award no mark 1 (L3) Patrick Brannac (a) 1 (L7) placenta (ii) any one from • their mother or Pam has freckles M13. (ii) cilia move in a wave or from side to side accept ‘they waft or carry it along’ accept ‘the hairs move it along’ accept ‘the hairs or cilia waft or move’ ‘the hairs’ or ‘the cilia’ are insufficient 1 (L6) (ii) (ii) reproductive system if more than one box is ticked, award no mark (b) (i) embryo: stage 3 accept ‘3’ foetus: stage 4 accept ‘4’ both answers are required for the mark 1 (L7) (ii) uterus accept ‘womb’ 1 (L6) (c) (i) any two from • a reference to genes or genetic material or DNA or chromosomes accept for one mark ‘to be the same as someone else you need exactly the same genes’ • it has a different combination (of genes) • it is made from an egg and sperm accept for two marks ‘it only has half the DNA or chromosomes from each parent’ • (it gets genetic information) from both parents www.SmashingChemistry.com 2 (L7) Page 31 of 35 (ii) human characteristic eye colour skin colour weight food or gets rid of waste accept responses that refer to a baby rather inherited and affected than a foetus inherited only by environmental conditions • the foetus needs oxygen or food or to remove waste ‘the foetus needs blood from the placenta’ is insufficient 1 (L7) all three ticks are required for the mark if there is more than one tick in any row, award no mark 1 (L7) [7] M14. (a) oviduct if more than one box is ticked, award no mark 1 (L6) (b) any one from • some eggs or sperm might be eaten or lost • eggs or sperm are not protected inside the body • to increase the chance of an egg being fertilised accept ‘to make fertilisation more likely’ • some eggs might not be fertilised • some are washed away accept ‘some die’ • some of the offspring might be eaten accept ‘more tadpoles’ 1 (L5) (c) (i) any one from • to let oxygen or air into the egg • to let carbon dioxide or waste gases out • to allow gas exchange accept ‘for respiration’ do not accept ‘to let waste out’ 1 (L5) (ii) any one from • for protection • to stop the egg drying out accept ‘it stops it drying out’ • it stops infection or disease accept ‘it stops micro-organisms or bacteria or viruses or germs getting in’ accept ‘to retain the contents’ ‘it stops infection getting in’ is insufficient 1 (L7) (b) any one from • the number or mass of red blood cells increases accept ‘they need (to make) more red blood cells’ ‘the mass of blood increases’ is insufficient • iron is needed for the formation of red blood cells accept ‘for haemoglobin’ ‘the number of blood cells increases’ is insufficient ‘for red blood cells’ is insufficient 1 (L7) (c) placenta amniotic fluid both answers are required for the mark ‘umbilical cord’ is insufficient answers may be in either order 1 (L7) (i) • windpipe lungs mother’s red blood cells award a mark for ‘windpipe’ and ‘lungs’ in the first places in the correct order • placenta umbilical cord accept ‘umbilical’ or ‘cord’ blood of foetus accept ‘umbilical cord’ and ‘blood of foetus’ in either order award a mark for ‘placenta’, ‘umbilical cord’ and ‘blood of foetus’ in the last three places in an appropriate order all five answers are required for two marks (d) 1 (L5) (d) any one from • food passes from the mother to the embryo or baby accept ‘the mother provides food’ • the embryo is fed through the placenta accept ‘it is fed through the umbilical cord’ • it gets food from the mother’s blood do not accept ‘it gets food from the blood’ 1 (L6) [5] M15. (a) any one from • the placenta provides or passes oxygen or Patrick Brannac • as the foetus develops it needs more (food or oxygen from the placenta) ‘it needs or provides more oxygen’ is insufficient as the meaning is ambiguous accept, for two marks, ‘the placenta provides more oxygen or food or waste removal’ accept, for two marks, ‘the foetus needs more oxygen or food or waste removed as it grows’ a two mark answer must include one of the first two marking points and a reference to the foetus needing more food or oxygen from the placenta www.SmashingChemistry.com Page 32 of 35 2 (L7) (ii) any one from • less oxygen passes through the placenta • less oxygen in the foetus’ blood accept ‘the foetus’ heart beat rises’ or ‘the foetus’ blood pressure goes up’ • smaller or brain damaged foetus accept ‘less oxygen in the mother’s blood’ accept ‘less oxygen for the foetus’ do not accept ‘no oxygen’ • baby may be premature accept responses that refer to a baby rather than a foetus accept ‘the red blood cells of the foetus will contain carbon monoxide’ do not accept ‘only carbon monoxide passes through the placenta’ ‘it passes to the foetus’ blood’ is insufficient ‘it poisons the foetus’ is insufficient 1 (L7) [7] M16. (a) (i) • sperm 1 (L3) (ii) • testis accept ‘testes’ (i) • ovum or egg (ii) • ovary accept ‘ovaries’ 1 (L4) (c) fertilisation (d) (i) (ii) • 1 (L3) foetus 1 (L4) uterus 1 (L3) [7] M17. (a) any one from • the placenta provides or passes oxygen or food or gets rid of waste accept responses that refer to a baby rather than a foetus • the foetus needs oxygen or food or to remove waste ‘the foetus needs blood from the placenta’ is insufficient 1 (L7) • as the foetus develops it needs more (food or oxygen from the placenta) ‘it needs or provides more oxygen’ is insufficient as the meaning is ambiguous accept, for two marks, ‘the placenta provides more oxygen or food or waste removal’ accept, for two marks, ‘the foetus needs more oxygen or food or waste removed as it grows’ Patrick Brannac 1 (L7) (c) placenta amniotic fluid both answers are required for the mark ‘umbilical cord’ is insufficient answers may be in either order 1 (L7) 1 (L3) • 1 (L7) (b) any one from • the number or mass of red blood cells increases accept ‘they need (to make) more red blood cells’ ‘the mass of blood increases’ is insufficient • iron is needed for the formation of red blood cells accept ‘for haemoglobin’ ‘the number of blood cells increases’ is insufficient ‘for red blood cells’ is insufficient (i) • windpipe lungs mother’s red blood cells award a mark for ‘windpipe’ and ‘lungs’ in the first places in the correct order • placenta umbilical cord accept ‘umbilical’ or ‘cord’ blood of foetus accept ‘umbilical cord’ and ‘blood of foetus’ in either order award a mark for ‘placenta’, ‘umbilical cord’ and ‘blood of foetus’ in the last three places in an appropriate order all five answers are required for two marks (d) 1 (L4) (b) a two mark answer must include one of the first two marking points and a reference to the foetus needing more food or oxygen from the placenta 2 (L7) (ii) any one from • less oxygen passes through the placenta • less oxygen in the foetus’ blood accept ‘the foetus’ heart beat rises’ or ‘the foetus’ blood pressure goes up’ • smaller or brain damaged foetus accept ‘less oxygen in the mother’s blood’ accept ‘less oxygen for the foetus’ do not accept ‘no oxygen’ • baby may be premature accept responses that refer to a baby rather than a foetus accept ‘the red blood cells of the foetus will contain carbon monoxide’ do not accept ‘only carbon monoxide passes through the placenta’ ‘it passes to the foetus’ blood’ is insufficient ‘it poisons the foetus’ is insufficient www.SmashingChemistry.com Page 33 of 35 [7] accept ‘that is when an egg is released’ ‘it is in the middle of the cycle’ is insufficient 1 (L5) (iii) any one from • so that a fertilised egg can be implanted • to receive an egg 1 (L7) M18. (a) • 1 (L7) 9 (b) (i) any one from • it protects the baby • it helps to maintain a constant temperature • it allows the baby to move accept ‘it keeps it safe’ accept ‘it keeps the baby warm’ accept ‘it absorbs shocks’ accept ‘it protects against infection or disease’ 1 (L6) (ii) • muscles contract accept ‘contractions’ ‘the uterus or it contracts’ is insufficient 1 (L6) (c) any one from • (through the) placenta • (through the) umbilical cord • (from the) mother’s blood ignore references to food ‘through the blood’ is insufficient ‘it gets everything from the mother’ is insufficient do not accept ‘the mother breathes for the child’ 1 (L7) (b) (i) • a line which continues to rise or remains horizontal after day 28 accept a line rising or remaining horizontal after day 1 1 (L7) (ii) any one from • menstruation stops accept ‘the embryo or foetus or baby needs a blood supply’ ‘provides support’ is insufficient • so the ovum or embryo will implant accept ‘the lining is not shed’ 1 (L7) [5] M20.(a) 1 (L5) (d) • alveolus ‘air sac’ is insufficient 1 (L6) [5] M19. (a) (i) any one from • menstruation • the lining of the uterus is shed accept ‘the period’ accept ‘the lining of the uterus breaks up’ accept ‘the wall of the uterus breaks down’ do not accept ‘the uterus is shed’ ‘the wall of the uterus breaks’ is insufficient both the answer and the correct explanation are required for the mark 1 (L7) (ii) a day from day 14 to day 18 accept ‘in the middle’ do not accept ‘around day 14’ any one from • it is just after ovulation or day of ovulation • that is when an egg is likely to be in the oviduct or fallopian tube • that is just after an egg is released • an egg is released on day 14 two lines from any box will not gain a mark 3 (b) • • • any one from: brightly coloured (petals) / large petals smell or perfume nectar (c) pollen tube grows down style / into ovule 1 1 pollen nuclei fuse with / fertilise 1 egg cell nucleus (to form embryo) 1 and endosperm nuclei (to form seed) 1 [8] Mark Scheme Patrick Brannac www.SmashingChemistry.com Page 34 of 35 Patrick Brannac www.SmashingChemistry.com Page 35 of 35