* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cervical lymphadenopathy
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Cervical cancer wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
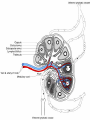
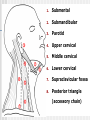
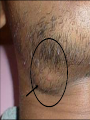
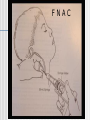
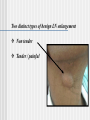
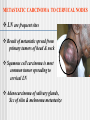
CERVICAL LYMPHADENOPATHY Dept of Oral Medicine & Radiology Yenepoya Dental College Mangalore Lymphnodes are encapsulated centres of lymphocyte differetiation and proliferation Small, oval or reniform bodies About 0.1 – 2.5 cm long Numerous in neck, mediastinum, post abdominal wall & pelvis about - 400 - 450 LN Head and neck - 60 – 70 LN FUNCTIONS Generate mature and prime B and T cells Add antibodies to circulation Filter particles, microbes from lymph 1. Submental 2. Submandibular 3. Parotid 4. Upper cervical 5. Middle cervical 6. Lower cervical 7. Supraclavicular fossa 8. Posterior triangle (accessory chain) Lymphadenitis - an inflammation or infection of lymph node and frequently occurs when an infection is present in the tissues drained by particular node pathway CAUSES I . INFECTION BACTERIAL / VIRAL / PARASITIC II. NEOPLASIA PRIMARY SECONDARY- Ca / Mal Malanoma III. MISCELANIOUS SARCOIDOSIS / DRUG REACTION/C T DISEASES Infectious Causes Non-infectious causes 1. Adenovirus 1. Hodgkin's disease 2. CMV 2. Lymphomas 3. Enterovirus 3. Leukemia 4. EBV 4. Metastatic disease 5. Herpes simplex 5. Histiocytosis 6. Staphlococcus infection 6. SLE 7. Cat Scratch Diseas 7. Kawasaki Disease LYMPH NODES a. SITE , b. SIZE , c. NUMBER , d. TENDERNESS e.CONSISTANCY, f.. FIXITY, INVESTIGATION HISTORY CLINICAL EXAMINATION TEMP/ DRAINAGE/ DENTAL & MUCOSAL /ENT SPECIAL INVESTIGATION BLOOD PICTURE CHEST X RAY SEROLOGY KVIEM TEST MANTOUX TEST FNAC / FNAB BIOPSY FNAC Two distinct types of benign LN enlargement Non tender Tender / painful NON TENDER LYMPHOID HYPERPLASIA Persistent chronic lymphadenitis or A permanenly enlarged LN after acute or chronic lymphadenitis LN are solitary, discrete, asymtomatic and freely movable Submandibular ,submental and subdigastric LN D/D Secondary carcinoma – hard & fixed Management Patient recalled after 2 week & evaluated If doubtful – removal of node & examination ACUTE LYMPHADENITIS: Most common pathologic cervical enlargement Primary infection in oral cavity, nasal cavity , tonsils or Pharynx Cause painful , swollen nodes in submental, submandibular / subdigastric Rapid regression of inflammation - nodes Normal & non- palpable SEVERAL NODES MAY BE INVOLVED MOVABLE OR FIXED D/D LUDWIG’S ANGINA INFECTED CYST MANAGEMENT When primary infection eliminated Lymphadenitis regress Adequate doses of antibiotics METASTATIC CARCINOMA TO CERVICAL NODES LN are frequent sites Result of metastatic spread from primary tumors of head & neck Squmous cell carcinoma is most common tumor spreading to cervical LN Adenocarcinoma of salivary glands, Scc of skin & melonoma metastasize Lymphatic trunks drain upper extremities & rest of body below clavicles, so solitary metastatic nodes can be from primary tumors of breast, lungs & stomach FEATURES Usually painless Detected on clinical examination Feel stony hard & freely movable till they penetrate node capsule & Invade surrounding tissues Submandibular & subdigastric nodes most frequent sites D/D Fibrosed nodes or nodes undergone non tender lymphoid hyperplasia Lymphoma (rubbery) MANAGEMENT Combination of resection, radiation & chemotherapy Prognosis is guarded LYMPHOMA A neoplastic proliferation within the reticuloendothelial system that occurs as primry tumor of lymph node FEATURES Solitary / multiple Unilateral / bilateral Usually rubbery Advanced cases – patient is ill with fever, TC & DLC may be markedly changed Other node groups axillae, groin & mediastinum involved D/D Multiple & disseminated nodal involvement occur in certain viral diseases & in mononucleosis Nodes are tender & painful MANAGEMENT Radiation & chemotoxic drugs conclusion PALPABLE NODE CHARACTERISTICS ACUTE INFECTION—LARGE,SOFT AND TENDER CHRONIC INFECTION—LARGE,FIRM,LESS TENDER,MOBILE LYMPHOMA—RUBBERY HARD,PAINLESS MULTIPLE TUBERCULOSIS—MULTIPLE,MATTED MALIGNANCY—STONY HARD AND FIXED