* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Definition
Market analysis wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Michael Aldrich wikipedia , lookup
Competitive intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
E-governance wikipedia , lookup
Darknet market wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Supermarket wikipedia , lookup
Customer relationship management wikipedia , lookup
Services marketing wikipedia , lookup
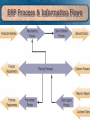
Chapter 2 plus, little bit of chapter 7 and 8 Competing with IT Enterprise Systems Why Study Strategic IT? • Technology is no longer an afterthought in forming business strategy, but the actual cause and driver. • IT can change the way businesses compete. Strategic View of IS • Information systems are vital competitive networks. • Information systems are a means of organizational renewal. • An IS can enable a businesses to reengineer or reinvent itself in order to survive and succeed in today’s dynamic business environment. Porter’s Competitive Forces To survive and succeed, a business must develop and implement strategies to effectively counter the: 1. Rivalry of competitors within its industry 2. Threat of new entrants into an industry and its markets 3. Threat posed by substitute products which might capture market share 4. Bargaining power of customers 5. Bargaining power of suppliers Rivalry of competitors • Online-shopping, price comparison tools (Froogle, Shopzilla, etc.) increase rivalry. • Industries with high rivalry – Automotive – Cell Phone – Retail Clothing – Fast Food • Industries with low rivalry? Threat of new entrants • Internet/E-commerce enables a business to emerge overnight • Almost any medium-sized retail store can become a global ecommerce competitor at little cost. It costs a lot to become a global donut competitor Substitute Products • Internet makes substitutes easier to find. – Can’t afford to fly...take a train. – Ipod not available...buy a Dell DJ – Thomas the Tank Engine costs too much...consider Imaginarium. Bargaining power Customer: • Suppliers: • Here is where the Internet has empowered the customer • Home Depot, Walmart, etc. can persuade suppliers to lock-out the little guys • Buy forcing suppliers into investing SCM software – Ebay – Lending Tree – Reverse auctions Competitive Strategies 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Cost Leadership Differentiation Innovation Growth Alliance Cost Leadership Strategy • Becoming a low-cost producer of products and services • Finding ways to help suppliers and customers reduce their costs • Increase costs of competitors Differentiation Strategy • Developing ways to differentiate a firm’s products and services from its competitors’ Innovation Strategy • Development of unique products and services • Entry into unique markets or market niches • Making radical changes that alter the fundamental structure of an industry Growth Strategy Eric’s Quick Lube, Movie Theater and Dentist’s Office • Significantly expanding a company’s capacity to produce goods and services • Expanding into global markets • Diversifying into new products and services • Integrating into related products and services Alliance Strategy • Establishing new business linkages and alliances with customers, suppliers, competitors, consultants, and other companies Examples Cost Leadership: Priceline.com Bidding Buyer set pricing Examples Differentiation: Moen Online customer design Increase in market share Examples Innovation: E-trade Online discount stock trading Market leader, then problems... Examples Growth: Walmart Beer, diapers, discount beef jerky, country music CD’s, NASCAR merchandise, cheap plastic furniture, and every ingredient you need to make napalm (all at low prices). Market leadership Examples Alliance: Walmart & Proctor N’ Gamble Beer, diapers, discount beef jerky, country music CD’s, NASCAR merchandise, cheap plastic furniture, every ingredient you need to make napalm, and oxycontin (all at low prices). Even more Market leadership Other Competitive Strategies • Locking in customers or suppliers by building valuable new relationships with them. • Building switching costs so a firm’s customers or suppliers are reluctant to pay the costs in time, money, effort, and inconvenience that it would take to switch to a company’s competitors. Other Competitive Strategies • Raising barriers to entry that would discourage or delay other companies from entering a market. • Leveraging investment in information technology by developing new products and services that would not be possible without a strong IT capability. Advantage vs. Necessity • Competitive Advantage – developing products, services, processes, or capabilities that give a company a superior business position relative to its competitors and other competitive forces • Competitive Necessity – products, services, processes, or capabilities that are necessary simply to compete and do business in an industry Customer-Focused Business A business that: • can anticipate customers’ future needs. • responds to customer concerns. • provides top-quality customer service. Value Chain Definition: • View of a firm as a series, chain, or network of basic activities that add value to its products and services, • and thus add a margin of value both to the firm and its customers. Business Process Reengineering Definition: • Fundamental rethinking and radical redesign of business processes to achieve dramatic improvements in cost, quality, speed, and service. Agility • The ability of a company to prosper in rapidly changing market – continually fragmenting global markets – market demands high-quality, high performance, customer-configured products and services. Agile Company Definition: • A company that can make a profit in markets with – broad product ranges – short model lifetimes • can produce orders individually and in arbitrary lot sizes. Mass Customization Definition: • Providing individualized products while maintaining high volumes of production Enterprise Information Systems Definition: • Information systems implemented on an extranet among a company and its – suppliers, – customers, – subcontractors, and – competitors • with whom it has formed alliances. Virtual Company Definition: • An organization that uses information technology to link people, organizations, assets, and ideas. Virtual Company Virtual Company Strategies • Share infrastructure and risk with alliance partners. • Link complementary core competencies. • Reduce concept-to-cash time through sharing. Virtual Company Strategies • Increase facilities and market coverage. • Gain access to new markets and share market or customer loyalty. • Migrate from selling products to selling solutions. Knowledge-Creating Companies Definition: • Consistently creating new business knowledge, disseminating it widely throughout the company, and quickly building the new knowledge into their products and services. Types of Knowledge • Explicit Knowledge – data, documents, things written down or stored on computers • Tacit Knowledge – the “how-to’s” of knowledge, which reside in workers Knowledge Management Definition: • Techniques, technologies, systems, and rewards for getting employees to share what they know and to make better use of accumulated workplace and enterprise knowledge. • Knowledge Management Systems – manage organizational learning and business know-how Levels of Knowledge Management Enterprise Systems • Integrate/”Bring together” the value chain in multiple Companies Mattel Toys GE Plastics Amazon.com Enterprise Systems • The Umbrella the covers a virtual company. ERP System monitors the integrated value-chains of all these connected firms A Small company can have the information and power of a large conglomerate Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Definition: • enterprise system that integrates and automates many of the customer-serving processes in – sales, – marketing, and – customer services • that interact with a company’s customers CRM Application Clusters CRM to ERP • Firms themselves are customers of other firms. • Shared interests leads to... – Shared information • which leads to – Shared information systems Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Definition: • A cross-functional enterprise system driven by an integrated suite of software modules that supports the basic internal business processes of a company • Company may be virtual • Value chain may cross-over to multiple partner firms ERP Process & Information Flows ERP Benefits • Quality and Efficiency – ERP creates a framework for integrating and improving a company’s internal business processes that results in significant improvements in the quality and efficiency of customer service, production, and distribution • Decreased Costs – Significant reductions in transaction processing costs and hardware, software, and IT support staff ERP Benefits • Decision Support – Provides vital cross-functional information on business performance quickly to managers to significantly improve their ability to make better decisions in a timely manner • Enterprise Agility – ERP breaks down many former departmental and functional walls of business processes, information systems, and information resources Costs of ERP Causes of ERP Failures • Business mangers and IT professionals underestimate the complexity of the planning, development, and training needed • Failure to involve affected employees in the planning and development phases • Trying to do too much too fast in the conversion process • Failure to do enough data conversion and testing Trends in ERP