* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Complications of IV drug Therapy
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
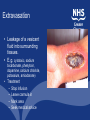
Intravenous medicine Administration Nursing Aspects Risk Assessment • Is the treatment necessary? • Is there a lower risk alternative? Patient assessment • Ask yourself about the patient, are there any conditions you will have to note: • Renal – Fluid restriction • Liver – Fluid restriction – sodium restriction • Diabetes – Dextrose restriction • High serum sodium – Normal values? 135-145 mmol/l Allergies • Does the patient have any allergy • May range from mild itch to full blown anaphylaxis • Do you know what you are giving? Do these contain Penicillin? – Amoxicillin? – Co amoxiclav (Augmentin)? – Co-trimoxazole (septrin)? – Tazocin? – Gentamicin? Prior to preparation • Staff trained appropriately – Only those who have completed NHSGG&C’s training programme and maintained their professional knowledge and competence may perform IV medicine administration • 2 people check medicine, prescription and any calculation • Read information (monograph) before preparation • Clean area, wash hands Risk assessment of medicine • What factors should we take in to consideration: – Stability – Special procedure for making up • What else can be drawn up into the vial? – Needle size 23g or use a blunt filter needle – Reconstitution device General Principles for the Preparation of medicines • Prepare medicines immediately before use • Peel wrappers from needles and syringes • Disinfect all vial/ampoule closures/infusion ports with 70% alcohol solution and allow to dry • Do not add any more than one medicine to any solution • No interruptions while prescribing, preparing or administering medicines Recent critical incident • Patient prescribed clarithromicin • Nurse prepared • Interrupted and left syringe with neat clarithromicin on side with chart • FY1 asked to give the medicine • Saw syringe and vial • Gave undiluted medicine to patient Always label a medicine if left unattended If interrupted, and start again. Site Where do you want to give the medicine? • Peripheral • Central Delivery How do you want to give it? • Bolus • Intermittent • Continuous If you are using a pump do you know how it works? If not...ASK and CHECK Important Aspects The Prescription: Clear, legible and signed Read carefully Question any changes The Patient: • • • • • Ensure correct patient Obtain consent from patient Ascertain allergy history Know other medication the patient is receiving Observe response during and after administration – document any reactions Important Aspects Administration of the medicine: • Never administer a medicine prepared by another practitioner when not in their presence • Check that the medicine has not already been administered Flushing • 10ml syringes used for flushing • Flush with sodium chloride 0.9% solution before, between and after administration of each medication unless the medication is not compatible with NaCl • Push pause method • Positive pressure • Flush must be prescribed or covered by a PGD Speedshock • Rapid administration of a medicine • Toxic levels in the blood • Floods organs rich in blood, i.e heart, liver, brain • Fainting, shock and cardiac arrest Phlebitis • Irritant medications • Cannula too big • Cannula not secured Documentation • Document administration • Document cannula condition – phlebitis score • Document fluid administered Infiltration • Leakage of fluid from the vein to the surrounding tissues. • Caused by cannula piercing the vessel wall. • Pain, paraesthesia, cold • Prevention? • Treatment? Extravasation • Leakage of a vesicant fluid into surrounding tissues. • E.g. cytotoxic, sodium bicarbonate, phenytoin, dopamine, calcium chloride, potassium, amiodarone) • Treatment – Stop infusion – Leave cannula in – Mark area – Seek medical advice Case study • Patient prescribed regular vancomicin • Cannula difficulties mean infusion rarely completed • Medicine signed as given on all occasions • What effect does this have on blood levels? Conclusion ALWAYS CHECK Right patient Right medicine Right route Right time Right dose You as the one who administers, are accountable. • 1902 Richet & porter – Ana = against, prophylaxis = protection – Disordered reactions of immune system – Due to • medicines • Nuts • Shell fish • Insects • latex Major allergens causing severe anaphylaxis Other antibiotics NSAIDS Anaphylaxis and medicines Paracetamol Iodine Cephalosporins Latex others amoxycillin How is it caused? • Allergen causes mast cells to produce histamine and other mediators – Bronchoconstriction > Dyspnoea – Angiooedema (swelling of the head and neck) – Vasodilation > Hypotension – Skin reactions > rashes Treatment • Emergency, most serious symptom first, ABC • Airway – Maintain, ? Intubate, adrenaline 0.5mg IM • Breathing – 100%O2 • Circulation – Restore, adrenaline 0.5mg IM – Fluids…Which ones Immediate actions • • • • • • Remove allergen Call for help 0.5mg adrenaline IM 100% O2 via trauma mask Fluids if needed Later chlorpheniramine (10-20mg IM)and Hydrocortisone(100-500mg IM)































![My_Body[1] - Junior2TopicWiki](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008060165_1-be31cd2568d5e2c9fee6ce67732b07b4-150x150.png)