* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ohm`s law
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Valve audio amplifier technical specification wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
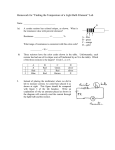
OHM'S LAW Objective To study the relationship between the electrical current flowing through a circuit element and the voltage applied. Equipment Power supply, 10 ohm resistor, 50 ohm resistor, automotive bulb, 2-multimeters. Procedure 10 Ohm Resistor 1. Make sure the power supply is off. Connect the 10-Ohm resistor to the power supply with the ammeter in series and the voltmeter in parallel with it. Do not connect an ammeter to the power supply without a resistor in series or you will destroy it! 2. Before the power supply is turned on, have your instructor inspect the circuit. Turn on the power supply and slowly increase the voltage until the ammeter reads 100 mA. Record the voltage drop across and current through the resistor in ten steps up to a maximum of 1.0A. 50 Ohm Resistor 3. Replace the 10-Ohm resistor with the 50-Ohm resistor and repeat the measurement. The maximum possible current for this resistor is lower; go no higher than 0.5 A. Automotive Bulb 4. Replace the resistor with the automotive lamp and repeat the measurement. Do not exceed 1.0 A at any time. See your instructor if you do not get a result from this step. Do not exceed the power rating of the resistors (P=IV). Graphs and Diagrams: 1. Make a schematic diagram of the circuit used in this experiment. Use the notation found in the textbook to indicate each component. Label all components. 2a. Plot the voltage drop across the 10 Ohm resistor versus the current through it. 2b. Plot the voltage drop across the 50 Ohm resistor versus the current through it. 3. Plot the voltage drop across the light bulb versus the current through it. Questions and Calculations: 1. Describe the data plotted in graphs 2a and 2b. Do these resistors obey Ohm's law? How can you tell? What is the characteristic of the graphs that indicates whether or not Ohm's law is obeyed? 2. From graphs 2a and 2b find the resistance of each of the two resistors and compare to the accepted values. 3. Describe graph 3. Does the light bulb obey Ohm's law? Explain.