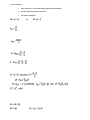* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2014 Equations
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
For each equation Draw a picture for a scenario in which you would use the equation List what quantity each letter represents List units for each letter hanging rope F=λgy If nonconservative forces Power Rate of energy transfer Center of mass Momentum Collisions then Elastic : Momentum and Energy is conserved! v1i+v1f=v2i+v2f Inelastic: only momentum conserved! Completely inelastic: momentum conserved but max Impulse Impulse increases when object bounces due to change of direction Rotation Tangential displacement Tangential acceleration and angular acceleration are zero if angular velocity is constant Constant angular acceleration equations Moment of inertia disk or cylinder: Rod: Angular Momentum then If pinned down means linear momentum not conserved, but no net external torque means angular momentum is conserved Torque Rotational Kinetic Energy Rolling pure rolling: f(R)=Iα down Incline: mgsin slipping could be tension instead of friction a=Rα f=-ma Work Power Static Equilibrium Hanging signs, ladders Gravity Kepler 1. Elliptical orbits, sun/planet at focus (faster sun/planet at near focus, slower sun/planet at far focus) 1. Radius vector sweeps out equal areas in equal times mvr=mvr 2. Gravitational Potential Energy Escape velocity Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation R=radius of circle r=center to center Inside planet R= Radius of Planet Acceleration due to gravity Oscillations Definition of simple harmonic motion Energy Pendulum Electricity and Magnetism Significant Equations Point Charges Coulomb’s Law: Force between two charges Force on a point charge due to Electric Field N/C or V/m Gauss’s Law (Graphs!) conductors vs insulators Subtract for empty space A=2 A=4 r2 Electric Potential Energy due to an electric field Electric Potential Energy between two point charges Work to bring charge distribution together Electric Potential due to an Electric Field : (Constant inside conductors) start at infinity: If constant E then Electric potential due to a point charge (equipotential lines=circles around a point charge, scalar...add!) Electric potential due to many point charges Capacitance Farads dielectric Energy stored in capacitors Parallel Plate This is true only because E=uniform between plates Battery connected Voltage doesn’t change Battery not connected charge on capacitor doesn’t change Capacitors in Series Cylindrical/spherical capacitors (outside in) Electric Current Current Density used for Ampere's Law Drift velocity Ohm’s Law Resistivity Power Watts (rate of energy) Resistors in Parallel Resistors in Series Kirchhoff Rules RC charging( graphs!!! initially capacitor acts like a wire) i=dq/dt Energy = RC discharging (maintain voltage) ( graphs!!! initially capacitor acts like battery) Magnetic Force on a point charge due to a magnetic field Magnetic force on a wire due to a magnetic field : electric motors Magnetic force between two wires currents the same direction attract Velocity selector (constant velocity) mass spectrometers Torque on a loop due to a magnetic field Hall Effect- piece of metal/measuring voltage across, use left hand for electrons!!! B-S Law (rings of wire) Multiply by cos θ if ring on an axis Solenoid (know derivation) motors : n= number of turns per unit length of solenoid Ampere’s Law inside vs. outside wires Torrid : N=number of turns Magnetic Induction Webers CALCULUS Faraday’s / Lenz’s Law ds=2πr Inductance Inductor (inductors maintain current) : generators Energy Stored in an inductor LC circuit Gauss’ Law Gauss’ Law for Magnetism Faraday’s Law Ampere’s Law with Maxwell’s displacement current Transformer