* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5.3 unit 2 theme 1 Hormones
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Anatomical terminology wikipedia , lookup
Animal nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthermia wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
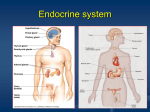
Hormones 5.3 Unit 2, Theme 1, My Family Learning objectives • What are hormones? • What do hormones do? • What is homeostatis? Automatic systems • The body has automatic systems • Constantly monitor and control it’s internal environment • E.g. right temperature • Right amount sugar in your blood stream hormones • Both temperature and blood-sugar level are controlled by hormones hormones • • • • • Chemical messengers Travel round your body Made in glands Secreted into blood Carried round body hormones • Cause a response in specific cells found in target organs Nerves and hormones nerves hormones Speed of response Very fast slower Length of response Short acting Longer acting Area targeted Very precise area Larger area Time of reaction immediate Longer term question • Where are hormones produced in the body? question • What role do hormones play in the body? Produce adrenaline Involved in flight or fight reaction that occurs in response to danger Produce testosterone – causes sperm production, hair growth, shoulders to widen Produces insulin and glucogen – controls blood sugar level Produce oestrogen –causes eggs to mature, pubic hair to grow, breasts to enlarge question • Name two hormones that are responsible for the changes take place in puberty • http://www.bbc.co.uk/education/clips/ztt9jxs homeostasis • • • • What is homeostasis Keeping the conditions in your body constant Essential for the body to function normally Is maintained by the nervous system and hormones , enzymes • Require exactly the right conditions to work effectively • Some enzymes build molecules that are needed by the body for growth • Others break down molecules – to digest food for example • Slight changes can prevent this from working question • What does homeostasis mean? • http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/sc ience/aqa_pre_2011/human/hormonesact.sht ml Which body systems are controlled by homeostasis? • Body temperature • Controlled by changes in the skin Which body systems are controlled by homeostasis? • Blood glucose (sugar) concentrations • Controlled by hormones in the liver and pancreas Which body systems are controlled by homeostasis? • Blood carbon dioxide concentrations • Controlled by lungs Which body systems are controlled by homeostasis? • Body water concentrations • Controlled by the kidneys Key points • Hormones are secreted by glands • They are chemical messengers that travel around your body in blood • Hormones control body processes that need constant adjustment to maintain a constant internal environment • Homeostasis is the maintenance of a constant internal environment A bit of Brian Cox • http://www.bbc.co.uk/education/clips/zgt87t y