* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download key - Scioly.org
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
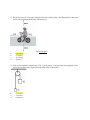
Michigan - East Side Tournament Hovercraft Exam 2017 Please work quietly with your partner to complete this exam. Please speak only to your partner. Sorry, you may not talk to anyone else while working on this exam. Multiple Choice Clearly indicate the best answer for each question on both the test booklet – AND – on the bubble sheet provided. Response earns + 10 points for each correct answer. Lowest time period to complete the exam and submit will be used in the case of a tie exam score. *** Please be prepared to use BOTH 9.8 m/sec2 – and – 10 m/sec2 for the acceleration of gravity here on Earth *** 1) David has a mass of 51-kg and is riding his bike to his friend’s house. The diagram below shows the forces acting on David and his bike in Newtons (N). What is the magnitude of David’s resulting acceleration? a. 0.59 m/sec2 b. 1.7 m/sec2 c. 16.7 m/sec2 d. 30 m/sec2 2) In the Atwood machine shown below, if M = 0.60 kg and m = 0.40 kg, what is the magnitude of the acceleration of the system? (Ignore friction and the mass of the pulley.) a. b. c. d. 2.0 m/sec2 5.3 m/sec2 3.9 m/sec2 0.98 m/sec2 3) A ladder at rest is leaning against a wall at an angle. Which of the following forces must have the same magnitude as the frictional force exerted on the ladder by the floor? a. b. c. d. The force of gravity on the ladder The normal force exerted on the ladder by the floor. The frictional force exerted on the ladder by the wall. The normal force exerted on the ladder by the wall. 4) The figure below shows Bertha’s size = large, athletic hand pushing a 15 kg - Block A with a 120 Newton force. In front of this Block is a 60 kg - Block B. The two blocks move together along a frictionless surface. What is the acceleration of Block B ? a. b. c. d. 8.0 m/sec2 2.7 m/sec2 2.0 m/sec2 1.6 m/sec2 5) Two boxes of masses m and 2m are connected by a rope - as shown in the diagram below. If the forward tension force applied on the more massive box is TA, what is the tension in the connecting rope, TB ? (assume the surface is friction-less) a. 3 TA b. c. d. TA 6) Monkey Kong hangs motionless by his tail from a tree branch (as shown below). Newton’s Third Law states that for every action force there is an equal and opposite reactive force. If the action force is the monkey’s weight, then what is the most correct reactive force? a. Force of Earth on monkey. b. Force of monkey on Earth. c. Force of monkey on tree branch. d. Force of tree branch on monkey. 7) A large massive truck and a very small car traveling at the same speed have a head-on collision. The vehicle that experiences the larger force will be a. the small car. b. the large truck. c. neither—both are the same d. not enough information to determine Use the information below to answer the next two questions: Sparky is standing at the edge of a seaside cliff and kicks a stone over the edge with an initial horizontal velocity of 18 m/sec. The cliff is 52 meters above the water’s surface, as shown. It takes the stone exactly 3.3 seconds to hit the water below. 8) What is the final speed that rock is traveling an instant before it makes contact with the water surface below.? a. 18 m/sec b. 33 m/sec c. 37 /m/sec d. 52 m/sec 9) What is the acceleration of the stone - after it has been falling for exactly 3.0 seconds? a. 0 m/sec2 b. - 10 m/sec2 c. - 20 m/sec2 d. - 30 m/sec2 Use the information below to answer the next two questions: Sightseer Sparky has a mass of 80-kg and accidentally falls out of a helicopter that is traveling East at a constant horizontal velocity of 15 m/sec – above Lake St. Clair. The sightseer plunges safely into the water exactly 2.7 seconds later. Assume no air resistance and consider Sightseer Sparky to be an object in free fall during his decent. 10) What is the horizontal component (vx) of Sparky’s velocity just before he hits the water? a. 10 m/sec, East b. 15 m/sec, East c. 20 m/sec, East d. 25 m/sec, East 11) What was the vertical height of the helicopter when Sightseer Sparky fell out (in other words, what distance did he fall?) a. 37 meters b. 10 meters c. 27 meters d. 15 meters Use the information below to answer the next two questions: The graph above shows the velocity versus time for an object moving in a straight line. Define - positive (+) direction as moving rightward. 12) At what time after time = 0 does the object again pass through its initial position? a. Between 0 and 1 seconds b. at 1 second c. Between 1 and 2 seconds d. at 2 seconds 13) At 2 seconds after time = 0, what position from the origin is the object? a. 3 meters b. 2 meters c. 1 meter d. 0.5 meter 14) An object is thrown upward with a speed of 12 m/s on the surface of planet X where the acceleration due to gravity is 1.5 m/s2. What is the maximum height reached by the object? a. 18 meters b. 144 meters c. 48 meters d. 8 meters Please use this passage to answer the next two questions: Pirate Captain Bertha is in her ship and spies her first mate Sparky in a dinghy five kilometers away. Captain Bertha sails her ship toward the dinghy at a rate of eight kilometers per hour. First Mate Sparky rows his dinghy toward the pirate ship at a rate of two kilometers per hour. 15) How much time does it take for the pirate ship and dingy to meet? a. 20 minutes b. 30 minutes c. 40 minutes d. 50 minutes 16) How far must the first mate row the dingy? a. 2.0 km b. 1.5 km c. 1.0 km d. 0.5 km Please use the information shown to answer the next two questions: A 0.20 kg object moves along a straight line in the direction of an applied force. The net force acting on the object varies with the object's displacement as shown in the graph. The object starts from rest at displacement x = 0 and time t = 0 and is displaced a distance of 20 m. (assume no friction) 17) Determine the speed of the object at displacement x = 12 m. (select best estimate) a. 12 m/sec b. 22 m/sec c. 25 m/sec d. 48 m/sec 18) What is the acceleration of the object when its displacement x is 6 meters? a. 0.8 m/sec2 b. 8 m/sec2 c. 20 m/sec2 d. 40 m/sec2 Please use the information below to answer the next two questions Sparky throws a rock of mass m horizontally off a building from a height h, as shown in the diagram. The speed of the rock as it leaves Sparky’s hand at the edge of the building is v0 19) How much time does it take the rock to travel from the edge of the building to the ground? a. b. c. d. 20) What is the kinetic energy of the rock just before it hits the ground? a. mgh b. c. d. 21) A toy fire truck has a mass of 6 - kg and is 0.20 meters in length. The toy fire truck rolls at a constant velocity while taking 4 seconds to travel 12 meters down a hallway. What is the kinetic energy of the toy fire truck? a. 12 Joules b. 54 Joules c. 9 Joules d. 27 Joules 22) A horizontal pipe consists of three sections as shown in the diagram to the right. The right section, C, is open to the air where water flows out at a speed of 12.00 m/s. (The speed, of course, is the same just inside and just outside the pipe.) Section A is not open to the air. The diameter of sections A and C is 2.00 cm. The diameter of section B is 4.00 cm. What is the velocity of the water in section B? a. 8.0 m/sec b. 6.0 m/sec c. 3.0 m/sec d. 1.5 m/sec Please use the information below to answer the next two questions A block of iron of dimensions 50.0 cm × 50.0 cm × 10.0 cm is placed in a large tank of mercury. The specific gravity of iron is 7.860 (density = 7,860 Kg/m3) and the specific gravity of mercury is 13.520. (density = 13,520 Kg/m3) 23) What height of the iron block will float above the mercury? a. 5.56 cm b. 4.44 cm c. 5.81 cm d. 4.19 cm 24) What is the maximum buoyant force this block would experience in mercury? a. 1386 N b. 1926 N c. 3312 N d. 5237 N 25) A hydraulic lift is best understood by applying _____________________ a. Pascal’s Principle. b. Euler’s Angles. c. Bernoulli’s Equation. d. The continuity equation. 26) You hold a piece of wood in one hand and a piece of cement in the other hand. Both pieces have the same volume, and you hold them fully under water at the same depth. At the moment you let go of them, which one experiences the greater buoyancy force? a. The piece of wood. b. The piece of cement. c. They experience the same buoyancy force. d. More information is needed. 27) The Birth of the Air Cushion Vehicle/Hovercraft Industry can best be classified into what time period? a. 1800 to 1850. b. 1850 to 1900. c. 1900 to 1950 d. 1950 to 1964 28) The world’s largest Hover Craft Museum is most nearly located near which city? a. Canberra, Australia b. Amsterdam, Netherlands c. Copenhagen, Denmark d. London, England 29) On March 14, 1964, the world’s first Hovercraft race was held which included 12 competitors and drew more than 30,000 spectators. The location of this event was located near which city? a. Canberra, Australia b. Amsterdam, Netherlands c. Copenhagen, Denmark d. London, England 30) Shaken – not Stirred! In the 1971 film, Diamonds are Forever, James Bond travels across the English Channel to Holland in a Hovercraft while posing as a diamond smuggler. What more recent James Bond film includes a substantial movie scene displaying use of a Hovercraft? a. 1995, GoldenEye b. 1997, Tomorrow Never Dies c. 1999, The World Is Not Enough d. 2002, Die Another Day 31) A hovercraft, also known as an air-cushion vehicle or ACV, is capable of travelling over land, water, mud, ice, and other surfaces. Hovercraft are considered _________________________. a. a hybrid craft operated by a conductor. b. a marine vessel operated by a captain. c. an aircraft operated by a pilot. d. a vehicle operated by a driver.