* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 2: Body Structure Chapter Objectives
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
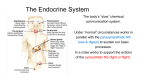
Chapter 2: Body Structure Chapter Objectives On completion of this chapter participant will be able to: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Differentiate between anatomy and physiology. Describe the levels of organization of the body. Identify terms used to describe cells, tissue, and glands. Identify body planes, directions and cavities. Define the roots that apply to the body systems. Recognize, define, spell, and pronounce terms related to procedures of glands and tissue. Describe the major medical specialties as they pertain to the body systems. Complete the review exercise at the end of the chapter. This chapter will introduce you to some of the basic concepts that are related to the study of the human body. This will prepare you to consider the roots that apply to the various body systems. Anatomy and Physiology The terms “anatomy” and “physiology” are terms that will be referred to throughout this text, and their meaning is the same regardless of the body system being discussed. Anatomy is the study of the parts or structures of the body, while physiology is the study of how the body parts work. Other terms which refer to the structure and function of the body systems are outlined in table 2.1. Table 2.1 Terms related to anatomy and physiology Term Meaning Pathophysiology (path-oh-fiz-ee-ol-oh-jee) Study of changes in the function of a body system caused by disease. Pathology (pah-thol-oh-jee) Study of the nature and cause of abnormal conditions. Etiology (ee-tee-ol-oh-jee) Study of the cause of a disease. Body Organization All living things consist of very small structures called cells. These cells perform a variety of functions in the body. Regardless of their function they are all similar in their structure. The next level of organization is tissue, which is the grouping of a number of cells together to form something that is larger and more complex than a single cell: e.g. Revised September 2001 -11- muscle, bone. A number of tissues then combine to form organs, such as the heart, lungs, brain, etc. All of the organ systems we have go together to form the human body. The Cell The cell is the basic structural unit of the body. Each cell is specialized and when these specialized cells are grouped together they form the tissue of the body. The cell is made up of: Protoplasm: (material that makes up the cell) This includes the: Û Cell Membrane that is the structure that surrounds and protects the cell. Û Cytoplasm is material located inside the cell that is not part of the nucleus. Û Nucleus is the powerhouse of the cell. It sustains the life of the cell and because of the chromosomes it contains allows the cell to reproduce. Cell Membrane Nucleus Cytoplasm Figure Tissue Tissue is a group or layer of similarly specialized cells that join together to perform certain specific functions. The study of the structure, composition and function of tissue is referred to as histology (hiss-tol-oh-jee). The root hist means tissue and the suffix logy means study of. The types of tissue that you find in the body are: Û Epithelial (ep-ih-thee-lee-al) Covers both the internal and external surfaces of the body. Revised September 2001 -12- Û Table 2.2 Connective Holds the organs of the body in place and binds all parts of the body together. Types of connective tissue are: bone, cartilage and adipose or “fat”. Medical Terms Related to Tissue Term Meaning Aplasia (ah-play-zee-ah) Lack of development of tissue or an organ. (Prefix “a” means without) Hypoplasia (high-poh-play-zee-ah) Incomplete development of tissue or an organ. (Prefix “hypo” means below, decreased or deficient) Hyperplasia (high-per-play-zee-ah) Abnormal increase in the number of normal cells in a tissue. (Prefix “hyper” means above, increased or excessive) Dysplasia (dis-play-see-ah) Abnormal development or growth of cells. (Prefix “dys” means difficult, painful or bad) Anaplasia (an-ah-play-zee-ah) Change in the structure of cells and their orientation to each other. (Prefix “ana” means without) Glands A gland is a group of specialized cells that secrete a material used somewhere else in the body. The root for gland is aden/o. There are two types of glands in the body. Exocrine (eck-soh-krin) glands secrete their substances into ducts that take it to the area of the body where it will be used. An example of an exocrine gland is the sweat gland. Endocrine (en-doh-krin) glands don’t have ducts and their secretions flow directly into the blood stream. The blood transports it to the area of the body where it will be used. An example of an endocrine gland is the thyroid gland. We have one gland in the body, the pancreas, which functions both as an exocrine and an endocrine gland. Organs and Body Systems There are twelve organ systems (often referred to as body systems) found in the human body. These systems work together to perform all the necessary functions of life. The table on page 14 outlines all the body systems and their functions. Some of the common roots that apply to that system are also included. A more detailed list of roots for the system will appear in the chapter where the body system is discussed. Revised September 2001 -13- Table 2.3 Body Systems Body System Common Roots Major Functions Skeletal System Bones oste/o Joints arthr/o Cartilage chondr/o Support and shape the body. Protection, storage of minerals, and production of blood cells. Muscular System Muscles my/o Fascia fasci/o Tendons ten/o, tend/o, tendin/o Movement of the body. Holds the body erect and generates body heat. Cardiovascular System Heart cardi/o Arteries arteri/o Veins ven/o, phleb/o Blood hem/o, hemat/o Carries food and needed oxygen to body cells. Lymphatic and Immune System Lymph nodes & vessels lymph/o Tonsils tonsill/o Spleen splen/o Provide nutrients and removes waste from the tissue. Protects the body from harmful substances. Respiratory System Nose nas/o Pharynx pharyng/o Trachea trache/o Larynx laryng/o Lungs pneum/o, pneumon/o Brings oxygen into the body for use by the cells and removes the waste product carbon dioxide. Digestive System Mouth or/o Esophagus esophag/o Stomach gastr/o Small intestine enter/o Large intestine col/o Liver hepat/o Pancreas pancreat/o Digestion of food and absorption of the nutrients needed for life. Elimination of solid body wastes. Urinary System Kidney nephr/o, ren/o Ureters ureter/o Urinary bladder cyst/o, vesic/o Urethra urethr/o Filters blood to remove waste products and maintain the right fluid balance in the body Nervous System Nerves neur/o Brain encephal/o, cerebr/o Spinal cord myel/o Coordinating mechanism within the body. Transmits messages throughout the body Integumentary System Skin derm/o, dermat/o, cutane/o Protection of the body. Controls temperature and water regulation. Endocrine System Adrenal adren/o Pituitary pituit/o Thyroid thyroid/o Integrates body functions and growth. Reproductive System Testes orch/o, orchid/o Ovaries oophor/o, ovari/o Production of new life. Revised September 2001 -14- Medical Specialities For each of the major body systems there is a medical term to describe that special branch of medicine and also a term to describe the doctor who specializes in that type of medicine. The suffix for the study of that body system is “-logy”. There are a number of suffixes for the physician who specializes in a particular body system. The most common is “-logist”. Other suffixes that refer to a specialist of a particular body system are: Û Û Û Û Û Û Table 2.4 -iatrist -iatrics -iatry -ian -ician -ist Medical Specialties and Specialists Body System Doctor Who Specializes Medical Specialty Digestive System Gastroenterologist Gastroenterology Nervous System Neurologist Neurology Reproductive System (Female) Gynecologist Gynecology Urinary System Urologist Nephrologist Urology Nephrology Cardiovascular System Cardiologist Cardiology Immune System Immunologist Immunology Musculoskeletal system Orthopedic Specialist Orthopedics Respiratory System Respirologist Respirology Endocrine System Endocrinologist Endocrinology Integumentary System Dermatologist Dermatology Body Direction Just as we have direction terms (north, south, east, west) to describe where we live, we have direction terms to describe the various locations in the body. Because the body can assume so many different positions (sitting, standing, lying down) it creates difficulty in trying to describe location, so we consider the anatomical position when we are trying to define direction. Revised September 2001 -15- Table 2.5 Directional Terms Term Definition and Examples Medical Term Above or toward the head Example: The head is superior to the neck Below; toward the tail Example: The neck is inferior to the head. super/o Toward the front surface of the body Example: The abdominal cavity is anterior to the spinal cavity Toward the back surface of the body. Example: The spinal cavity is posterior to the thoracic cavity anter/o ventr/o Medial Toward the midline of the body (Midline is an imaginary line drawn down through the center of the body from the head to the feet) Example: The big toe is medial to the small toe medi/o Lateral Away from the midline Example: The ear is lateral to the nose later/o Proximal Toward the point of origin, or nearest the point of attachment to the trunk. Example: The elbow is proximal to the wrist and the wrist is proximal to the fingers. proxim/o Distal Farthest away from the point of origin or farthest away from the point of attachment to the trunk. Example: The intestines are distal to the stomach and the stomach is distal to the esophagus. dist/o Peripheral Away from the center Example: Peripheral nerves are those that go away from the brain and spinal cord. Supine Lying on the back and facing up Prone Lying on the abdomen, facing down. Superior Inferior Anterior or Ventral Posterior or Dorsal infer/o poster/o dors/o Body Organization Just as a backpack is divided into different sections, the body consists of a number of cavities. The two main body cavities are the: Û Û Dorsal (door-sal): the back. Ventral (ven-tral): the front. Revised September 2001 -16- Each of these cavities is further divided into smaller cavities: Û Dorsal Û Ventral % % % % % Cranial (kray-nee-al) Spinal (spy-nal) Thoracic (thoh -ras-ick) Abdominal (ab-dom-ih-nal) Pelvic (pel-vick) Summary Highlights for Chapter 2 The levels of organization within the body are: cells > tissues > organs > systems > organism. The major cavities of the body are the dorsal and ventral. Each of these cavities is further subdivided. Summary Exercises: Chapter 2 Exercise 2.1 Fill in the blank with the correct answer. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. The cavity that contains the kidneys is the _________________________ cavity. Sally Trotter’s dentist said the lesion was on the ______________________ of her tongue. This means it was located on the upper surface of the tongue. Mr. Holm’s had a fracture of the _______________________ forearm. This means the fracture was located at the point of the forearm farthest away from the shoulder joint. Lying on the abdomen, face down, describes the __________________ position. The ________________________________________ is proximal to the elbow. A/An ________________________________ specializes in the diagnosis of heart problems. A/An _____________________________ is the basic structural unit of the body. The study of the nervous system is called ______________________________. If you were being treated by a skin specialist you would be seeing which type of doctor__________________________________________________________. ___________________ and ____________________ are two types of connective tissue. Revised September 2001 -17- Exercise 2.2 Select the option provided that best answers the question. 1. The term meaning toward the midline? 1. Medial 2. Distal 3. Lateral 2. The basic structural unit of the body is the: 1. Heart 2. Cell 3. Tissue 4. Gland 3. Which term best describes the act of rotating the arm so the palm of the hand is turned downward? 1. Circumduction 2. Supination 3. Pronation 4. Which directional term means situated below? 1. Medial 2. Inferior 3. Distal 5. Which term means away from the center? 1. Peripheral 2. Superficial 3. Supine 6. Which term refers to the back of the body or organ? 1. Cephalic 2. Ventral 3. Dorsal 7. Which term means lowermost, below, or toward the feet. 1. Inferior 2. Sagittal 3. Superior 8. A physician who specializes in the study of diseases of glands that secrete directly into the blood is a/an: 1. Immunologist 2. Pathologist 3. Endocrinologist 4. Internist Revised September 2001 -18- 9. The study of the structure, composition and function of tissue is referred to as: 1. Cytology 2. Histology 3. Pathology 4. Oncology 10. The correct medical root for gland is: 1. Adren/o 2. Aden/o 3. Anter/o Exercise 2.3 Match the term in Column A with the correct definition in Column B. Column A Column B 1. 2. Aplasia Hyperplasia 3. Anaplasia 4. Hypoplasia _____ Incomplete tissue development. _____ A change in the structure of cells and in their orientation to each other. _____ An abnormal increase in the number of normal cells. _____ Lack of development of tissue. Exercise 2.4 Label the parts of the cell on the diagram below A: _________________________ B: _________________________ C: _________________________ A B C Revised September 2001 -19- Challenge Exercise Using the following word parts as your reference, complete the following statements. aden/o = gland geront/o = old age gynec/o = female hist/o = tissue nephr/o = kidney neur/o = nerve -oma = tumor, neoplasm -logist = specialist -logy = study of -pathy = disease, suffering 1. A/An __________________________________ is a tumor of kidney tissue. 2. The study of the nervous system is called __________________________. 3. _______________________ is the study of the process of aging. 4. ____________________ is a specialist in the study of cells. 5. ____________________ is the medical specialty concerned with diseases of the female reproductive system. 6. ________________________ means disease of the glands and usually involves swelling. Revised September 2001 -20-