* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download I-ready Textbook
Rotation matrix wikipedia , lookup
Plane of rotation wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Rotation formalisms in three dimensions wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
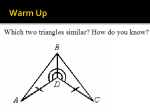
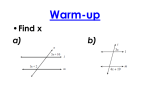
Unit 2 Review! Objective: to review the concept of congruence Common Core State Standards: 8.G.1; 8.G.2; 8.G.5; 8.G.6; 8.G.7 Let’s Explore!! I-ready Textbook- Period 1 Work with your partner: Complete pg 162-164 Independently: Will be collected Complete 165 Transformations The four main Transformations are: Translation (Slide) Reflection (Flip) Rotation (Turn) Dilation (Scale) A translation is a transformation that slides a figure in any direction. Translation Rule: Ta,b (x, y) = (x + a, y + b) Example T0,4 (2, 3) = (2 + 0, 3 + 4) = (2, 7) A rotation is a transformation that turns a figure about a fixed point called the center of rotation. The measure of the rotation is the angle of rotation. Rotation Rules: A reflection is a transformation that flips a figure over a line of reflection. The distance from a point to the line of reflection is the same as the distance from the point's image to the line of reflection. Reflection Rules: Y axis: (x, y) (-x, y) X-Axis: (x, y) (x, -y) Y=X: (x, y) (y, x) Y=-X: (x, y) (-y, -x) A dilation is a transformation that makes a figure larger or smaller. This means the two figures are similar (same shape/different size). A scale factor is the ratio of the side lengths of the image to the corresponding side lengths of the original figure. Dilation Rule: (x,y) (kx, ky) k>1: enlargement 0<k<1: reduction Let’s Practice I-ready Textbook Period- 2 Independently 1. Complete pg 168 - 173 Assessment – Will be collected 2. Answer pg 174 - 175 Congruence A two-dimensional figure is congruent to another if the second can be obtained from the first by a sequence of rotations, reflections, and translations. Always list corresponding vertices in the same order – ORDER IS IMPORTANT! Congruent Figures: Same size and same shape and congruent corresponding parts. Symbol for congruence is Tick Marks are used to indicate congruent segments Arcs are used to indicate congruent angles 9 Similarity A two-dimensional figure is similar to another if the second can be obtained from the first by a sequence of dilations, rotations, reflections, and translations. Always list corresponding vertices in the same order – ORDER IS IMPORTANT! Similar Figures: Same shape but size may be different (due to a dilation). Corresponding angles are congruent and corresponding sides are proportional (constant ratio between all sides-BIG/SMALL or SMALL/BIG). Symbol for similarity is 10 ~ Angle-Angle Similarity If two angles of one triangle are congruent to two angles of another triangle, then the triangles are similar. Indirect Measurement Indirect Measurement is a technique that uses proportions to find a measurement when it is not possible to measure something directly. Use similar figures and proportions: 1) Draw a sketch to identify similarities (height/width/shadow etc.) 2) Create a proportion substituting values for the given measurements 3) Solve for X 11 Types of Slopes Positive Negative Zero Undefined Similar Triangles & Slopes The ratio of the rise to the run of two slopes triangles formed by a line is equal to the slope of the line (HEIGHT OVER WIDTH) 12 Area & Perimeter of Similar Figures 1) Find the ratio of the corresponding side BIG/SMALL (this is the scale factor). 2) The perimeter of the bigger figure is equal to the perimeter of the smaller figure times the scale factor. 3) The area of the bigger figure is equal to the area of the smaller figure times the scale factor squared. 3 1) Scale Factor = 9/3 = 3 2) Perimeter of small figure = 12. Perimeter of big figure is 12*3 = 36 3) Area of small figure = 9. Area of big figure is 9*32 = 9*9 = 81 9 Let’s Practice I-ready Textbook Period- 3 Independently 1. Complete pg 178- 181 Assessment – Will be collected 2. Answer pg 182 - 183 Period 3- Types of Angles Matching! Transversal Exterior angles that are on opposite sides of the transversal (equal to each other) Alt Int. Angles Angles in the same position with respect to the lines and transversal (equal to each other) Alt Ext. Angles Angles that are opposite from each other formed by the intersection of 2 lines (equal to each other) Corr. Angles Vertical Angles A line that cuts across two or more (usually parallel) lines Interior angles that are on opposite sides of the transversal (equal to each other) All About Triangles! The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a triangle is 180° y° x° + y° + z° = 180° x° z° The measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the measures of its two remote interior angles. y° x° x° + y° = p° p° Pythagorean Theorem: In a right triangle, the square of the lengths of the hypotenuse c is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the legs a and b. a c a2 + b2 = c2 b Midpoint & Distance on the Coordinate Plane Midpoint x1 x2 y1 y2 M , 2 2 Distance d ( x2 x1 ) ( y2 y1 ) . 2 2 Let’s Explore I-ready Textbook Period- 3 Work with your partner: 1. Complete pg 186 - 1888 Assessment – Will be collected 2. Answer pg 189 Let’s Practice I-ready Textbook Period- 4 Independently 1. Complete pg 192 -194 Assessment – Will be collected 2. Answer pg 195 Let’s Practice I-ready Textbook Period- 5 Independently 1. Complete pg 215 - 217 Assessment – Will be collected 2. Answer pg 218 - 219 Volume of Cylinders, Cones & Spheres The volume of a 3D figure is the amount of space that the object occupies. The volume is the number of cubes the object can hold. Each cube represents a unit of measure called a cubic unit V = (p r )(h) 2 1 2 V = ( )(p r )(h) 3 4 3 V = ( )(p r ) 3 Let’s Practice I-ready Textbook Period- 6 Work With your partner 1. Complete pg 222-224 Assessment – Will be collected 2. Answer pg 225 Let’s Practice I-ready Textbook Period- 7 Independently 1. Complete pg 229 - 233 Assessment – Will be collected 2. Answer pg 234- 235 Unit 3 – Interim Assessment I-ready Textbook Period 9 Complete pg 236 - 238 Let’s Practice! MAP PLUS BOOKLET QUESTIONS #8, 18, 34, 36, 43, 44, 56, 64 Exit Ticket After reviewing and practicing Unit 2, rate yourself on how you feel about the same questions in the MAP Plus Book.