* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Horizontal Gaze Palsy
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
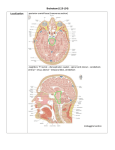
HARVARD MEDICAL SCHOOL DEPARTMENT OF NEUROLOGY MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL One and a Half Syndrome Shirley H. Wray, M.D., Ph.D. Professor of Neurology, Harvard Medical School Director, Unit for Neurovisual Disorders Massachusetts General Hospital The One-and-a-Half Syndrome On horizontal gaze there is: An ipsilateral gaze paresis or palsy An internuclear ophthalmoplegia (INO) on contralateral gaze At rest, the eyes are: Orthophoric, or, in acute stage Ipsilateral eye esotropic or Contralateral eye exotropic (Paralytic pontine exotropic) Three possibilities to account for an ipsilateral horizontal gaze palsy: may be due to unilateral lesion affecting The ipsilateral PPRF only The ipsilateral abducens nucleus alone Both the ipsilateral PPRF and abducens nucleus Abducens Nucleus All the cells necessary for ipsilateral horizontal gaze: Motoneurons whose axons form the sixth nerve (VIN) to innervate the ipsilateral lateral rectus muscle Internuclear neurons which send axons across the midline to opposite MLF and ultimately to the medial rectus motoneurons in the contralateral oculomotor nucleus (III N). Pathogenesis of Certain Signs Ocular Motor Deficit Possible Pathophysiologic Substrate Ipsilateral adduction weakness Interruption of axons of abducens internuclear motoneurons Ipsilateral slowed abducting saccades Inadequate inhibition of medial rectus motoneurons Contralateral abduction nystagmus Impaired inhibition of contralateral medial rectus or Interruption of descending fibers to contralateral abducens nucleus or Involvement of adjacent PPRF Neurology 1983; 33:971-980 Reported cases Brainstem Infarct 12 Multiple Sclerosis 2 Pontine Glioma 2 Arteriovenous Malformation 1 Pontine Hemorrhage 8 Basilar Artery Aneurysm 0 Cerebellar Astrocytoma 2 Metastatic Melanoma 1 Ependymoma Fourth Ventricle 1 29 Table 1. The one-and-a-half syndrome: Etiology Boston series 4 14 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 20 Total 16 16 3 1 8 1 2 1 1 49 Diplopia 12 Blurred Vision 8 Oscillopsia 4 Difficulty looking to one side 2 “Quivering” of the eye 1 No visual complaint 3 Table 2. One-and-a-half syndrome (N = 20): Visual Symptoms (N = 20) Gaze-evoked upbeat nystagmus 12 Skew deviation 8 Horizontal ipsilateral gaze nystagmus 4 Rotary component to horizontal ipsilateral gaze nystagmus 2 Spontaneous nystagmus to the contralateral side 1 Absent or impaired convergence 5 Saccadic vertical pursuit 9 Gaze-evoked downbeat nystagmus 4 Impaired upward gaze 1 (N = 11) Exotropia 4 Esotropia 3 Orthotropia 4 Table 3. One-and-a-half syndrome (N = 20;11): Associated ocular motility signs Cranial Nerve Involvement I 0 II 1 III 0 V 3 VII 4 VIII 2 IX 3 XI 0 XII 2 Horner’s Syndrome 1 Weakness or spasticity 6 Sensory deficits 7 Abnormally brisk or asymmetric reflexes 5 Extensor plantar responses 9 Incoordination 10 Table 4. One-and-a-half syndrome (N = 20): Associated neurologic signs Esotropia of the ipsilateral eye Patient 1. The one-and-a-half syndrome (A) Mild left INO looking right. (B) Esotropia OS (ipsilateral) in the primary position of gaze. (C) Horizontal conjugate gaze palsy attempting to look left. (D) Normal convergence. Paralytic Pontine Exotropia Patient 2. Paralytic pontine exotropia. (A) Horizontal conjugate gaze paresis looking right. (B) Exotropia OS (contralateral) in the primary position of gaze. (C) Right INO looking left. (D) Right “peripheral-type” ipsilateral facial palsy. (E) Impaired convergence. Patient 2. Paralytic Pontine Exotropia A. Horizontal conjugate palsy looking right. B. Exotropia OS contralateral in the primary position of gaze. C. Right INO looking left D. Right “peripheral-type” ipsilateral facial palsy E. Impaired convergence In paralytic pontine exotropia the exotropic eye shows: Abduction nystagmus during attempts to move it laterally Extreme slowness of adduction saccades when eye fixing to move it to the midline Paralytic Pontine Exotropia attributed to: Tonic contralateral deviation of the eyes Implies acute ipsilateral PPRF lesion Failure of ipsilateral eye to deviate medially explained by the INO Paralytic pontine exotropia OS Paralytic pontine exotropia right horizontal gaze palsy http://www.library.med.utah.edu/NOVEL