* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download STAAR Science Vocabulary 2016
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
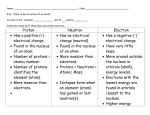
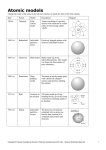
Science STAAR Vocabulary-8th Grade Atom—smallest particle of an element; made of electrons, protons, and neutrons Atomic Mass—mass of atom; equal to number of protons and neutrons in the atom Balanced Equation—represents a chemical equation; both sides contain equal numbers of atoms of each element N2 + 3H2 2NH3 Chemical Formula—shorthand notation that uses chemical symbols and numbers as subscripts to represent type and number of atoms present H2O Electrical Charge—electrons are negatively charged; protons are positively charged; the numbers of protons and electrons in the atom determine the charge of the atom. The proton determines the charge of the nucleus because the neutron is neutral and has no charge. Electron—negatively charged, subatomic particle found in electron cloud outside the nucleus; EElectron Cloud—area surrounding the nucleus of the atom where the electrons are found Neutron—subatomic particle in the nucleus of the atom that has no charge; N0 Nucleus—very dense, positively charged region at the center of the atom; P+ and N0 Proton—positively charged particle in the nucleus of the atom; P+ Atomic Number—number of protons in the nucleus; equals # of electrons, too. Energy Level—rings of electrons outside the nucleus; found in electron cloud Valence Electrons—electrons in the outermost energy level that influences how an element will react with other substances Reactivity—influenced by number of valence electrons; Group 8 is non-reactive while Group 1 is highly reactive Metal—solid, shiny, malleable and a good conductor; most elements are metals Nonmetal—usually a gas or brittle solid, not shiny, not malleable and not a good conductor Metalloids—elements that have properties of both metals and nonmetals; often called semiconductors Element—pure substance; cannot be separated into simpler substances; made of the same atom Groups—columns on the Periodic Table; arrange elements by number of valence electrons Periods—rows in the Periodic Table; classify the elements by the number of electron shells Chemical Reaction—process by which one or more substances change to produce one or more different substances Coefficient—number placed in front of a chemical formula; 2H3 Law of Conservation of Matter—mass of all reactants must equal mass of all products Reactants—substance that takes part in and undergoes change during a chemical reaction; in front of the arrow 2NH3 N + 3H 2 2 Product—substance produced during a chemical reaction; comes after the arrow N2 + 3H2 2NH3 Endothermic—process that absorbs heat; heat goes IN Exothermic—process that releases heat; heat EXITS Precipitate—a solid that is deposited from a solution Motion—change in an object’s position Friction—force that opposes motion Force—a push or pull that can change the motion of an object; Net Force—sum of ALL the forces acting on an object Balanced Forces—forces acting on an object that combined do not change the movement of the object; NO MOTION; forces are equal Unbalanced Forces—forces acting on an object that cause change in the motion of the object; MOTION; forces are not equal Speed—rate of change over time; s = d/t Velocity—speed and direction; 55 mph East Acceleration—the rate of change in an object’s speed. Inertia—tendency of an object to remain still or continue moving, unless force is applied Newton’s Law of Inertia—an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion unless acted on by an outside force; also known as Newton’s First Law Newton’s Law of Force and Acceleration—acceleration of an object depends on the object’s mass and magnitude of the force acting upon it; also known as Newton’s Second Law; F = m x a Newton’s Law of Action-Reaction—for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction; also known as Newton’s Third Law of Motion Axis—imaginary line through the Earth that extends from the North Pole to the South Pole; the center of Earth’s rotation Orbit—curved path of an object around a point in space Revolution—moving in an elliptical path around a point in space; Earth revolves around the Sun Rotation—spin on an axis; Earth’s spinning on its axis causes day and night Tilt—the slant of Earth’s axis; 23.5o; North Pole always point to the North Star, Polaris Seasons—four divisions of the year based on changes in temperature due to varied amounts of Sunlight; caused by the tilt of the Earth on its axis New Moon—phase when Moon is between the Sun and the Earth; NONE of the illuminated portion is facing the Earth Crescent Moon—shape of the Moon that is less than a quarter Moon First Quarter Moon—half of the disk is illuminated; the cycle is in the waxing phase Gibbous Moon—shape of the Moon that is greater than a quarter Moon, but not full Full Moon—entire disk illuminated Last or Third Quarter Moon—half of the disk is illuminated; the cycle is in the waning phase Waning—weakening or getting smaller Waxing—growing or getting larger Ocean Tide—daily changes in the level of ocean water; caused by Moon’s gravitational pull Neap Tide—tides with the smallest daily tidal range; Sun, Earth, Moon form a 90 degree angle Spring Tide—tides with the largest daily tidal range; Sun, Earth and Moon are in a line Galaxy—large grouping of stars in space Elliptical Galaxy—galaxy with long, oval shape, bright center Irregular Shaped Galaxy—galaxy with no specific shape Spiral Galaxy—galaxy with a bulge in the center with distinct long arms winding around a center; our Milky Way Galaxy Star—self-luminous celestial body; most made of hydrogen and helium Hertzprung-Russell Diagram—diagram of stars’ surface temperature (color) and (H-R) luminosity (brightness) Luminosity—intensity of light from a celestial body; brightness Main Sequence—stable stars, such as the Sun; diagonal belt on the H-R Diagram Black Hole—remains of a star that collapsed under its own gravity; light cannot escape Nebula—cloud of gas and dust in space; location of star formation Supernova—the death of a large star by explosion Electromagnetic Spectrum—grouping of electromagnetic radiation from radio waves to gamma rays; all can travel through space; do not need a medium to travel Light Year—unit of length; distance light travels in one year; 9.5 trillion km Continental Drift—theory that continents were once connected but have drifted apart Theory of Plate Tectonics—lithosphere is divided into tectonic plates that move slowly on the asthenosphere Convergent Boundary—plates collide; can create mountains, trenches, volcanic islands Subduction—denser plate is pushed under less dense when they plates collide; oceanic-oceanic and continental-oceanic boundaries Divergent Boundary—when two plates move away from each other; can create rift valleys or mid-ocean ridges Transform Boundary—two plates slide past each other; creates earthquakes Topographic Maps—map showing changes in Earth’s elevation; contour lines show elevation Convection Currents—heat transfer caused by the rising of hot, less dense fluids and the sinking of colder, more dense fluids Ocean Currents—directional movement of ocean water; surface currents result from winds; deep currents result from density variations due to temperature and salinity differences Coriolis Effect—deflection of moving air; result of Earth’s rotation Cold Front—border between advancing mass of cold, dense air and a receding mass of warm air Warm Front—border between advancing mass of warm, moist air & a receding mass of cool air Humidity—amount of water vapor/moisture in the air Autotroph—organism that makes its food, such as plants Heterotroph—organism that must use other organisms for food, such as animals Carnivore—an animal that eats other animals Herbivore—an organism that eats only plants Omnivore—an organism that consumes both plants and animals Consumer—organism that feeds on other organisms in a food chain Decomposer—organisms such as bacteria & fungi; break down the remains of dead organisms Host—an organism upon or within which another organism live; leech on your leg Parasite—organism that survives on a host organism and causes harm to the host Predator—an animal that lives by killing and eating other animals Prey—an animal that is eaten by another animal Producer—organism that makes its food using energy from light/the Sun or chemical compounds Abiotic Factors—non-living factors that affect the ecosystem; light, temperature, shelter, water Biotic Factors—factors that are living or produced by living things; animals, plants, relationships Competition—when more than one individual or population relies on the same limited resources Adaptation—process by which an organism/population becomes better suited for its environment Invasive Species—a species that enters an area from somewhere else and disrupts the native ecosystem