* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cosmetic correction of Anterior Staphyloma : A rare surgery
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
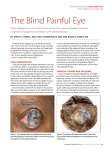
International J. of Healthcare and Biomedical Research, Volume: 05, Issue: 01, October 2016, 49-52 Case Report: Cosmetic correction of Anterior Staphyloma : A rare surgery *Dr. Aayush Tandon, **Dr. SomenMisra , **Dr. Neeta Misra *Resident, ** Professor, Department of Ophthalmology Rural Medical College, Pravara Institute of Medical Sceiences , Loni ( DU) , Maharashtra , India Corresponding author: Dr. Aayush Tandon Abstract Anterior Staphyloma is an ectasia of pseudocornea which results after sloughing of cornea with iris plastered behind. Our patient presented with loss of vision, white corneal opacity & abnormal bulging of the right eye since childhood following penetrating ocular trauma by a wooden stick.Patient had come to the hospital only to seek cosmetic improvement. Clinical diagnosis of Anterior Staphyloma was made. After informed written consent patient was taken up for surgery and a Evisceration was performed under local anaesthesia by placing a silicone orbital implant within the scleral pocket.Patient was sent for customised ocular prosthesis after 2 months of surgery. A customised ocular prosthesis over the well formed sclero -conjunctival pocket can bring back some amount of movement with complete cosmetic recovery which apparently appears normal, thus an ocular prosthesis should be provided as soon as possible for the psychological well being of the patient. Background to complete loss of vision, 1 year post trauma. Patient had A staphyloma is a clinical condition characterised by an come to the hospital only to seek cosmetic improvement. ectasia of the outer coats ( cornea or sclera or both ) of the On general examination patient was averagely built and well eye with 1 incarceration of the uveal tissue .The basic nourished. Systemic examination for the respiratory system, underlying pathology is weakening of the eye ball which can cardiovascular be caused by many inflammatory or degenerative diseases abnormality. Ocular examination revealed thatvisual acuity 1 system, and abdomen revealed no involving these structures . Corneal (anterior) staphyloma of the patient was 6/6 in left eye and No PL in right eye. can develop following small pox, corneal ulcer, trauma and Left Eye findings were within normal limits.In the right eye 2 keratomalacia .Anterior Staphyloma is an ectasia of Cornea was bulging forward between the lids .Exposed pseudocornea( the scar formed from organised exudates and portion of conjunctiva was lustreless.Cornea was opaque, fibrous tissue covered with epithelium) which results after thinned out and ectatic andiris tissue was adhered to the 2 sloughing of cornea with iris plastered behind . It can be back of the cornea inferiorly .There was no vascularisation complete or partial depending upon the part of the cornea over the cornea (Photograph 1 & 2). Other details could not involved 3. be appreciated. Digitally the intraocular pressure was found Case report to be normal. Clinical diagnosis of Anterior Staphyloma was A 21 year old female patient came to Pravara Rural hospital made . and presented with loss of vision, white corneal opacity & After informed written consent patient was taken up for abnormal bulging of the right eye since childhood. Patient surgery and a Evisceration was performed under local was having history of penetrating ocular trauma by a anaesthesia by placing a silicone orbital implant within the wooden stick in childhood followed by pain redness scleral pocket. After application of proparacaine 0.5% and watering from the same eye .After trauma she developed povidone iodine 0.3% eye drops a four quadrant peribulbar gradual painless progressive diminution of vision, white block was given with 3ml of xylocaine 2% ⁄ adrenaline opacity and abnormal bulging of right eye ultimately leading 1:200 000 in each quadrant. A speculum was placed between the eyelids after painting draping under complete 49 www.ijhbr.com ISSN: 2319-7072 International J. of Healthcare and Biomedical Research, Volume: 05, Issue: 01, October 2016, 49-52 asepsis. A 360° peritomy was done using Wescott scissors. scisso implemented by us caused no complications. Patient was Care was taken to preserve as much conjunctiva as possible. called for customised ocular prosthesis after 2 months of A full-thickness thickness limbal incision was made with a 11 number surgery. blade scalpel. The remainder of the limbus was cut with impression technique, which involved conversion of alginate scissors, allowing for removal of the corneal button along impression ression into a wax model. The wax model was then with adhered iris tissue (Photograph 3).. The intraocular sculpted to match for its size (horizontally, vertically and contents were then removed with the aid of an “evisceration “evisc antero-posteriorly) posteriorly) and shape as close as possible to the spoon” a round relatively flat curette (Photograph 4). 4) normal eye; then the iris–corneal corneal position was recorded. Careful attention was given to the complete removal of all Final wax model was moulded and the prosthesis was uveal tissues( In theory this decreases (possibly ssibly eliminates) fabricated using medical grade acrylic material.8,9.The the risk of sympathetic ophthalmia). prosthesis were immersed in a disinfectant (Chlorhexidine The inner surface of the sclera was then bathed in alcohol. gluconate B.P 0.3% W/V, Cetrimide B.P 3.0% W/N) for 24 The purpose of this step is to denature any residual protein h and rinsed with normal saline prior to insertion. After that is, insertion of ocular prosthesis (Photograph 6 ))the patients sympathetic ophthalmia. Sclerotomy rotomy was performed at 3,6,9 was placed on topical antibiotics eye medications. FollowFollow and 12 ‘0’ clock position allowing for placement of larger up visits were scheduled at 1, 2 and 6 weeks and then 3 implant. PMMA ball was implanted in the empty scleral months postoperatively. The patients was taught how to pocket (Photograph 5) and Sclera was sutured end to end remove and reinsert the prosthesis. S She were also instructed using silk 6-0 followed by conjunctival suturing by vicryl 8- on what to do if there was any discharge from the socket at 0 covering the scleral wound.. Eye was pressure dressed and a any ny time (such as removing the ocular prosthesis at night bandaged for 48 h to prevent haemorrhage.. Patient was and use of topical antibiotics and reportin reporting to the hospital). started on steroid - antibiotic drops and systemic Patient wascounselled on the importance of maintain maintaining a analgesics/anti-inflammatory drugs post operatively and was healthy socket by the way they handled the prosthesis. might discharged otherwise after Photograph 1 Photograph 3 7 incite days. inflammation, The surgical that Prosthesis was fabricated using modified procedure Photograph 2 Photograph 4 50 42 www.ijhbr.com ISSN: 2319-7072 2319 International J. of Healthcare and Biomedical Research, Volume: 05, Issue: 01, October 2016, 49-52 Photograph 5 Photograph 6 : Final Outcome Discussion staphyloma A staphyloma is a clinical condition characterised by an Evisceration with the placement of an orbital implant is the ectasia of the outer coats (cornea or sclera or both both) of the most preferred treatment modality 6. eye with incarceration of the uveal tissue1. The basic whileothers others are scleral staphylomas. Most Surgeons prefer doing evisceration over enucleation, underlying pathology is weakening of the eye ball which can favouring final aesthetic outcome and to avoid 6 be caused by many inflammatory or degenerative diseases complications of post-enucleation enucleation socket syndrome . Eyes 1 involving these structures . Staphyloma are caused due to are generally the first features of face to be noticed. various conditions. Corneal (anterior) staphyloma can Removal of this organ either due to tumors, trauma or any develop following small pox, corneal ulcer, trauma traum and other condition not only cause unaesthetic look but causes of 2 keratomalacia . Ocular malignancies,traumatized diseases globes, like painful intraocular blind function and has a psychological effect on the patient eyes, 7 . Thus, ocular prosthesis should be provided as soon as staphylomas, disfigured globes, etc. are the common possible for the psychological well being of the patient. indications for eye removal surgeries (i.eenucleation enucleation or Conclusion evisceration). These procedures can be performed along Anterior staphyloma is not cosmetically acceptable in the with the placement of an orbital implant wherever indicated population especially among young ones. After evisceration depending on the underlying cause 4,5 . of anterior staphyloma an implant of PMMA ball was Staphylomas, one of the clinical indications for eye removal, implanted within the scleral pocket to maintain approximate clinically present with a localizedbulging or protrusion of shape and movement nt of the globe. A customised ocular globe. It is an infiltration iltration of the uveal tissue through weak or prosthesis over the well formed sclero -conjunctival pocket thinned out outer coat (cornea or sclera). They can be either can bring back some amount of movement with complete congenital or acquired, and also can be unilateral or cosmetic recovery which apparently appears normal. In this bilateral. Depending on the site of lesion,staphylomas can be patient, we have tried the above mentioned proc procedure with categorized under anterior,intercalary, calary, ciliary, equatorial and good cosmetic outcome. We recommend the same for 2 posterior Staphyloma . Anterior staphyloma is a corneal cosmetic reconstruction, particularly among young patients. References 1.Sihota-Tandon. Tandon. ‘Parson’s diseases of eye’. 22nd edition 2015 :229 2. Pramod TK.’ Best Aid to Ophthalmology’ 1st edition 2013 : 130 3.Mukherjee .Mukherjee PK. Clinical Examination in Ophthalmology. Elsevier Health Sciences;2006:63-83 Sciences;2006:63 51 42 www.ijhbr.com ISSN: 2319-7072 2319 International J. of Healthcare and Biomedical Research, Volume: 05, Issue: 01, October 2016, 49-52 4.Nunery WR, Chen WP. Enucleation and evisceration.Bosniak S, editor. Vol. 2. Principles and Practice of Ophthalmic Plastic and ReconstructiveSurgery.Philadelphia: WB Saunders Company; 1996. 5.Baylis H, Shorr N, McCord CD Jr, Tanenbaum M: Evisceration, enucleation and exenteration. McCord C Jr and Tanenbaum M (eds): Oculoplastic Surgery, 2nd ed.New York, Reven Press,1987:408-430 6. Sreedhar A, Sundar G, Honavar S, et al. Managing a Cosmetic Blemish. Kerala J Ophthalmol2008;20(2):192-96 7. Sykes LM. Custom made ocular prosthesis: A clinical report. J Prosthet Dent 1996;75:1-3. 8.Allen L, Webster HE. Modified impression method of artificial eye fitting. Am J Opthalmol 1969;67:189-218. 9.. Allen L, Bulgarelli DM. Obtaining and understanding the Alginate Impressions. J Am SocOcularists1988;19:4-13. 52 www.ijhbr.com ISSN: 2319-7072 42