* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
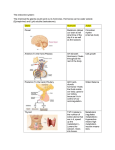
Biology 30: Endocrine Themes Endocrine Themes: Metabolism & Calcium Homeostasis Homeostatic themes: Composed of a GLAND – HORMONE – TARGET – FUNCTION Example: hGH feedback loop APG – hGH – Somatic Cells – Growth & Repair A typical loop has a start point to “turn it on” and to “turn it off” Growth & Repair is a daily thing usually as we sleep & rest for the next day THEME #1 – Metabolism: This includes how your body maintains body temperature (higher rate in winter; lower rate in summer), rate of which the body burns fuels, rate at which we grow, rate at which we convert food into body tissue GLANDS: Hypothalamus, APG & Thyroid HORMONES: TRH, TSH & Thyroxin TARGETS: APG, Body Cells FUNCTIONS: Let’s See You are Cold Hypothalamus TRH _______ TSH _______ In Presence of ______ Thyroxin Release Somatic Cells stimulated to burn fuels We warm up What will the Hypothalamus due as body temperature rises? Is this Positive Feedback or Negative Feedback? What would happen to levels of TRH & TSH if the Thyroid fails to respond? THEME #2 – Calcium: Calcium is used in the body to build up Bones & Teeth Calcium is also stored in the bones when the body needs it for blood clotting & delivery to muscles who need it to function properly. Consume Calcium: Absence of Calcium in blood: SWITCH ON: Chemoreceptors detect rise in blood calcium SWITCH ON: Chemoreceptors detect low blood calcium GLAND: Thyroid GLAND: Parathyroid Gland HORMONE: Calcitonin is released into blood HORMONE: PTH released into blood TARGET: Bones & Teeth are activated TARGET: Bones & Teeth are activated FUNCTION: Bones & Teeth absorb blood calcium. Calcium levels DROP! FUNCTION: Bones & Teeth release calcium into the blood. Calcium levels RISE! RESPONSE: Thyroid slows Calcitonin release! RESPONSE: Parathyroid continues until diet supplies calcium! Biology 30: Endocrine Themes Endocrine Themes: Sugar & Water Homeostasis Homeostatic themes: Composed of a GLAND – HORMONE – TARGET – FUNCTION Example: Milk Production & Release APG – Prolactin – Mammary Gland – Milk Production PPG – Oxytocin – Mammary Gland – Milk Release A typical loop has a start point to “turn it on” and to “turn it off” Milk Production is stimulated by baby “latching onto its mother” & continues until weaning. THEME #3 – Sugar: Sugar is the primary fuel of the body The body stores excess glucose as either fat (long term) or as glycogen (short term) If needed, the body can use the glucose that is stored Consume Glucose: Hunger, After exercise or between meals: SWITCH ON: Chemoreceptors detect rise in blood sugar GLAND: Pancreas SWITCH ON: Chemoreceptors detect low blood sugar GLAND: Pancreas HORMONE: Insulin release into blood HORMONE: Glucagon release (glucose is gone) TARGET: somatic cells (absorb & burn/convert to fat; Liver & Muscle absorb glucose TARGET: Liver & Muscle FUNCTION: Glucose stored as Glycogen FUNCTION: Glycogen releases Glucose into blood RESPONSE: BS Pancreas slows insulin release RESPONSE: BS Pancreas slows glucagon release THEME #4 – Water & Salt Retention: Water cannot be stored in the body, only conserved! Diuretics increase urine output (alcohol, caffeine, some medications, excess fluid consumption Thirst: Consume a Diuretic: SWITCH ON: Osmoreceptors in Hypothalamus detect low water levels GLAND: Pituitary (PPG) SWITCH ON: Excess fluids in the blood GLAND: Pituitary (PPG) HORMONE: ADH release into blood TARGET & FUNCTION: Kidneys pass more fluids TARGET: Kidneys FUNCTION: Kidneys retain water RESPONSE: Less urine, continues until you drink Salt Retention: G H HORMONE: No/less ADH release T/G RESPONSE: Continues until Blood fluid levels normalize! F/H T F Low BP APG ACTH Adrenal Cortex Aldosterone Kidney Retain Salts Water will follow salt back into the blood, BP will be maintained Biology 30: Endocrine Themes GLAND HORMONE Pineal Melaonin APG T A G F L M P PPG O A Thyroid T C Parathyroid P Pancreas I G Adrenal Cortex C A Adrenal Medulla A N Testes T I Ovary E P R Chorion HCG Hypothalamus (chemoreceptors) TRH Hypothalamus (chemoreceptors) GnRH TARGET Thalamus FUNCTION Makes me drowsy