* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Test 1
Pattern recognition wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz transformation wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Eigenvalues and eigenvectors wikipedia , lookup
Scalar field theory wikipedia , lookup
Linear algebra wikipedia , lookup
Laplace–Runge–Lenz vector wikipedia , lookup
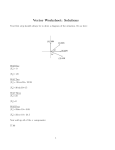
Test 1 phy 240 1. a) What are primitive concepts? Give an example. b) Write all four conditions which must be satisfied by a scalar product. (Use different symbols to distinguish operations on vectors from operations on numbers.) c) Define the magnitude of a vector. d) What does it mean that multiplication of a vector by a number is distributive over addition of vectors? (Use different symbols to distinguish operations on vectors from operations on numbers.) 2. The Cartesian coordinates of a point (scalar components of the position vector) are r = (−3.5m, −2.5m). a) Identify the scalar components of this vector. b) Identify the vector components of this vector. c) Find the polar coordinates of this point. 3. The one kilogram standard is a platinum-iridium cylinder 39 mm in height and 39 mm in diameter. What is the density of the material? 4. Two vectors A and B have precisely equal magnitudes. For the magnitude of A+B to be 100 times greater than the magnitude of A-B what must the angle between them be? -1- a) Primitive concepts are not formally defined. Understanding of these concepts is based on intuition. Mass, length, time are examples of primitive concepts. b) The following conditions are satisfied by scalar product: 1. A o B = B o A 2. (α • A ) o B = α(A o B) 3. (A ⊕ B ) o C = (A o C) + (B o C) (commutative) (mixed associative) (distributive over addition of vectors) 4. A2 ≥ 0 A2 = 0 if and only if A = 0 c) The magnitude of a vector is defined as the square root of the scalar square of the vector: A = A2 If α is an arbitrary number, and A and B are two arbitrary vectors then α • (A ⊕ B ) = α • A ⊕ α • B -2y rx θ j i x ry r a) The scalar components of the position vector r are given in the problem: x = −3.5 m y = −2.5 m b) The vector components are: rx = (−3.5m) i ry = (−2.5m) j c) Following the definition, the magnitude of this vector is r = r2 = (− 3.5m)2 + (− 2.5m)2 = 4.3m The Cartesian components are also related to the angle θ indicating the direction of the vector tan θ = y − 2.5m = x − 3.5m Since the vector is in the third quadrant, the angle with the x-axis is θ = 180° + arctan − 2.5m = 216° − 3.5m -3- 39.0 mm 39.0 mm From the definition of density ρ, for a uniform object, its mass m is directly proportional to the volume V 1) m= ∫ ρdV = ρ ⋅ ∫ dV = ρV object object The volume of a cylinder depends on its radius r and height h 2) V = πr 2 h The rest is algebra: ρ= m m 1kg kg = = ≈ 2.15 × 104 2 V πr 2 h m3 π ⋅ 19.5 × 10− 3 m ⋅ 39.0 × 10− 3 m ( ) ( ) -4- A+B A A-B B θ -B Solution 1 Let θ represent the angle between the directions of the two vectors. Since A and B have the same magnitudes, A, B, and A+B form an isosceles triangle in which the angles are (π-θ), θ/2 and θ/2. Similarly A, B, and A-B form an isosceles triangle in which the angles are θ, (π-θ)/2 and (π-θ)/2. From the law of cosines, the magnitude of both A+B and A-B can be expressed in terms of the magnitude of vector A (and B) A + B = A 2 + B2 − 2AB cos(π − θ ) = 2A 2 (1 + cosθ ) = 2A cos A − B = A 2 + B2 − 2AB cosθ = 2A2 (1 − cos θ) = 2A sin θ 2 θ 2 The ratio given in the problem yields the following trigonometric equation tan θ 1 = 2 100 from which θ = 2 ⋅ arctan 1 ≈ 0.02 ≈ 1.15° 100 (Solution 2 One can avoid using the law of cosines. From the definition of magnitude θ A + B = (A + B )2 = A 2 + B 2 + 2A o B = 2A 2 (1 + cosθ) = 2A cos 2 θ A − B = (A − B)2 = A2 + B2 − 2A o B = 2A2 (1 − cosθ) = 2A sin ) 2