* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1/28 Ratio and Proportion notes File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
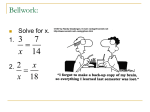
Ratio and Proportion 8.1-8.2 Unit IIA Day 1 Do Now Simplify each fraction 12/15 14/56 21/6 90/450 Computing Ratios If a and b are two quantities that are measured in the same units, then the ratio of a to b is a/b. Can also be written as _____. Because a ratio is a quotient, its denominator cannot be ________. Ratios are usually expressed in simplified form. For instance, the ratio of 6:8 is usually simplified to _____ Ex. 1: Simplifying Ratios a. Simplify the ratios (be careful of units!): 12 cm b. 6 ft c. 9 in. 4m 18 in. 18 in. Ex. 2: Using Ratios The perimeter of rectangle ABCD is 60 centimeters. The ratio of AB:BC is 3:2. Find the length and the width of the rectangle. Ex. 3: Using Extended Ratios The measures of the angles in ∆JKL are in the extended ratio 1:2:3. Find the measures of the angles. Properties of proportions An equation that equates (sets equal) two ratios is called a __________________ The numbers a and d are called the extremes of the proportions. The numbers b and c are called the means of the proportion. Means Extremes = Properties of proportions Cross product property: The product of the “extremes” equals the product of the “means”. If = , then ________. Reciprocal property: If two ratios are equal, then their reciprocals are also equal. If = , then ________. Ex. 5: Solving Proportions Solve the proportion. a) b) 4 5 = x 7 3 2 = y +2 y Geometric Mean The geometric mean of two positive numbers a and b is the positive number x such that a x = x b If you solve this proportion for x, you find that x = _____ which is a ______ number. Homework #46 The ratio of the width to the length for each rectangle is given. Solve for the variable. Homework #57 The ratios of the side lengths of ΔPQR to the corresponding side lengths of ΔSTU are 1:3. Find the unknown lengths. Comparing Arithmetic and Geometric Means If x is the arithmetic mean of a and b, then x is the same ___________ from a and b. Find it by __________ a and b and then _____________. If x is the geometric mean of a and b, then x is the same ___________ from a and b. Find it by __________ a and b and then _____________. Ex. 7: Using a Geometric Mean International standard paper sizes all have the same width-to-length ratios. Two sizes of paper are shown. The distance labeled x is the geometric mean of 210 mm and 420 mm. Find the value of x. Closure What distinguishes a ratio from a quotient?