* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Forensic Fingerprint Science Biological basis? Fingerprint science is
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
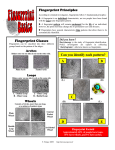
Forensic Fingerprint Science Biological basis? Fingerprint science is bas used ed on a number of related hard sciences (it is an applied science) Your fingerprints never change throughout life Grew (1684) phubished first paper that observed ridfe structure on fingers Bidloo (1685) etc. Bertillion (classification) Galton (ridge characteristics, 1st book –plagerized from Darwin) Vucetic/Henry used fingerprints for crime Locard established rules and could identify really easily,’ How do you make fingerprints Fingerprints are unique, they are randomly formed using volar pads (bubbles on fingers, determines shape of patterns, inherited because they are based upon bone structure Formed at 10 weeks, completely done by 25th week. Create loops or whorls or arches. Caused by the mechanics of stress Primary ridge is the higher part (accommodates sweat ducts, secondary ridge is the lower bit Remains constant forever (or until you star your fingers What is the scientific basis? Fingerprints are permanent (basal layer—provides nutrients to build more skin cells) Ridge formations are unique It is statistically and biologically impossible for duplication In over 100 years of use which includes automation, no two persons were ever found to have the same identical relationship of ridge features. Some areas of lesser details can be duplicated. Not even identical twins have same fingerprints—come get close fut never Even clones have different fingerprints Galtan characteristics = points of identification FRICTION RIDGE IDENTIFICATION • “The individualization of an impression is established by finding agreement of corresponding individual characteristics of such number and significance, as to preclude the possibility of their having occurred by mere coincidence, and establishing that there are no differences that cannot be accounted for” • Harold Tuthill Individualization: Principles and Procedures in Criminalistics The Scientific Principle Of The Fingerprint Identification Process • ANALYSIS • COMPARISON • EVALUATION – In order to establish a positive identification, a sufficient number of ridge characteristics must be in the approximate same position, and the exact same unit relationship – Unit relationship is the same number of intervening ridges between one ridge characteristic and another, in both impressions • VERIFICATION Evaluation sees latent vs inked copy—try to find characters prior to viewing sample (thus sufficient uniqueness of ridge detail to conclude that the two impressions are from the same people What is sufficient? Clearer image, less reuired Used to have 12 point rule—1972 FBI you can identify in less than 12 but 12 will always be sufficient Locard’s Tripartite Rule • In 1914, Dr. Locard published his conclusions of the fingerprint identification and the criteria that should be used to assure reliability based upon statistical analysis study. His study showed the following tripartite rule summarized as follows • If more than 12 concurring points are present and the fingerprint is sharp, the certainty of identity is beyond debate. • If 8 to 12 concurring points are involved, then the case is borderline and the certainty of identity will depend on: • the sharpness of the fingerprints; • the rarity of its type; • the presence of the center of the figure [core] and the triangle [delta] in the exploitable part of the print; • the presence of pores [poroscopy]; • the perfect and obvious identity regarding the width of the papillary ridges and valleys, the direction of the lines, and the angular value of the bifurcations [ridgeology / edgeoscopy]. • If a limited number of characteristic points are present, the fingerprints cannot provide certainty for an identification, but only a presumption proportional to the number of points available and their clarity (inconclusive result) International Assoc. for Identification (IAI) • In 1973 and 1974 the IAI attempted to establish a fingerprint standard for conclusions (determined that there is no standard) • The Ne’urim (in 1995) declaration was a new citation to supplement the 1973 IAI statement • Up to the 1990’s quantification was still being utilized by most – “Because fingerprint science is objective and exact, conclusions reached are absolute and final” • Advances in fingerprint technologies 1991 H. Lee • Practitioners were governed by arbitrary restrictions by the IAI for standards of conclusions that were contrary to other impression evidence sciences –Repealed in 2010 – The latent print is made by subject A – The latent print is not made by subject A – The latent print is of no value for individualization Closest non match had 8 match How did the paradigm shift occur? • I was an instructor of latent fingerprints at the California Criminalistics Institute from 1989-2001 • In the late 1990’s I observed paradigm shift towards Ridgeology from classes that were being taught throughout the United States and abroad by David Ashbaugh and Pat Wertheim • “Friction ridge identification is established through the agreement of friction ridge formations, in sequence, having sufficient uniqueness to individualize” – David Ashbaugh - Ridgeology Handbook • Ashbaugh went to great lengths to document the results of research on the friction ridge shape and attributes of pores. He discounted point counting and emphasized the biological uniqueness of every ridge • Defined terms for 3 levels of detail of the fingerprint – Level 1 - Ridge Flow / Level 2 - Ridge Path (edgeoscopy) / Level 3 - Ridge Shapes , edged and pores) • Sufficiency has yet to be defined within Ridgeology Shift not universal . • Ridgeology discounted quantification based standards – Since there was no validity to count to a particular number of points – Many Ridgeologists believed that they did not need to count any number of points • The arguments for Ridgeology were largely philosophical based upon biological uniqueness that nature never repeats itself- The Snowflake Paradigm – Ear prints • Biological uniqueness is the guiding principal, and an impression can only come from one source – If the known and unknown impressions look the same, they must come from a common source Nature never repeats itself, however the basis for this uniqueness is more complex There needed to be a standard, because the only standard in that one was the examiner Ridgeology • Some Ridgeology practitioners dismissed needing any numbers to individualize, and some even denied looking at level 2 features • Practitioners supplanted level 2 with level 3 value rather than supplementing levels 1 and 2 with level 3 So then ACE-V method • Used by Ashbaugh to describe the process of individualization – Analyze, Compare, Evaluate- Verify • “ACE-V is a process, which will guarantee precision of application, not accuracy of the conclusion” • To be scientifically reliable and accurate, a scientifically validated standard or theory must be established prior to the ACE-V application - V-ACE-V – V is an objective measure from scientific testing – ACE-V is the subjective judgment of the examiner if V has been reached in the examination at hand • "We have reviewed available scientific evidence of the validity of the ACE-V method and found none.“ Numerical standards are based upon statistical modeling which can estimate the proanolotu of a non-mate fingerprint impression sharing a certain number of characteristics This standard gives a predictable reliability Sufficiency after 12 minutiae Still no set standard for the world SWIGFAST standard After Mayfield • National Academy of Science 2009 Report – Strengthening Forensic Science in the United States: A path Forward • Following numerous forensic errors, incompetence and fraud– highly critical - many recommendations • 2013 Proposed legislation in Committee – Criminal Justice and Forensic Science Reform Act- Senator P. Leahy – The Forensic Science and Standards Act – Senator J. Rockefeller • National Commission on Forensic Science – U.S. DOJ/NIST – Established 2013 – “30 members consisting of academic researchers, prosecutors, defense attorneys, judges and other relevant stakeholders to develop policy recommendations for the Attorney General. The commission will consider guidance on practices for federal, state and local forensic science laboratories developed by groups* of forensic science practitioners and academic researchers administered by NIST.” • Forensic Discipline Guidance Groups* to replace SWG’s Can’t determine age of fingerprents All fingerprints are circumstantial unless in victims blood