* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download COURSE MAPPING:
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
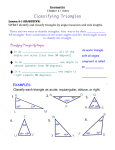
COURSE MAPPING: Subject: Math Course: Geometry Basics of Geometry: 23 days NJCCC Standards Content Topics/ Key Skills Enduring Understandings Essential Questions Assessment 4.3.8.A.1, 4.5.D.5 a) Patterns and Reasoning: Describing patterns, Completing patterns, Conjectures and counterexamples Find & describe patterns. What is next number or pattern in sequence? How would you describe a pattern? What is a conjecture? 4.2.8.A.1, 4.2.6.A.1 b) Points, Lines, Planes: Vocab: point, line, segment, ray, plane, collinear, coplanar, opposite rays, intersection Name, draw, & visualize intersections of points, lines & planes. When are points collinear? When are points coplanar? Where do planes intersect? How do you draw and label points, lines, segments & rays? Quiz - sec a & b: Patterns and Reasoning, Points, Lines, Planes 4.2.12.C.1, 4.2.12.E.1 c) Segments: Segment Addition Postulate, Distance Formula, Pythagorean Theorem, Congruency of segments Use of the Distance Formula. What is the Segment Addition Postulate? What is the Distance Formula? What is the Pythagorean Theorem? When are segments congruent? Quiz - sec c: Segments 4.2.8.A.1 d) Angles: Vocab: angle, vertex, sides, congruent angles, protractor, measure, interior of angle, exterior, angle addition postulate, Classify as: acute, right, obtuse or straight Classification of angles. What are parts of angles? How do you read a protractor? What is the Angle Addition Postulate? What are the 4 ways to classify angles? Co-Curricular Support Activities/ Experiences Science patterns: patterns of the moon, and doubling period of bacteria Relate to pictures & photos 4.2.8.A.1, 4.2.8.C.1, 4.2.12.C.1 e) Midpoints and Bisectors: Angle bisectors, Finding midpoints using formula, Finding endpoints, Setting congruent angles equal to solve algebraically, Finding angle measures Find midpoints & endpoints What is the midpoint formula? How do you find a midpoint? How do you find the next endpoint? How do you algebraically solve for congruent angles? Pop Quiz - sec e: Midpoints and Bisectors Algebraic problems with angle measures 4.2.8.A.1, 4.3.12.D.2 f) Angle Pairs: Vertical angles, Linear Pair, Complementary angles, Supplementary angles, Finding angle measures Identify particular angle pairs. Quiz - sec d,e & f : Angles, Midpoints and Bisectors, & Angle Pairs Algebraic problems with angle measures 4.2.8.E.1, 4.3.12.C.1 g) Perimeter & Area: Formulas for squares, rectangles, triangles and circles Find perimeter & area using formulas. What are the special angle pairs? What is a Linear Pair? What are Vertical angles? When are angles Complementary? When are angles Supplementary? What are the formulas for area and perimeter of special figures? Quiz - sec g: Perimeter & Area Real-life perimeter & area problems Unit Test Reasoning and Proof: 21 days NJCCC Standards Content Topics/ Key Skills Enduring Understandings Essential Questions 4.2.12.A.4, 4.5.D.5 a) Conditional Statements: 7 postulates on points, lines and planes, Draw diagrams, Vocab: conditional, hypothesis, conclusion, converse, inverse, negate, contrapositive, Types of conditional statements, Give Counterexamples. Analyze conditional statements. What are the postulates for points, lines & planes? How do you write conditional statements? Which part is the Hypothesis? Conclusion? What is the Converse? Inverse? Contrapositive? What is the Instance? Counterexample? b) Reasoning with Algebra Properties: Properties for Equality and Congruency: Reflexive, Symmetric, Transitive, Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, Division, Substitution, Congruent Segments, Segment Addition Use properties from Algebra. 4.2.12.A.4, 4.5.D.3, 4.5.D.5 Write postulates using conditional statements. What are the algebraic properties for Equality and Congruency? Assessment Co-Curricular Support Activities/ Experiences English grammar: correct usage with if-then statements Quiz - sec a & b: Conditional Statements, 7 postulates, & Reasoning with Algebra Properties 4.2.12.A.4, 4.5.D.3, 4.5.D.6 c) Proving Statements about Segments & Angles = Proofs: Setting up proofs 2 ways - 2 column table method with Statements (the steps) & Reasons (the properties) or a paragragh giving more of a logical thinking of the steps to take (also with the reasons). Justify statements & write reasons. How do you set up a formal proof? How do you set up a paragraph proof? Which key definitions can be reasons? What other reasons can you use? Pop Quiz - sec c: Proving Statements about Segments & Angles Quiz - sec c: Proofs Group work setting up proofs Unit Test Perpendicular and Parallel Lines: 24 days NJCCC Standards Content Topics/ Key Skills Enduring Understandings Essential Questions 4.2.8.A.1, 4.2.12.A.3 a) Lines, Planes and Angles: Parallel lines & planes, Perpendicular lines & planes, Skew lines, Transversal, Angles formed by 2 lines with a transversal, Alternate Interior ∠s, Consecutive Interior ∠s, Alternate Exterior ∠s, Corresponding ∠s Identify relationships between lines & angles. What are the relationships between lines? Between planes? What pairs of angles are formed by a transversal and 2 lines? b) Parallel Lines and Transversals: Angle relationships when lines are parallel, Solve Algebraic equations for angle relationships, Congruent and supplementary ∠ equations c) Proving Lines are Parallel = Proofs: 3 types of proofs: a) 2 column (formal) b) paragraph (informal) c) flow uses boxes, Proofs for theorems and postulates for lines Prove and use results about parallel lines and transversals. What are the postulates and theorems of parallel lines and a transversal? Which ∠s are ≅ ? Which ∠s are supplementary ? How do you relate them algebraically? Use properties of parallel lines and transversals to write proofs. What are the 3 types of proofs? What is a formal proof? What is an informal proof? What is a flow proof? How are they similar? How are they different? What proof reasons may be used? Which key definitions can be reasons? 4.2.8.A.1, 4.2.12.A.3 4.2.12.A.4, 4.5.D.3, 4.5.D.6 Prove results about perpendicular lines. Assessment Co-Curricular Support Activities/ Experiences Science: leaf veins & stems relate to parallel lines and transversals. Pop Quiz - sec a & b: Lines, Planes and Angles & Parallel Lines and Transversals Quiz - sec a & b Quiz - sec c: Proving Lines are Parallel = Proofs Algebraic problems with angle measures related to parallel lines and transversals Group work setting up proofs 4.2.8.C.1, 4.2.12.C.1, 4.3.12.B.1, 4.3.12.B.2 4.2.8.C.1, 4.2.12.C.1, 4.3.12.B.1, 4.3.12.B.1 4.5.B.2, 4.2.12.C.1, 4.3.12.B.1, 4.3.12.B.2 d) Coordinate Plane & Graphing: Slopes: visually uses "rise over run", slope formula, and ⊥ slopes, and ⊥ equations, equations in y = mx + b form, standard form, graph lines using a table, graph lines using y = mx + b form, Graph 2 equations on same grid & look for point of intersection e) Writing equations of lines: Writing equations - 3 types: (using y = mx + b twice), write equation from a slope & a point (x,y), write equation from 2 points, write or ⊥ equations from a point & equation Find slopes of lines. f) Writing tasks on graphing and equations: Parallel & Perpendicular slopes, Parallel & Perpendicular lines, graphing lines, writing equations, finding shapes between lines, use of state math Rubric for open-ended questions Complete open-ended writing tasks that could be used as HSPA Math prompts on lines, slopes & equations. Graph lines. Write equations given various information. How do you find slope visually? From formula? How do you find slope from an equation? How do you find and ⊥ slopes? How do you write and ⊥ equations? How do you graph lines using a table? How do you graph lines using y = mx + b form? Quiz - sec d: Coordinate Plane & Graphing How do you write equations from a graph? How do you write equations using y = mx +b? How do you write equation from a slope & a point (x,y)? How do you write equation from 2 points? How do you write or ⊥ equations from a point & equation? How do you answer openended questions? How are open-ended graded with State Rubric? How do you graph equations? How do you use equations to graph shapes on plane? How to write equations that are or ⊥ ? Quiz - sec e: Writing equations of lines Art: graphic artists use slopes to create designs Pop Quiz - sec d Project related to graphs & equations Unit Test Quiz - sec f: Writing tasks on graphing and equations English grammar: correct usage with writing tasks on lines and their relationships Assessment Co-Curricular Support Activities/ Experiences Congruent Triangles: 15 days NJCCC Standards Content Topics/ Key Skills Enduring Understandings Essential Questions 4.2.8.A.1, 4.2.12.A.3, 4.3.8.D.4 a) Triangle concepts: Classify by sides, classify by angles, parts of triangles, right Δs, isosceles Δs, equilateral Δs, sum of 3 ∠s of Δ = 180 °, sum of 2 remote ∠s = exterior ∠ Classify triangles. How do you classify Δs ? What are the parts of Δs ? What is the sum of the 3 ∠s of the Δ? How do you find the measure of the exterior ∠? How do you find ∠ measures in Δs? Find angle measures of triangles. Algebraic problems with angle measures of triangles 4.2.8.A.1, 4.2.12.A.3, 4.3.8.D.4 b) Congruence of Triangles: Naming ≅ parts of ≅ polygons, apply algebraic solving to find missing parts of 2 ≅ Δs c) Proving Triangles are Congruent:: Congruency postulates for ≅ Δs with drawings, 6 possibilities: 4 work for ≅ Δs: ASA, SSS, SAS, AAS, and 2 don't work: AAA & SSA, finding missing parts that are needed to prove congruency d) Proofs for triangles: Use of ASA, SSS, SAS, and AAS in proofs, use of CPCTC in proofs, reflexive prop used for "common side", use vertical angles, bisect & midpoint, perpendicular, alternate interior angles, etc. Identify congruent figures and corresponding parts. What are corresponding parts? How do you name corresponding parts? What is CPCTC ? Quiz - sec a & b: Triangle concepts & Congruence of Triangles Use of congruence postulates to prove triangles are congruent. What are the 6 congruency postulates for ≅ Δs ? Which 4 postulates work? Which 2 don't work? What is needed to prove 2 Δs ≅? How do you determine the missing needed parts? Quiz - sec c: Proving Triangles are Congruent NJCCC Standards Content Topics/ Key Skills Enduring Understandings Essential Questions 4.2.8.A.1 4.2.12.A.3 4.2.8.A.5 a) Perpendicular and Angle Bisectors: Perpendicular bisector, equidistant from 2 pts, perpendicular bisector theorem, angle bisector, angle bisector theorem, find distance of point to the sides of angle, conclude if point is on the bisector, use bisectors in proofs with triangle congruency, steps for congruency of triangles, circumcenter, incenter Use properties of perpendicular bisectors and angle bisectors. What is a perpendicular bisector? What is an angle bisector? How do you represent the shortest distance of point to line? How do you know if the point is on the perpendicular bisector? How do you know if point is on the angle bisector? What is the circumcenter? What is the incenter? 4.2.8.A.1, 4.2.12.A.3 4.2.12.A.4, 4.5.D.3, 4.5.D.6 Plan & write proofs on congruent triangles. How do you set up a proof? What concepts can be used as reasons for proofs? Which definitions can be used as reasons? What new reasons can be used for these triangles? When do you use CPCTC? When do you use the Δ ≅ statement? Properties of Triangles: 20 days Architecture: triangles in architecture – use of Internet Unit Test Group work setting up proofs Assessment Co-Curricular Support Activities/ Experiences 4.2.8.A.1 4.2.12.A.3 4.2.8.A.5 4.2.8.A.1 4.2.12.A.3 4.2.8.A.5 4.2.8.A.2 4.2.12.A.3 4.2.8.C.1 4.2.12.C.1 4.2.8.A.2 4.2.12.A.3 4.2.8.C.1 4.2.12.C.1 b) Altitudes and Medians of Triangles: Use medians, altitudes and centroid relationships: Median, altitude, centroid, orthocenter, ratio for the 2 sections of the median c) Midsegment Theorem: Use midpoints & midsections of triangles: Midsegment = segment connects midpts of 2 sides, midsegment is parallel and 1/2 the length of side, Include midpoints, coordinate grids, slopes, distance formula, perimeter of 2 Δs d) Angle & Side Relationships of Triangles: Use relationships of sides and angles of a triangle: shortest side of Δ is opposite the smallest ∠, sum of 2 short sides must be greater than the long side of Δ, 3rd side: difference of 2 sides < x < sum of 2 sides e) Hinge Theorem: Use the Hinge Theorem for 2 Δs: If 2 sides of Δ are ≅ to 2 sides of 2nd Δ, then the larger 3rd ∠ is opposite the larger 3rd side(and converse), as the angle widens the opposite side also gets longer Use properties of altitudes and medians of triangles. What is a median? What is an altitude? Where do the medians intersect? What is the ratio for the 2 sections of the median? What is the centroid? What is the orthocenter? Quiz - sec a & b: Perpendicular and Angle Bisectors & Altitudes and Medians of Triangles Drawings: construct angle bisectors and medians to investigate concurrent lines Use properties of midsections of triangles. What is the midsection of a triangle? How does the midsection relate to the side of the triangle? What happens when you connect 3 midsections? How does the inner small Δ relate to outer large Δ? Connected midsections make what type of triangles? How do sides of Δ relate to angles? Which size ∠ is opposite the largest side? What must be the relationship of 2 sides of a triangle to the third side? How do you find the limits for the 3rd side of Δ ? How do you know if the 3 sides will make a Δ ? Quiz - sec c: Midsegment Theorem Art & Technology: Fractals – use Internet to research What is the Hinge Theorem for 2 Δs? As the angle widens, what happens to the opposite side? What must be true for the Hinge Theorem to apply? Quiz - sec d & e: Angle & Side Relationships of Triangles & Hinge Theorem Use triangle inequality to decide which angles and sides are largest or smallest. Use Hinge Theorem and its converse to compare side lengths and angle measures. Unit Test Quadrilaterals: 20 days NJCCC Standards Content Topics/ Key Skills Enduring Understandings Essential Questions Assessment Co-Curricular Support Activities/ Experiences 4.2.8.A.2 4.2.12.A.3 4.2.8.C.1 4.2.12.C.1 4.2.8.A.2 4.2.12.A.3 4.2.8.C.1 4.2.12.C.1 4.2.8.A.3 4.2.12.C.1 4.2.8.A.3 4.2.12.C.1 4.2.8.A.3 4.2.12.C.1 4.2.8.E.1 4.2.12.E.2 a) Polygons: Definition of polygon, 3 conditions, names per # sides, regular & irregular, convex & concave, if a triangle's angles total 180° then a quadrilateral = 360° b) Parallelograms: Parallelogram Properties: opp sides are parallel, opp sides & angles are congruent, consecutive angles are supplementary, diagonals bisect each other, 3 ways to prove if 4 pts are vertices of a parallelogram using slopes and distance formula c) Rhombuses, Rectangles, and Squares: Use properties of special parallelograms: squares, rectangles & rhombus d) Trapezoids and Kites: Use properties of trapezoids & kites, midsegment of trapezoid = 1/2 sum of the 2 bases e) Areas of Triangles and Quadrilaterals: Area Formulas for triangle, square, parallelogram, rectangle, rhombus, kite and trapezoid: Identify and describe polygons. Use rule for sum of angle measures of polygons. Use properties of parallelograms. Determine if 4 pts are vertices of a parallelogram using slopes and distance formula. Use properties of special parallelograms and their diagonals. Use properties of trapezoids and kites. Find areas of special polygons using formulas. What is a polygon? What is a diagonal? What are the names of special polygons? When is a polygon regular? Convex? Concave? What are the properties of a parallelogram? What is the sum of the 4 angles of a parallelogram? Which angles are congruent? Which angles are supplementary? When is a Quadrilateral a Parallelogram? How do you prove that 4 points are actually the vertices of a parallelogram? What are the properties of rectangles? What are the properties of squares? What are the properties of a rhombus? What are the properties of a trapezoid? What are the properties of an isosceles trapezoid? What are the properties of a kite? What is the Area formula for each special quadrilateral? Why are there 2 formulas for the area of the rhombus? Traffic signs: some signs are International warning signs – which polygon for which sign? Quiz - sec a & b: Polygons & Parallelograms Create charts with properties of all the special parallelograms Quiz - sec c & d: Rhombuses, Rectangles & Trapezoids and Kites Pop Quiz - sec e: Areas of Triangles and Quadrilaterals Algebraic problems using properties of special parallelograms and quadrilaterals Algebraic problems using areas of special polygons Unit Test Transformations: 6 days NJCCC Standards Content Topics/ Key Skills Enduring Understandings Essential Questions 4.2.8.B.1 4.2.8.C.2 4.2.12.B.1 a) Symmetry: Lines of symmetry for reflections, Rotational symmetry, turns & degrees, Symmetry in alphabet Find either or both types of symmetry in objects. What are the 2 types of symmetry? Rotate how many degrees? What are the lines of symmetry? How many? What are the 3 types of transformations? Assessment Co-Curricular Support Activities/ Experiences Art: designs that show lines of symmetry 4.2.8.B.1 4.2.8.C.2 4.2.12.B.1 4.2.8.B.1 4.2.8.C.2 4.2.12.B.1 4.2.8.B.1 4.2.8.C.2 4.2.12.B.1 b) Translations : Translation = slide to another position, add or subtract to coordinates c) Reflections: Reflection = flip over line or an axis, mirror image, Identify, describe, and use translations. How do coordinates change when you translate image up? Down? Left? Right? Identify, describe, and use reflections. How do coordinates change when you reflect image over X axis? Over Y axis? Over X =Y? d) Rotations: Rotation = spin around point, Clockwise or counterclockwise, Degrees: 90, 180 or 270, Rotate around a point or the origin Identify, describe, and use rotations. How do coordinates change when you rotate image 180° ? 90° ? Around a point on the image? around the origin? Writing task Quiz on sec b - d: Translations, Reflections & Rotations Writing tasks on Translations, Reflections & Rotations Project on Translations, Reflections & Rotations – show all 3 transformations on a cartoon design More Proofs: 6 days NJCCC Standards Content Topics/ Key Skills Enduring Understandings Essential Questions Assessment Co-Curricular Support Activities/ Experiences 4.2.12.A.4, 4.5.D.3, 4.5.D.6 a) Writing formal proofs: List of possible reasons: Include triangle congruencies, definitions, postulates & theorems Plan & write proofs on additional topics using any definition or property studied. How do you set up a proof? What are the types? What reasons you can use? Does it make logical sense? Does it flow smoothly? Does it prove what it is supposed to prove? Quiz - sec a: Writing formal proofs Group work setting up proofs Assessment Co-Curricular Support Activities/ Experiences Similarity: 17 days NJCCC Standards Content Topics/ Key Skills Enduring Understandings Essential Questions 4.1.8.A.3, 4.2.8.A.4, 4.2.12.E.1 a) Ratios & Proportions: Ratios = comparison of 2 items, fraction form or : form, Solve Proportions by cross multiply and divide Find and simplify ratios. What are the forms of ratios? How do you convert units of ratios? How do you solve a proportion? b) Geometric Proportion Properties: Use the properties of proportions, use ratios for parts of triangles, Cross products, means = extremes, the geometric mean: x = square root a x b Use properties of proportions. 4.1.8.A.3, 4.2.8.A.4, 4.2.12.E.1 Set up and solve proportions. Use the geometric mean. What is the Cross Product Property? What is the Reciprocal Property? What is the geometric mean? How do you find the geometric mean? Quiz - sec a & b: Writing formal proofs & Geometric Proportion Properties 4.1.8.A.3, 4.2.8.A.4, 4.2.12.E.1 4.1.8.A.3, 4.2.8.A.4, 4.2.12.E.1 4.2.12.E.1 c) Similar Polygons: Similarity symbol is ~, Angles are ≅, Sides are proportional to scale factor, Similar Polygons have Proportional perimeters, writing Proportionality statements, writing Similarity statements d) Similar Triangles: Apply properties of similar triangles: Use: ≅ ∠s, proportionality with sides, determining similarity to solve for x & y, scale factors, reduced forms Identify similar polygons. e) Proportions and Similar Triangles: Apply similarity postulates to triangles: AA Sim, SSS Sim, SAS Sim, proportionality theorems with parallel lines Apply similarity postulates to triangles. Use scale factors to find to find sides of similar polygons. Use properties of similar triangles. When are polygons proportional? What are scale factors? How do you write similarity statements? What is a Proportionality statement? What is a Similarity statement? How do you set up proportions with polygon similarity? What are the properties of similar triangles? What are scale factors used for? Quiz - sec c: Similar Polygons What are the postulates of similar triangles? When do you use AA Sim? SSS Sim? SAS Sim? What are the proportionality theorems with parallel lines? What is relationship of the angle bisector to the opposite side? Quiz - sec d & e: Similar Triangles & Proportions and Similar Triangles Project – Use scale factors for scale drawings to calculate size of real-life objects Algebraic problems using similarity to solve for x & y values Unit Test Right Triangles and Trigonometry: 18 days NJCCC Standards Content Topics/ Key Skills Enduring Understandings Essential Questions 4.1.8.B.3, 4.2.12.E.1 a) Operations with square roots: Review applications of square roots: simplify squares and simplify not squares, add, multiply, & rationalize the denominator Simplify radical expressions. How do you simplify square roots? How do you add and subtract radicals? How do you rationalize the denominator? Why do you rationalize the denominator? 4.1.8.B.3, 4.2.8.A.2, 4.2.12.E.1 b) The Pythagorean Theorem: a² + b² = c², b² = c² - a², finding the hypotenuse, finding the leg, Pythagorean triple Use the Pythagorean Theorem in real-life problems. What is the Pythagorean Theorem? How do you find the hypotenuse? How do you find one of the legs? How do you apply the Pythagorean Theorem to Area of Triangles? Assessment Co-Curricular Support Activities/ Experiences Algebraic problems using the Pythagorean Theorem 4.1.8.B.3, 4.2.8.A.2, 4.2.12.E.1 c) Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem: c² = a² + b² is right ∠, c² < a² + b² is acute ∠, c² > a² + b² is obtuse ∠ Use the Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem. 4.1.8.B.3, 4.2.8.A.2, 4.2.12.E.1 d) Similar Right Triangles: Theorems of similar right Δs: Use proportions & geometric means to relate similar Right Δs, 3 sets of triangle drawings and proportions Use the altitude of the right triangle as a geometric mean. 4.1.8.B.3, 4.2.8.A.2, 4.2.12.E.1 e) Special Right Triangles: Draw 30,60,90 & 45,45,90 triangles, relationships of the angles & legs, 45,45,90 →legs x, x, & x√2 = hypotenuse, 30,60,90 → legs are x√3 with hypotenuse = 2x f) Trigonometric Ratios: Use of trig ratios and the calculator transformations: Sine, Cosine & Tangent, sin = opp / hyp, cos = adj / hyp, tan = opp / adj, ratios switch to decimals, use of calc with angle degrees Find the side lengths of the special right triangles. 4.2.12.E.1 Use lengths of sides of triangles to classify them. Use trigonometric ratios to find the angle of elevation and indirect measurements. How do you classify triangles? When is it a Right Δ? When is it an Acute Δ? When is it an Obtuse Δ? How do you apply the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem to classify Triangles? Quiz - sec a, b & c: Operations with square roots, Pythagorean Theorem & Converse of Pythagorean Theorem What does the altitude form in a right triangle? How does the altitude & geometric mean relate to the hypotenuse? How does the leg & geometric mean relate to a right triangle? How do you set up the proportions related to these theorems? What are the special relationships for 45,45,90 and 30,60,90 triangles? How do you set up the proportions related to these theorems? Quiz - sec d & e: Similar Right Triangles & Special Right Triangles What are the 3 trig ratios? What does SohCahToa mean? How do you set up trig ratios? Quiz - sec f: Trigonometric Ratios Unit Test Construction: Use of the Pythagorean Theorem to develop drawings and measurements for construction of buildings Algebraic problems using trigonometric ratios in real-life situations UNIT MAPPING: Subject: Math Course: Geometry Basics of Geometry: 23 days Units a) Patterns and Reasoning NJCCCS 4.3.8.A.1, 4.5.D.5 Essential Questions What is next number or pattern in sequence? How would you describe a pattern? What is a conjecture? Content / Skill Describing patterns, Completing patterns, Conjectures and counterexamples b) Points, Lines, Planes 4.2.8.A.1, 4.2.6.A.1 When are points collinear? When are points coplanar? Where do planes intersect? How do you draw and label points, lines, segments & rays? Vocab: point, line, segment, ray, plane, collinear, coplanar, opposite rays, intersection Quiz - sec a & b c) Segments 4.2.12.C.1, 4.2.12.E.1 What is the Segment Addition Postulate? What is the Distance Formula? What is the Pythagorean Theorem? When are segments congruent? Segment Addition Postulate, Distance Formula, Pythagorean Theorem, Congruency of segments Quiz - sec c d) Angles 4.2.8.A.1 What are parts of angles? How do you read a protractor? What is the Angle Addition Postulate? What are the 4 ways to classify angles? Vocab: angle, vertex, sides, congruent angles, protractor, measure, interior of angle, exterior, angle addition postulate, Classify as: acute, right, obtuse or straight e) Midpoints and Bisectors 4.2.8.A.1, 4.2.8.C.1, 4.2.12.C.1 What is the midpoint formula? How do you find a midpoint? How do you find the next endpoint? How do you algebraically solve for congruent angles? Angle bisectors, Finding midpoints using formula, Finding endpoints, Setting congruent angles equal to solve algebraically, Finding angle measures Pop Quiz - sec e f) Angle Pairs 4.2.8.A.1, 4.3.12.D.2 What are the special angle pairs? What is a Linear Pair? What are Vertical angles? When are angles Complementary? When are angles Supplementary? Angle pairs: Vertical angles, Linear Pair, Complementary angles, Supplementary angles, Finding angle measures Quiz - sec d,e & f g) Perimeter & Area 4.2.8.E.1, 4.3.12.C.1 What are the formulas for area and perimeter of special figures? Perimeter & Area: Formulas for squares, rectangles, triangles and circles Quiz - sec g Unit Test Assessment Reasoning and Proof: 21 days Units a) Conditional Statements NJCCCS 4.2.12.A.4, 4.5.D.5 Essential Questions What are the postulates for points, lines & planes? How do you write conditional statements? Which part is the Hypothesis? Conclusion? What is the Converse? Inverse? Contrapositive? What is the Instance? Counterexample? Content / Skill 7 postulates on points, lines and planes, Draw diagrams, Vocab: conditional, hypothesis, conclusion, converse, inverse, negate, contrapositive, Types of conditional statements, Give Counterexamples. Assessment b) Reasoning with Algebra Properties 4.2.12.A.4, 4.5.D.3, 4.5.D.5 What are the algebraic properties for Equality and Congruency? Properties for Equality and Congruency: Reflexive, Symmetric, Transitive, Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, Division, Substitution, Congruent Segments, Segment Addition Quiz - sec a & b c) Proving Statements about Segments & Angles = Proofs 4.2.12.A.4, 4.5.D.3, 4.5.D.6 How do you set up a formal proof? How do you set up a paragraph proof? Which key definitions can be reasons? What other reasons can you use? Setting up proofs 2 ways - 2 column table method with Statements (the steps) & Reasons (the properties) or a paragraph giving more of a logical thinking of the steps to take (also with the reasons). Pop Quiz - sec c Quiz - sec c Unit Test Perpendicular and Parallel Lines: 24 days Units a) Lines, Planes and Angles NJCCCS 4.2.8.A.1, 4.2.12.A.3 Essential Questions What are the relationships between lines? Between planes? What pairs of angles are formed by a transversal and 2 lines? Content / Skill Parallel lines & planes, Perpendicular lines & planes, Skew lines, Transversal, Angles formed by 2 lines with a transversal, Alternate Interior ∠s, Consecutive Interior ∠s, Alternate Exterior ∠s, Corresponding ∠s b) Parallel Lines and Transversals 4.2.8.A.1, 4.2.12.A.3 What are the postulates and theorems of parallel lines and a transversal? Which ∠s are ≅ ? Which ∠s are supplementary ? How do you relate them algebraically? Angle relationships when lines are parallel, Solve Algebraic equations for angle relationships, Congruent and supplementary ∠ equations Pop Quiz - sec a & b, Quiz - sec a & b c) Proving Lines are Parallel = Proofs 4.2.12.A.4, 4.5.D.3, 4.5.D.6 What are the 3 types of proofs? What is a formal proof? What is an informal proof? What is a flow proof? How are they similar? How are they different? What proof reasons may be used? Which key definitions can be reasons? 3 types of proofs: a) 2 column (formal) b) paragraph (informal) c) flow - uses boxes, Proofs for theorems and postulates for lines Quiz - sec c d) Coordinate Plane & Graphing 4.2.8.C.1, 4.2.12.C.1, 4.3.12.B.1, 4.3.12.B.2 How do you find slope visually? From formula? How do you find slope from an equation? How do you find and ⊥ slopes? How do you write and ⊥ equations? How do you graph lines using a table? How do you graph lines using y = mx + b form? Slopes: visually uses "rise over run", slope formula, and ⊥ slopes, and ⊥ equations, equations in y = mx + b form, standard form, graph lines using a table, graph lines using y = mx + b form, Graph 2 equations on same grid & look for point of intersection Quiz - sec d, Pop Quiz - sec d e) Writing equations of lines 4.2.8.C.1, 4.2.12.C.1, 4.3.12.B.1, 4.3.12.B.1 How do you write equations from a graph? How do you write equations using y = mx +b? How do you write equation from a slope & a point (x,y)? How do you write equation from 2 points? How do you write or ⊥ equations from a point & equation? Writing equations - 3 types: (using y = mx + b twice), write equation from a slope & a point (x,y), write equation from 2 points, write or ⊥ equations from a point & equation Quiz - sec e Unit Test f) Writing tasks on graphing and equations 4.5.B.2, 4.2.12.C.1, 4.3.12.B.1, 4.3.12.B.2 How do you answer open-ended questions? How are open-ended graded with State Rubric? How do you graph equations? How do you use equations to graph shapes on plane? How to write equations that are or ⊥ ? Parallel & Perpendicular slopes, Parallel & Perpendicular lines, graphing lines, writing equations, finding shapes between lines, use of state math Rubric for open-ended questions Quiz - sec f Assessment Congruent Triangles: 15 days Units a) Triangle concepts NJCCCS 4.2.8.A.1, 4.2.12.A.3, 4.3.8.D.4 b) Congruence of Triangles 4.2.8.A.1, 4.2.12.A.3, 4.3.8.D.4 c) Proving Triangles are Congruent d) Proofs for triangles Essential Questions How do you classify Δs ? What are the parts of Δs ? What is the sum of the 3 ∠s of the Δ? How do you find the measure of the exterior ∠? How do you find ∠ measures in Δs? What are corresponding parts? How do you name corresponding parts? What is CPCTC ? Content / Skill Classify by sides, classify by angles, parts of triangles, right Δs, isosceles Δs, equilateral Δs, sum of 3 ∠s of Δ = 180 °, sum of 2 remote ∠s = exterior ∠ Assessment Naming ≅ parts of ≅ polygons, apply algebraic solving to find missing parts of 2 ≅ Δs Quiz - sec a & b 4.2.8.A.1, 4.2.12.A.3 What are the 6 congruency postulates for ≅ Δs ? Which 4 postulates work? Which 2 don't work? What is needed to prove 2 Δs ≅? How do you determine the missing needed parts? Congruency postulates for ≅ Δs with drawings, 6 possibilities: 4 work for ≅ Δs: ASA, SSS, SAS, AAS, and 2 don't work: AAA & SSA, finding missing parts that are needed to prove congruency Quiz - sec c 4.2.12.A.4, 4.5.D.3, 4.5.D.6 How do you set up a proof? What concepts can be used as reasons for proofs? Which definitions can be used as reasons? What new reasons can be used for these triangles? When do you use CPCTC? When do you use the Δ ≅ statement? Use of ASA, SSS, SAS, and AAS in proofs, use of CPCTC in proofs, reflexive prop used for "common side", use vertical angles, bisect & midpoint, perpendicular, alternate interior angles, etc. Unit Test Properties of Triangles: 20 days Units a) Perpendicular and Angle Bisectors NJCCCS 4.2.8.A.1 4.2.12.A.3 4.2.8.A.5 Essential Questions What is a perpendicular bisector? What is an angle bisector? How do you represent the shortest distance of point to line? How do you know if the point is on the perpendicular bisector? How do you know if point is on the angle bisector? What is the circumcenter? What is the incenter? b) Altitudes and Medians of Triangles 4.2.8.A.1 4.2.12.A.3 4.2.8.A.5 What is a median? What is an altitude? Where do the medians intersect? What is the ratio for the 2 sections of the median? What is the centroid? What is the orthocenter? c) Midsegment Theorem 4.2.8.A.1 4.2.12.A.3 4.2.8.A.5 What is the midsection of a triangle? How does the midsection relate to the side of the triangle? What happens when you connect 3 midsections? How does the inner small Δ relate to outer large Δ? Connected midsections make what type of triangles? d) Angle & Side Relationships of Triangles 4.2.8.A.2 4.2.12.A.3 4.2.8.C.1 4.2.12.C.1 How do sides of Δ relate to angles? Which size ∠ is opposite the largest side? What must be the relationship of 2 sides of a triangle to the third side? How do you find the limits for the 3rd side of Δ ? How do you know if the 3 sides will make a Δ ? e) Hinge Theorem 4.2.8.A.2 4.2.12.A.3 4.2.8.C.1 4.2.12.C.1 What is the Hinge Theorem for 2 Δs? As the angle widens, what happens to the opposite side? What must be true for the Hinge Theorem to apply? Content / Skill Perpendicular bisector, equidistant from 2 pts, perpendicular bisector theorem, angle bisector, angle bisector theorem, find distance of point to the sides of angle, conclude if point is on the bisector, use bisectors in proofs with triangle congruency, steps for congruency of triangles, circumcenter, incenter Use medians, altitudes and centroid relationships: Median, altitude, centroid, orthocenter, ratio for the 2 sections of the median Assessment Quiz - sec a & b Use midpoints & midsections of triangles: Midsegment = segment connects midpts of 2 sides, midsegment is parallel and 1/2 the length of side, Include midpoints, coordinate grids, slopes, distance formula, perimeter of 2 Δs Use relationships of sides and angles of a triangle: shortest side of Δ is opposite the smallest ∠, sum of 2 short sides must be greater than the long side of Δ, 3rd side: difference of 2 sides < x < sum of 2 sides Quiz - sec c Use the Hinge Theorem for 2 Δs: If 2 sides of Δ are ≅ to 2 sides of 2nd Δ, then the larger 3rd ∠ is opposite the larger 3rd side(and converse), as the angle widens the opposite side also gets longer Quiz - sec d & e Unit Test Quadrilaterals: 20 days Units a) Polygons NJCCCS 4.2.8.A.2 4.2.12.A.3 4.2.8.C.1 4.2.12.C.1 Essential Questions What is a polygon? What is a diagonal? What are the names of special polygons? When is a polygon regular? Convex? Concave? Content / Skill Definition of polygon, 3 conditions, names per # sides, regular & irregular, convex & concave, if a triangle's angles total 180° then a quadrilateral = 360° Assessment b) Parallelograms 4.2.8.A.2 4.2.12.A.3 4.2.8.C.1 4.2.12.C.1 What are the properties of a parallelogram? What is the sum of the 4 angles of a parallelogram? Which angles are congruent? Which angles are supplementary? When is a Quadrilateral a Parallelogram? How do you prove that 4 points are actually the vertices of a parallelogram? Parallelogram Properties: opp sides are parallel, opp sides & angles are congruent, consecutive angles are supplementary, diagonals bisect each other, 3 ways to prove if 4 pts are vertices of a parallelogram using slopes and distance formula Quiz - sec a & b c) Rhombuses, Rectangles, and Squares 4.2.8.A.3 4.2.12.C.1 What are the properties of rectangles? What are the properties of squares? What are the properties of a rhombus? Use properties of special parallelograms: squares, rectangles & rhombus: d) Trapezoids and Kites 4.2.8.A.3 4.2.12.C.1 What are the properties of a trapezoid? What are the properties of an isosceles trapezoid? What are the properties of a kite? Use properties of trapezoids & kites, midsegment of trapezoid = 1/2 sum of the 2 bases Quiz - sec c & d e) Areas of Triangles and Quadrilaterals 4.2.8.A.3 4.2.12.C.1 4.2.8.E.1 4.2.12.E.2 What is the Area formula for each special quadrilateral? Why are there 2 formulas for the area of the rhombus? Area Formulas for triangle, square, parallelogram, rectangle, rhombus, kite and trapezoid: Pop Quiz - sec e Unit Test Transformations: 6 days Units a) Symmetry NJCCCS 4.2.8.B.1 4.2.8.C.2 4.2.12.B.1 Essential Questions What are the 2 types of symmetry? Rotate how many degrees? What are the lines of symmetry? How many? What are the 3 types of transformations? Content / Skill Lines of symmetry for reflections, Rotational symmetry, turns & degrees, Symmetry in alphabet b) Translations 4.2.8.B.1 4.2.8.C.2 4.2.12.B.1 How do coordinates change when you translate image up? Down? Left? Right? Translation = slide to another position, add or subtract to coordinates c) Reflections 4.2.8.B.1 4.2.8.C.2 4.2.12.B.1 How do coordinates change when you reflect image over X axis? Over Y axis? Over X =Y? Reflection = flip over line or an axis, mirror image, d) Rotations 4.2.8.B.1 4.2.8.C.2 4.2.12.B.1 How do coordinates change when you rotate image 180° ? 90° ? Around a point on the image? around the origin? Rotation = spin around point, Clockwise or counterclockwise, Degrees: 90, 180 or 270, Rotate around a point or the origin Writing task Quiz on sec b - d Project on sec b - d NJCCCS 4.2.12.A.4, 4.5.D.3, 4.5.D.6 Essential Questions How do you set up a proof? What are the types? What reasons you can use? Does it make logical sense? Does it flow smoothly? Does it prove what it is supposed to prove? Content / Skill List of possible reasons: Include triangle congruencies, definitions, postulates & theorems Assessment Quiz - sec a Assessment More Proofs: 6 days Units a) Writing formal proofs Similarity: 17 days Units a) Ratios and Proportions NJCCCS 4.1.8.A.3, 4.2.8.A.4, 4.2.12.E.1 Essential Questions What are the forms of ratios? How do you convert units of ratios? How do you solve a proportion? Content / Skill Ratios = comparison of 2 items, fraction form or : form, Solve Proportions by cross multiply and divide b) Geometric Proportion Properties 4.1.8.A.3, 4.2.8.A.4, 4.2.12.E.1 What is the Cross Product Property? What is the Reciprocal Property? What is the geometric mean? How do you find the geometric mean? Use the properties of proportions, use ratios for parts of triangles, Cross products, means = extremes, the geometric mean: x = square root a x b Quiz - sec a & b c) Similar Polygons 4.1.8.A.3, 4.2.8.A.4, 4.2.12.E.1 When are polygons proportional? What are scale factors? How do you write similarity statements? What is a Proportionality statement? What is a Similarity statement? How do you set up proportions with polygon similarity? Similar Polygons: Similarity symbol is ~, Angles are ≅, Sides are proportional to scale factor, Similar Polygons have Proportional perimeters, writing Proportionality statements, writing Similarity statements Quiz - sec c d) Similar Triangles 4.1.8.A.3, 4.2.8.A.4, 4.2.12.E.1 What are the properties of similar triangles? What are scale factors used for? Apply properties of similar triangles: Use: ≅ ∠s, proportionality with sides, determining similarity to solve for x & y, scale factors, reduced forms e) Proportions and Similar Triangles 4.2.12.E.1 What are the postulates of similar triangles? When do you use AA Sim? SSS Sim? SAS Sim? What are the proportionality theorems with parallel lines? What is relationship of the angle bisector to the opposite side? Apply similarity postulates to triangles: AA Sim, SSS Sim, SAS Sim, proportionality theorems with parallel lines Assessment Quiz - sec d & e Unit Test Right Triangles and Trigonometry: 18 days Units a) Operations with square roots NJCCCS 4.1.8.B.3, 4.2.12.E.1 Essential Questions How do you simplify square roots? How do you add and subtract radicals? How do you rationalize the denominator? Why do you rationalize the denominator? Content / Skill Review applications of square roots: simplify squares and simplify not squares, add, multiply, & rationalize the denominator b) The Pythagorean Theorem 4.1.8.B.3, 4.2.8.A.2, 4.2.12.E.1 What is the Pythagorean Theorem? How do you find the hypotenuse? How do you find one of the legs? How do you apply the Pythagorean Theorem to Area of Triangles? Pythagorean Theorem is a² + b² = c², b² = c² - a², finding the hypotenuse, finding the leg, Pythagorean triple c) Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem 4.1.8.B.3, 4.2.8.A.2, 4.2.12.E.1 Converse of Pythagorean Theorem: c² = a² + b² is right ∠, c² < a² + b² is acute ∠, c² > a² + b² is obtuse ∠ d) Similar Right Triangles 4.1.8.B.3, 4.2.8.A.2, 4.2.12.E.1 How do you classify triangles? When is it a Right Δ? When is it an Acute Δ? When is it an Obtuse Δ? How do you apply the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem to classify Triangles? What does the altitude form in a right triangle? How does the altitude & geometric mean relate to the hypotenuse? How does the leg & geometric mean relate to a right triangle? How do you set up the proportions related to these theorems? e) Special Right Triangles 4.1.8.B.3, 4.2.8.A.2, 4.2.12.E.1 What are the special relationships for 45,45,90 and 30,60,90 triangles? How do you set up the proportions related to these theorems? Draw 30,60,90 & 45,45,90 triangles, relationships of the angles & legs, 45,45, 90 →legs x, x, & x√2 = hypotenuse, 30,60,90 → legs are x√3 with hypotenuse = 2x Quiz - sec d & e f) Trigonometric Ratios 4.2.12.E.1 What are the 3 trig ratios? What does SohCahToa mean? How do you set up trig ratios? Use of trig ratios and the calculator transformations: Sine, Cosine & Tangent, sin = opp / hyp, cos = adj / hyp, tan = opp / adj, ratios switch to decimals, use of calc with angle degrees Quiz - sec f Unit Test Assessment Quiz - sec a, b & c Theorems of similar right Δs: Use proportions & geometric means to relate similar Right Δs, 3 sets of triangle drawings and proportions