* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 0 - Purdue Physics
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Surface-mount technology wikipedia , lookup
Rechargeable battery wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Battery charger wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
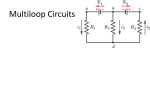
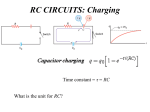
NOTES Resistors in Parallel and Series i R1 R2 ε i The same example (with parallel R combos) I3 I2 • Sketch the diagram • Simplify using equivalent resistors I1 • Label currents with directions • Use Junction Rule in labeling • Choose independent loops • Use Loop Rule Replace by equivalent R=2Ω first. I3 = I 1 + I 2 • Solve simultaneous linear equations Loop current example (with parallel R combos) I1 I2 I1 -I2 • Sketch the diagram • Simplify using equivalent resistors • Label loop currents with directions • Use Loop currents I1 and I2 • Choose interior clockwise loops . Set up cononical equations in Replace by equivalent R=2Ω first. . I1 I2 Ε format I1 (12 +6) +I2 (-6) = +18 (Emf) Left loop I1 (-6) + I2 (6+3+2) =+21 (Emf) Right loop Note Symmetry of Equations Finding Potential and Power in a Circuit But what is I? Must solve for I first! supplied by 12V battery The rest? Just means 0 V here into 4V battery (charging) dissipated by resistors Ammeter and Voltmeter Ammeter: an instrument used to measure currents • It must be connected in series. • The internal resistance of an ammeter must be kept as small as possible. Voltmeter: an instrument used to measure potential differences • It must be connected in parallel. • The internal resistance of a voltmeter must be made as large as possible. DEMO 6B-08 CLASSICAL GALVANOMETER ELECTRONIC VOLT- AMPERE - OHM, METER Galvanometer Inside Ammeter and Voltmeter Galvanometer: a device that detects small currents and indicates its magnitude. Its own resistance Rg is small for not disturbing what is being measured. galvanometer Ammeter: an instrument used to measure currents shunt resistor Voltmeter: an instrument used to measure potential differences galvanometer CAPACITOR IN RC CIRCUITS - TRANSIENTS I I charging discharging ε Switch closed at t=0. C initially uncharged, thus V0 = 0 across C and I0 = ε/R initially. Switch closed at t=0. C initially charged, thus V0 = Q0/C across C and I0 = V0/R initially. After a long time, C is fully charged and VC = ε across C and I∞ = 0. After a long time, C is fully discharged and VC = 0 across C and I∞ = 0. time constant Q = Q f (1 − e −t / RC ) Discharging a Capacitor in RC Circuits Eqns 1. Switch closed at t=0. Initially C is fully charged with Q0 2. Loop Rule: 3. Convert to a differential equation I 4. Solve it! Q(t) during Discharging time constant 0.37Q0 Current I(t) during Discharging DEMO 6C-03 FLASHER CIRCUIT 6C03 Charging a Capacitor in RC Circuits 1. Switch closed at t=0 C initially uncharged, thus zero voltage across C. 2. Loop Rule: 3. Convert to a differential equation 4. Solve it! (τ=RC is the time constant again) Charge Q(t) during Charging time constant Current I(t) during Charging Broken circuit = RC R in Lamp 110V C very small. i.e. RC very small. Instantly discharged BEHAVIOR OF CAPACITORS • Charging – Initially, the capacitor behaves like a wire. – After a long time, the capacitor behaves like an OPEN switch. • Discharging – Initially, the capacitor behaves like a battery. – After a long time, the capacitor behaves like an OPEN switch DOCCAM 2 ONE FARAD CAPACITOR and LED RESISTOR ENERGY CONSERVATION IN DISCHARGING A CAPACITOR Discharging: Energy lost by C Power dissipated by R Energy Conservation in Charging a Capacitor Charging: Work done by battery Energy stored in C The rest? Power dissipated by R Independent of R What if R=∞ ? What if R=0 ? PHYS 241 – Extra Quiz 3 All the capacitors below are identical and so are all the resistors. Which circuit have the longest time constant? A C B D E PHYS 241 – Extra Quiz 3 All the capacitors below are identical and so are all the resistors. Which circuit have the shortest time constant? A C B D E




























![Sample_hold[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008409180_1-2fb82fc5da018796019cca115ccc7534-150x150.png)
