* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 7TH CLASSES PHYSICS DAILY PLAN
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Wilson current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
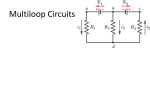
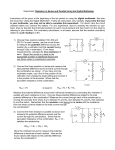
10TH CLASSES PHYSICS DATE:………………… DAILY PLAN b) Parallel combination: SUBJECT: Combination of resistors: AIM: students have to know the measurement of current and voltage of a combination of resistors DURATION: 80 min REAL LIFE: functions of resistors in an electric circuit PRESENTATION: The Measurement of Potential Difference, Current and Resistance: In a circuit, a potential difference can be measured by using an instrument called Voltmeter. A voltmeter is connected so that it must be placed in parallel with the resister. An ideal voltmeter has infinite resistance so that no current will pass through it. To measure the current, the instrument is called ammeter. An ammeter is constructed so that it must be placed in series with the current that it is to measure. Ideally, an ammeter should have zero resistance so as not to alter the current being measured. R +A_ +V_ + - V1 I1 R1 V2 I2 I R2 V In parallel combination potential differences are equal, currents are added. V1 = V2 = V.. ..I1 + I2 = I.. [This is because a charge must pass through R1 or R2] Equivalent resistance : R1 Req R2 I I I1 + I2 = I V1 V2 V + = R1 R 2 R eq 1 1 1 R1 R2 R eq Combination of resistors: Ex:12-13-14-15-16-17-18 a) Series combination: I V1 V2 R1 R2 HOMEWORK: pr.15-16-17-18-19 MULTIMEDIA: akadem.cerway3, electromag. DEMONSTRATION: measurement of current and voltage EXPERIMENT: ohm’s law V In series combination currents are equal, potential differences are added. I1 = I2 = I.. ..V1 + V2 = V.. [That is because charges pass through R1 and R2 losing energy on both of them.] Equivalent resistance: V V R1 Req R2 TEACHER: I I V = V1 + V2 I Req = I R1 + I R2 Req = R1 + R2.. DIRECTOR: