* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 8.6 World War II - JonesHistory.net
Wang Jingwei regime wikipedia , lookup
Fascism in Europe wikipedia , lookup
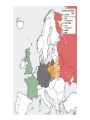
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
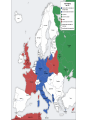
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
8.6 World War II
Der Führer
“Il Duce”
Hirohito
Worldwide economic depression, militant nationalism,
the rise of totalitarian rule, and the unsuccessful
efforts of the League of Nations to preserve peace
contributed to the outbreak of war in Europe and Asia
How the worldwide economic depression and
militant nationalism resulted in the rise of
totalitarian rule.
Fascist party advocated
• Glorification of the State
• Totalitarianism
• Single-party system with a strong ruler
“anocracy” = A political system which is neither fully democratic nor fully autocratic, often
being vulnerable to political instability.
Communists get support from working classes
Fascists get their support from business leaders and
landowners
ITALY
Fascists in Italy
• Il Duce – title
Mussolini gave himself
• Blackshirt – follower of
Mussolini
• Italians support
Mussolini in the 1920s
– prevented a Communist
revolution and brought
order to the country.
Mussolini
• Benito Mussolini
• 1922 power
• Played on anger at
Treaty of Versailles
– Denied Italy land it
wanted
• Played on fears of
Communists takeover
• Economic unrest
Il Duce
• All parties outlawed but
National Fascist Party
– Partito Nazionale
Fascista
• 1935 invasion Ethiopia
– Promise to restore
greatness of Rome
– League of Nations
cannot help b/c
Depression
– Ethiopia falls
GERMANY
Nazis
• National Socialist German Worker’s Party
– Nationalsozialistische Deutsche Arbeiterpartei
• Played on anger about Treaty of Versailles
– Blame for war
– Heavy reparation payments
• Hitler: “We didn’t really lose WWI; it was the Jews”
– scapegoat
Third Reich
• Third Reich – created by
Hitler to last 1000 years
• Der Fuhrer
• Reichstag – German
lawmaking body
• Many Germans did not
like the Weimar Republic
because they felt that it
had betrayed them by
accepting the Treaty of
Versailles
• The continued Great
Depression allowed Nazis
to increase their
influence throughout
Germany in the early
1930s
Adolf Hitler
• Skilled speaker
• Brownshirt – follower of
Hitler
• 1933 elected Chancellor
• 1935 end democratic
rule
• 1935 Nuremberg Laws
– stripped Jews of their
citizenship and their
rights
Expansion
• Hitler claims right to
expand east
– Lebensraum
• League of nations
protests
JAPAN
Brownshirt – follower of Hitler
Il Duce – title Mussolini gave himself
Third Reich – created by Hitler to last 1000
years
Reichstag – German lawmaking body
Blackshirt – follower of Mussolini
Fascist party advocated
• Glorification of the State
• Totalitarianism
• Single-party system with a strong ruler
Many Germans did not like the Weimar
Republic because they felt that it had betrayed
them by accepting the Treaty of Versailles
The continued Great Depression allowed Nazis
to increase their influence throughout
Germany in the early 1930s
The 1935 Nuremberg Laws stripped Jews of
their citizenship and their rights
The majority of Italians support Mussolini in
the 1920s because he had prevented a
Communist revolution and brought order to
the country.
The United States in World War II
To improve lecture quiz grade…
• … just come see me sometime within a week
to re-do as interview quiz…
From 1939 to 1941, the United States tried to
maintain neutrality while providing aid to Britain
but was drawn into the war by the Japanese
attack on Pearl Harbor. The United States fought
a war on multiple fronts. At home, the economy
was converted to war production, and essential
resources were rationed to ensure adequate
supplies for military use.
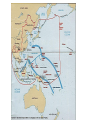
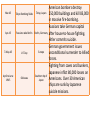
AMERICAN INVOLVEMENT IN WORLD
WAR II
1-Sep-39
Germany invades
Poland
PolishGerman
border
Following nonaggression treaty with
Soviet Union, German
troops invade Poland.
England and France
declare war on
Germany. Soviets invade
Poland from East.
During the first few months following
American entry into World War II, national
opinion was strongly against the war.
March-June
1940
Germany's
blitzkrieg
takes western
Europe
Denmark, Norway,
Netherlands,
Western Belgium,
Europe Luxembourg, and
France crushed by
German offensive
Fall 1940
Battle of Britain
Great
Britain
German bombers ruin
British cities in
attempt to obtain
British surrender
before U.S. entry.
Britain's breaking of
German code
("Ultra") helps
overcome air attacks.
Sep-40
U.S. enacts draft
bill
Sep-40
Destroyer for
Bases deal
Nov-40
Lend-Lease plan
Registration of all men
Washington between 21 and 35.
D.C.
Limit of 900,000 men in
time of peace.
U.S. transfers 50 old
Washington destroyers to Britain in
D.C. and exchange for use of
London
eight British Atlantic
bases.
U.S. would "lend"
Washington
military equipment to
D.C.
cash-strapped Britain.
Jun-41
Aug-41
7-Dec-41
8-Dec-41
Germany begins two-front war
Polish-Russian with invasion of Russia. Germans
Germany invades Russia
border
halt 15 miles from Moscow in
December 1941.
FDR and Churchill agree to war
North Atlantic aims, self-determination, and
Atlantic Charter
condemnation of Nazism.
361 Japanese warplanes attack
American airfields and shipyards,
disabling 19 ships, destroying 200
Japan attacks Pearl
Hawaii
planes, and killing over 2300
Harbor
men. Southeast Asia, Hong Kong,
Malaya, Philippines soon fall to
Japan.
Congress approves entry into war.
FDR asks for war on
Washington D.C. Germany and Italy declare war on
Japan
U.S.
Pearl Harbor
7 Dec 1941
Error #1: didn’t sink
aircraft carriers
Error #2: didn’t bomb oil
tanks in Hawaii; oil
became key to Pacific
war
Error #3: thought attack
would scare Americans
out of war
Atlantic Charter
1941: FDR and Churchill
goals for postwar world.
Agree: no territory will be taken
Agree: All people may choose their own form of
govt
Agree: Permanent system of security like League of
Nations (Becomes NATO)
“Beat Hitler First”
May-42
Battle of Coral Sea
Jun-42
Midway
Carrier-based U.S. planes
South Pacific halt Japanese advance on
Australia.
Threat on Hawaii ended as
Central Pacific four Japanese aircraft
carriers are sunk.
The Battles of the Coral Sea and Midway were
significant in stemming the tide of Japanese
advances in the Pacific.
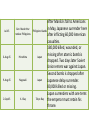
Feb-43
May-43
Guadalcanal
Solomon
Islands, South
Pacific
Germans surrender at Tunisia, North
Africa
Tunisia
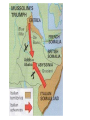
Jul-43
Allies invade Sicily
Sicily
Sep-43
Italy surrenders
Italy
Americans take first island in start of
island-hopping strategy.
Over 250,000 German and Italian troops
are captured and Allies prepare to invade
Sicily and Italy.
In largest amphibious invasion in history,
over 250,000 American and British troops
land. Germans and Italians escape to
mainland of Italy.
Although Italian troops quit fighting
Allies, Germans continue in fierce
fighting. Rome finally surrenders on June
4, 1944.
The first area to be liberated from Axis
occupation by the Allies was North Africa.
6-Jun-44
D-Day Invasion
Dec-44
Battle of the Bulge
Allies use 4600 ships to
invade German-held France.
Normandy coast of
Suffering heavy casualties,
France
the Allies were able to
retake Paris in August.
German counteroffensive
French-German- almost succeeds in retaking
Belgian border Belgium but is crushed with
Allied reinforcements.
Opening a Second Front: D-Day Invasion
Operation Overlord
June 1944 3 million
troops
6 June 1944 = D-Day
Landings in Normandy,
northern France
D-Day 6_6_44 (3min8)
The objective of the Manhattan Project was to
develop the atomic bomb.
Mar-45
Tokyo Bombing Raids
Tokyo, Japan
Apr-45
Russians take Berlin
Berlin, Germany
7-May-45
V-E Day
Europe
April to June
1945
Okinawa
Southern tip of
Japan
American bombers destroy
250,000 buildings and kill 83,000
in massive fire-bombing.
Russians take German capital
after house-to-house fighting.
Hitler commits suicide.
German government issues
unconditional surrender to Allied
forces.
Fighting from caves and bunkers,
Japanese inflict 80,000 losses on
Americans. Over 30 American
ships are sunk by Japanese
suicide missions.
Jul-45
Gen. MacArthur
retakes Philippines
6-Aug-45
Hiroshima
9-Aug-45
Nagasaki
2-Sep-45
V-J Day
After Manila's fall to Americans
in May, Japanese surrender here
Philippine Islands
after inflicting 60,000 American
casualties.
180,000 killed, wounded, or
missing after atomic bomb is
Japan
dropped. Two days later Soviet
Union enters war against Japan.
Second bomb is dropped after
Japan
Japanese delay surrender.
80,000 killed or missing.
Japan surrenders with one term:
Tokyo Bay
the emperor must retain his
throne.
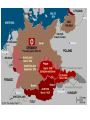
In the final months of World War II in Europe,
American and British forces entered Germany
from the west and Soviet troops entered
Germany from the east and occupied Berlin.
During World War II, the Japanese word
kamikaze referred to a suicide mission in which
a Japanese pilot purposely crashed his plane
into an enemy ship.
One of the two locations on which the United
States dropped atomic bombs was Nagasaki
IMPACT OF THE WAR ON THE
AMERICAN ECONOMY AND DAYTO-DAY LIFE
Mobilizing the Home Front
Need to train – we had a very weak and outdated
force
Govt takes charge of economy – War Production
Board
Sets
prices
Sets wages
Negotiates with labor unions
Mobilizing the Home Front
Industry transformed
from commercial goods
to war parts
Rationing – limits on
how much of certain
things you could buy
Mobilizing the Home Front
Victory gardens
“Rosie the Riveter”
African Americans at
war; racial tension;
FDR acts against
discrimination …
refuses to end
segregation in military
The famous image of "Rosie the Riveter“
symbolized the erosion of some of the
prejudice against women working in
traditionally male jobs.
The internment of Japanese Americans during World
War II
• The Supreme Court upheld their evacuation from
the West Coast.
• Reparations were finally paid to evacuees about
forty years after the war.
• Many of the evacuees were United States citizens.
• There is no evidence these Japanese Americans
were engaging in conspiracies
During the first few months following
American entry into World War II, national
opinion was strongly against the war.
The Battles of the Coral Sea and Midway were
significant in stemming the tide of Japanese
advances in the Pacific.
The first area to be liberated from Axis
occupation by the Allies was North Africa.
The objective of the Manhattan Project was to
develop the atomic bomb.
In the final months of World War II in Europe,
American and British forces entered Germany
from the west and Soviet troops entered
Germany from the east and occupied Berlin.
The famous image of "Rosie the Riveter“
symbolized the erosion of some of the
prejudice against women working in
traditionally male jobs.
JAPANESE RELOCATION CAMPS
US Relocation camps
West coast alarmed –
Japanese Americans …
sell … move
Japanese Internment
During World War II, the Japanese word
kamikaze referred to a suicide mission in which
a Japanese pilot purposely crashed his plane
into an enemy ship.
One of the two locations on which the United
States dropped atomic bombs was Nagasaki
The internment of Japanese Americans during World War
II
• The Supreme Court upheld their evacuation from the
West Coast.
• Korematsu v. United States
• Reparations were finally paid to evacuees about forty
years after the war.
• Many of the evacuees were United States citizens.
• There is no evidence these Japanese Americans were
engaging in conspiracies
FORT ONTARIO REFUGEE CENTER
Fort Ontario Emergency Refugee Shelter
• "Safe Haven"
• Oswego, New York
• first and only refugee center in US
• 1944 to 1945
• housed almost 1000 European refugees
• Mostly Jewish descent
• especially Yugoslavian, Austrian,
Polish, German and Czechoslovakian
• Run by War Relocation Authority
• had been responsible for Japanese
Relocation Centers
big concern = issue of immigration
• FDR: immigration laws were not going to be
ignored.
• refugees would be in the United States, not
a citizen
• Army would not permit any refugee escapes
• refugees would not be able to work
• would not be allowed to travel beyond
Oswego
60% of them had active immigration cases
pending when camp closed 1946
• some refugees chose to return to Europe
• some were desperate to remain in the
United State
• many were granted permanent or
temporary status
• sometimes ending up in the homes of
family or friends
More info. Here: http://www.safehavenmuseum.com/
TUSKEGEE AIRMEN
Tuskegee Airmen
• African-American military pilots
(fighter and bomber)
• World War II
• first African-American military
aviators in the United States
Armed Forces
• American military was racially
segregated, as was much of the
federal government.
• subjected to racial
discrimination, both within and
outside the army. All Black
military pilots who trained in the
United States trained at
• near Tuskegee, Alabama
• 992 pilots were trained in Tuskegee
from 1941 to 1946
• 84 lost their lives in accidents or
combat.
• 1578 combat missions
• At least one Silver Star
• 96 Distinguished Flying Crosses to 95
Airmen; Captain William A. Campbell
was awarded two.
• 14 Bronze Stars
• 744 Air Medals
• 8 Purple Hearts
Result: after the war,
African Americans
renewed their desire
for civil rights. Their
service in the war
entitled them to at
least that much, no?
How WW II Changed the World
THE HOLOCAUST
U.S. Soldier’s home movie…
“Shoah”
• Between 1933 and 1945, the German
government led by Adolf Hitler and the
Nazi Party carried out the systematic
persecution and murder of Europe’s Jews.
• This genocide is now known as the Holocaust.
• The Nazi regime also persecuted and killed
millions of other people it considered
politically, racially, or socially unfit.
Go Here to Holocaust Museum Silent Presentation…
THE ATOMIC BOMB
The Manhattan Project
• The U.S. built the first atomic bombs under what was
called “The Manhattan Project”
Project
• started by European
refugee scientists
(including Albert Einstein)
and American scientists
• feared that Nazi Germany
would also be working on
it!
Project
• eventually employed over
130,000 people
• at over 30 institutions
spread over the United
States
• one of the largest and
most costly research and
development programs of
all time
Hiroshima and Nagasaki
The Manhattan Project
• J. Robert Oppenheimer
– creator
• 1st successful test done
in New Mexico July 16,
1945
• Blast visible 180 miles
away
Pros:
1. Could fail
• Japanese might shoot
down test plane
• Might put POW’s in
testing area
2. Only way to make Japan
surrender
3. Need to justify the cost of
building the bomb and man
hours spent working.
4. It would end the war and
save countless U.S. military
lives
5. Give U.S. more power in
rebuilding Europe
• Mounting tensions w/Russia
A-Bomb Debate
Cons:
– Just a demonstration
– Would kill thousands of
Japanese civilians
– Would be immoral to
drop the bomb w/o prior
warning
Little Boy
• Hiroshima 6 Aug 1945
• 4.5 tons
• blast equivalent to approximately
13 militons of TNT
• instantly killing 70,000 – 80,000
people
• In 43 seconds – the city did not
exist
• Bombs only used 1/10th of 1% of
explosive capabilities.
• Japan still did not surrender
• Leukemia in children born post
WWII.
Fat Man
• 3 days later
• “Fat Man”
• heat estimated at 7000
degrees Fahrenheit
• winds estimated at 624
MPH
• on Nagasaki
– 39K killed instantly
– By end of year, 200,000
had died of injuries
and/or radiation
Effects of the Bombs
Keloids
Effects of the Bombs
Firestorm
After
After
After
Effects of Radiation
Hair loss
Thermal burns
Effects of Radiation
Thermal burns
Effects of Radiation
Severe thermal burns
Effects of Radiation
Keloids
Occupation of Japan
• Occupied by Gen. MacArthur
• 1,100 Japanese officials (including
Tojo) were put on trial
– 7 put to death
• Occupied for 6 years
• MacArthur’s Reforms:
– Free market economy
– New Constitution
• Women’s suffrage
• Basic freedoms
• Japanese Constitution still
called the “MacArthur
Const.”
THE UNITED NATIONS
The United Nations (UN)
• intergovernmental organization
established 24 October 1945
• to promote international cooperation.
• A replacement for the ineffective
League of Nations
• to prevent another World War.
• At its founding, the UN had 51
member states; there are now
193.
• headquarters = in Manhattan,
New York City,
• extraterritoriality
• financed by assessed and
voluntary contributions from its
member states.
Objectives of the UN
• maintaining international peace
and security
• promoting human rights
• fostering social and economic
development
• protecting the environment
• providing humanitarian aid in
cases of famine, natural disaster,
and armed conflict.