* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Events of WWII - Lesson Corner
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Operation Bodyguard wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Invasion of Normandy wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
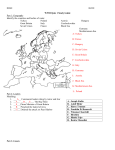
Title: Events of WWII Grade and Subject: 9th grade Modern World History Time Allotted: 1hr 30min WHII.11 a SOL #: NCSS Theme: What is the guiding question for this lesson? How will student understanding be assessed? III. People, Places, and Environment How did each of the main events of WWII cause each other? There will be a quiz on the material in the next class. Key Concept (no definition necessary): Guerilla Warfare SWBAT: 1. Identify and describe the main events of WWII. 2. Identify and describe the main leaders of WWII. Materials (List primary sources and additional materials): • Daily Agenda • Slot Notes • Pictures of: • • • • • • Fall of France Battle of Britain German invasion of the Soviet Union Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor D-Day (Allied invasion of Europe) Atomic bombs dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki • PowerPoint of the above events, the leaders related to them, and their importance in WWII Just Do It: Students will be shown a picture of the Munich Conference and will have to answer the following questions: 1. What do you see? 2. Who is in the picture? (answer only when applicable) 3. What is going on? 4. What do you think this is happening? 5. What do you think will happen next? (5 min) Obj # 1 Description of Lesson Procedure Check for Evidence of Understanding The classroom will be divided into I will model the process for five groups picked from random them, then I will go over the assignment. Each group will be directions, ask the students asked to analyze seven different to repeat them back to me, images by answering the following and have them written on questions: the overhead. The students 1. What do you see? will be monitored through 2. Who is in the picture? (answer only out the exercise to make when applicable) sure they stay on task and 3. What is going on? are completing the 4. Why do you think this is happening? assignment. We will also 5. What do you think will happen next? go over each group’s The pictures will be of the main answers and discuss how WWII battles, or events, such as: they came up with them. • Fall of France • • • • • 1, 2 1, 2 Battle of Britain German invasion of the Soviet Union Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor D-Day (Allied invasion of Europe) Atomic bombs dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki (15 min) Each group will then give their answers for each picture, and we will discuss the events of the picture after their answers. There will be a PowerPoint presentation that includes the information of the events, and it will mention the leaders and their importance in WWII. (50 min) Slot notes on the events of WWII. (15 min) The students will be continually monitored on how much attention they are paying to the discussion, and their participation. They will also be asked some review questions at the end of the lesson to check the complete understanding of the lesson. The slot notes are a fill-inthe-blank activity. They will be a review and will check for the students’ understanding of previous material. Closure: (Ties the lesson together and relates it to the lesson’s guiding question) The slot notes along with a list of questions to review the day’s lesson will be used as a closure to bring the lesson together. Students will also be asked to study for a quiz on the events of WWII. Daily Agenda March 15, 2006 Let’s Get Started 1.What do you see? 2.Who is in the picture? 3.What is going on? 4.What do you think this is happening? 5.What do you think will happen next? Today’s SOL: WHII. 11 a International Focus: How did each of the main events of WWII cause each other? Students Will Be Able To (SWBAT): 1.Identify and describe the main events of WWII. 2.Identify and describe the main leaders of WWII. Picture Activity In your groups answer the following questions about each picture: 1.What do you see? 2.Who is in the picture? (answer only when applicable) 3.What is going on? 4.What do you think this is happening? 5.What do you think will happen next? You will have two minutes for each picture. PowerPoint on the main battles and events of World War II Slot Notes • • • • • • • • • • • Checking For Understanding What did the German invasion of Poland cause Great Britain and France to do? What country did the Axis Powers conquer after Poland? How many allies did Great Britain have when France fell to the Axis Powers? What did the German plan to conquer Britain involve? Why where Germany and Russia allies? Why did Germany attack Russia? What slowed down the German advance in Russia? Why did Japan attack Pearl Harbor? Why did the Allies invade Normandy, France on D-Day? What was the end result of opening up the second front in France? Why did the President Truman order the use of the Atomic bomb on Japan? Homework Read pg 831-841, & 846-851 Study slot notes and the above questions for a quiz on Friday 3/17. Slot Notes After the Munich Conference of 1938 Hitler still wanted more land. Britain’s Prime Minister Chamberlain’s idea of APPEASEMENT had not worked to prevent another World War. He demanded parts of Poland, and then attacked Poland on September 1, 1939. Great Britain and France retaliated by declaring war on Germany. Germany had made a Nonaggression Pact with Russia to prevent war with them, while they were at war with Western Europe. After the fall of Poland the Axis powers turned their attention towards France. France signed an armistice on June 21, 1940. France was used as a base for the Axis powers to attack Great Britain. The Battle of Britain began because Hitler wanted to remove the threat of Britain from Germany’s left flank before he attacked Russia. The Battle of Britain was an all air battle, and resulted in the bombing of London. Germany failed to make Britain give up and so turned its attention away from Britain and towards Russia. The Axis powers invaded Russia to capture their oil and wheat fields to use for the army. The Axis powers made quick advances in Russia until the winter of 1941. The 1) Russian Winter and 2) Scorched Earth Policy slowed down the German attack. Russian Winter – Extreme cold the German army and equipment were not prepared for. Scorched Earth Policy – The Russian defense policy where the army and civilians retreat and destroy all useable materials while retreating. This leaves nothing for the invading army to use. The Soviet Campaign resulted in the turning point of the war for the Allies. Japan had been cut off of American oil exports because of their invasion into Indochina in 1941. In retaliation General Tojo and General Yamamoto planned an attack on Pearl Harbor, the American naval base in Hawaii. This resulted in drawing America into WWII. After the Axis invasion of Russia had stalled, the Allies planned to open up a second front in Western Europe in 1944. General Eisenhower, the commanding allied general, planned an attack on Normandy, France on June 6, 1944 known as D-Day. The attack established a second front and pushed the Axis powers back into Germany. After the surrender of Germany only Japan presented an obstacle to complete peace for the allies. After U.S. victories at Iwo Jima and Okinawa, the Allies were within striking distance of the Japanese mainland. The allies told the Japanese to surrender unconditionally or suffer extensive damages. This resulted in President Truman ordering the dropping of two Atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki. The Japanese surrendered unconditionally on August 15, 1945. Slot Notes After the ____________________________of 1938 Hitler still wanted more land. Britain’s Prime Minister Chamberlain’s idea of ___________________had not worked to prevent another World War. He demanded parts of Poland, and then attacked ___________ on September 1, 1939. Great Britain and France retaliated by declaring war on Germany. Germany had made a Nonaggression Pact with___________ to prevent war with them, while they were at war with Western Europe. After the fall of Poland the Axis powers turned their attention towards_______________. France signed an armistice on June 21, 1940. France was used as a base for the Axis powers to attack__________________. The _______________________began because Hitler wanted to remove the threat of Britain from Germany’s left flank before he attacked____________. The Battle of Britain was an all air battle, and resulted in the bombing of______________. Germany failed to make Britain give up and so turned its attention away from Britain and towards Russia. The Axis powers invaded Russia to capture their ______ and ___________fields to use for the army. The Axis powers made quick advances in Russia until the winter of 1941. The 1) ________________________and 2) _____________________________slowed down the German attack. Russian Winter – Extreme cold the German army and equipment were not prepared for. Scorched Earth Policy – The Russian defense policy where the army and civilians retreat and _____________ all useable materials while retreating. This leaves nothing for the invading army to use. The_________ Campaign resulted in the turning point of the war for the Allies. Japan had been cut off of ___________________oil exports because of their invasion into Indochina in 1941. In retaliation General _____ and General _________________ planned an attack on__________________, the American naval base in Hawaii. This resulted in drawing America into WWII. After the Axis invasion of Russia had stalled, the Allies planned to open up a second front in Western Europe in 1944. General __________________, the commanding allied general, planned an attack on ______________, France on June 6, 1944 known as _________. The attack established a second front and pushed the Axis powers back into Germany. After the surrender of Germany only ________ presented an obstacle to complete peace for the allies. After U.S. victories at Iwo Jima and Okinawa, the Allies were within striking distance of the Japanese mainland. The allies told the Japanese to surrender unconditionally or suffer extensive damages. This resulted in President _________ ordering the dropping of two __________________ on Hiroshima and Nagasaki. The Japanese surrendered unconditionally on August 15, 1945.