* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SNC1D Types of Electrical Circuits PowerPoint
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
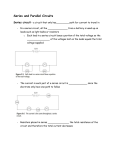
2017-03-28 Types of Electrical Circuits Mr. Masri SNC1D Humberside C. I. Think of all of the different circuits in your home. How can one light be turned on while another one is turned off? 1 2017-03-28 The answer lies in the way the circuits are wired! Circuits can be wired in two different ways: SERIES or PARALLEL 1. Series Circuit A series circuit has only one path for the electrons to follow (much like a race track). 2 2017-03-28 1. Series Circuit Example: + _ 2. Parallel Circuit A parallel circuit has multiple paths for the electrons to follow (much like city streets). 3 2017-03-28 2. Parallel Circuit Example: + _ Current in SERIES Circuits Since there is only one path to follow, all of the electrons must pass through every load in the circuit before they can get more energy from the power source ∴ the current through any load in the circuit is exactly the same as the current through all of the other loads in the circuit. 4 2017-03-28 Current in SERIES Circuits Equation: Itotal = I1 = I2 = I3 … etc Current in PARALLEL Circuits Since there are many paths to follow, the electrons splits down each pathway; this results in an uneven distribution of current through the loads. 5 2017-03-28 Like 3 students walking different paths from Humberside to Keele Station Option 1 Option 2 6 2017-03-28 Option 3 Think of the students like electrons Current in PARALLEL Circuits ∴ The sum of the currents through each of the loads in the circuit will add up to the total amount of current passing through all of the branches in the circuit when the paths rejoin. EQUATION: Itotal = I1 + I2 + I3 + … etc 7 2017-03-28 Potential Difference in SERIES Circuits As the electrons pass through successive loads in the circuit, the potential difference in each load will drop. Why? Potential Difference in SERIES Circuits The total sum of all of the potential differences in the loads will add up to the potential difference of the power source. Equation: Vtotal = V1 + V2 + V3 + … etc 8 2017-03-28 Potential Difference in PARALLEL Circuits The potential difference across any load in the circuit is exactly the same as any other load in the circuit (and the power source). Energy only gets lost when the electrons pass through a load. Equation: Vtotal = V1 = V2 = V3 … etc 9 2017-03-28 VT = voltage gain at source V1 = voltage drop at load 1 V2 = “ “ “ “ 2 In Summary, Series Circuit V1 + _ VT IT I1 IT = current out of source I1 = current through load 1 I2 = “ “ “ 2 I2 Mathematically, VT = V1 + V2 V2 IT = I1 = I2 In Summary, Parallel Circuit Mathematically, V1 V2 VT = V1 = V2 IT I1 I2 IT = I1 + I2 + _ VT junction point 10 2017-03-28 Sample Find V1 60 V Solution: + _ 120 V 30 V VT = V1+ V2 + V3 (series) 120 V = V1 + 30 V + 60 V V1 = 30 V V1 = ? Homework ! pg. 554 #1, 2, 4 and 6 ! Series and Parallel Circuits handout – diagrams on front – draw them and complete problems on bottom of back page 11