* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download c34f30ef92c9b40
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
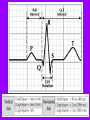
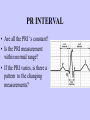
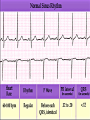
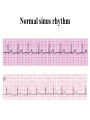
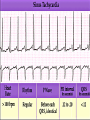
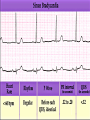
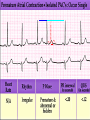
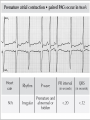
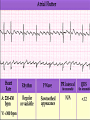
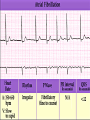
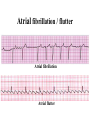
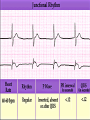
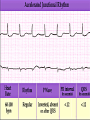
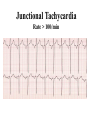
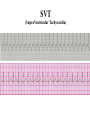
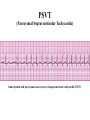
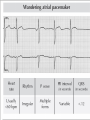
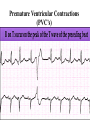
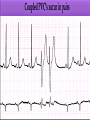
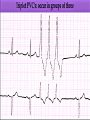
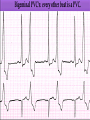
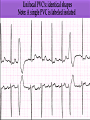
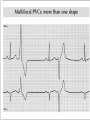
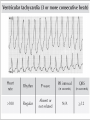
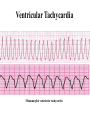
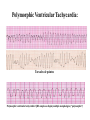
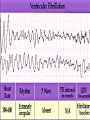
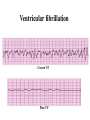
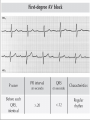
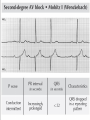
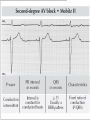
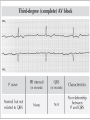
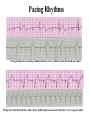
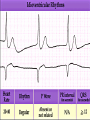
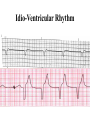
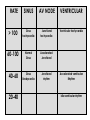
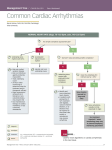
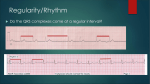
Prepared by : ANWAR ISSA RN-BSN-CCRT-ICU How to analyze a rhythm strip ? • • • • P wave : is P wave normal ? PR interval : is PR interval normal ? QRS complex : is QRS normal ? P-QRS relation : what is the relation between P wave and QRS ? • Rate : what is the rate ? P WAVE • Are the P waves regular ? • Is the P wave normal and upright in lead II ? • Do all P waves look alike ? PR INTERVAL • Are all the PRI ‘s constant? • Is the PRI measurement within normal range? • If the PRI varies, is there a pattern to the changing measurements? QRS COMPLEX • Are all the QRS complexes of equal duration? • What is the measurement of the QRS complex? • Is the QRS measurement within normal limits? • Do all the QRS complexes look alike? • Are the unusual QRS complexes associated with ectopic beats? P-QRS RELATION • Is there a P for every QRS and vice versa? • Are they related to each other? • More P’s? More QRS’s ? HEART RATE • What is the exact rate? • Is the atrial rate the same as the ventricular rate? - If the rhythm is regular--- 300/# of big squares between RR. - -If the rhythm is irregular --- count the R waves on a 6 second strip and multiply by 10. Normal sinus rhythm * Condition where SA node stops firing, causing pause in electrical activity. * During the pause, atrial and ventricularcontraction do not occur. MAT Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Multifocal atrial tachycardia: narrow-complex tachycardia at 140 to 160 bpm with multiple P-wave morphologies (arrows) Atrial fibrillation / flutter Atrial fibrillation Atrial flutter Junctional Tachycardia Rate > 100/min SVT (SupraVentricular Tachycardia) PSVT (Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia) Sinus rhythm with paroxysmal onset (arrow) of supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) Wolff-Parkinson-White Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome: normal sinus rhythm with delta wave notching of positive upstroke of QRS complex Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVC’s) Ventricular Tachycardia Monomorphic ventricular tachycardia Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia: Torsades de pointes Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia: QRS complexes display multiple morphologies (“polymorphic”) Ventricular fibrillation Coarse VF Fine VF Pacing Rhythms Pacing attempted: note pacing stimulus indicator (arrow) which is below threshold; no capture Pacing above threshold (60 mA): with capture (QRS complex broad and ventricular; T wave opposite QRS) Idio-Ventricular Rhythm 1 2 Asystole / Stand still RATE SINUS AV NODE VENTRICULAR > 100 Sinus tachycardia Junctional tachycardia Ventricular tachycardia 60-100 Normal Sinus Accelerated Junctional 40-60 Sinus Bradycardia Junctional rhythm 20-40 Accelerated ventricular Rhythm Idioventricular rhythm