* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download lecture 7 OPL and interference
Thomas Young (scientist) wikipedia , lookup
Nonimaging optics wikipedia , lookup
Dispersion staining wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Ellipsometry wikipedia , lookup
Optical flat wikipedia , lookup
Retroreflector wikipedia , lookup
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Interferometry wikipedia , lookup
Nonlinear optics wikipedia , lookup
Phase-contrast X-ray imaging wikipedia , lookup
Wave interference wikipedia , lookup
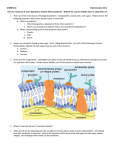
Optical path length opl = path length x η Δopl = Δ path length x Δη δ (phase shift) = 2π x Δopl / λ degs. rads. 90o 0π .5 π 180o 1π 270o 360o 1.5π 2π 0o 90o 0o 180o 360o 270o How far out of phase have these 2 waves become? http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/hframe.html One full wavelength λ, one full cycle, 360 degrees or 2 π Combine black ray or wave with grey one and derive resultant (or only relative phase and amplitude changes. Remember, this ene redistributed to another place in space (where is not always obvio Relative phase difference of 1/4 λ or 1/2 π. Relative phase difference of 1/2 λ of π. resultant energy in space In a phase contrast microsccope, a ring at the back plane of the rays (those that do not interact with the specimen) by one quarte combined with a ~one quarter λ retardation at the sample leads t interference at the image plane; differences in phase shifting pro amplitude differences. One full wavelength λ, one full cycle, 360 degrees or 2 π Relative phase difference of 1 λ or 2π. resultant reflection 1 2r 2t polym 3r 4 glass, 3t Solve for followin resultant transmitted Wavelengths of li Wavelengths of li Wavelengths of li Wavelengths of li t-transmitted, r-reflected 1 is a ray of white light When 1 hits polymer surface, it is split into 2t and 2r, 2r is phase shifted relative to 2t by 1/2 λ or π (low to high η interface). 2t continues on and is split into 3t and 3r at the glass surface, there is no phase shift with this reflection because it is a high to low η interface. 3r (in phase with 2t) will combine and interfere with 2r ( 3r + 2r = resultant, constructive + or destructive - depends on the λ). Since 2r has already shifted relative to 2t by 1/2 λ, for + interference to occur, 3r must be shifted in phase by 1/2 λ , 1 1/2 λ , 2 1/2 λ, etc. For - interference to occur, 3r must be shifted in phase by 0 λ , 1 λ , 2 λ, etc. So to solve this for maximum constructive reflective interference, we take: OPL (2t + 3r) must equal 1/2 λ or 1 1/2 λ or 2 1/2 λ OPL (2t + 3r) = 2(thickness of polymer x η polymer) so.... 1/2 λ or 1 1/2 λ or 2 1/2 λ = 2(thickness of polymer x η polymer) So to solve for this in maximum destructive reflective interference, we take: OPL (2t + 3r) must equal 0 λ or 1 λ or 2 λ OPL (2t + 3r) = 2(thickness of polymer x η polymer) so.... 0 λ or 1 λ or 2 λ or 3λ = 2(thickness of polymer x η polymer) Now try one in transmission: 2t is split into 3t and 3r; at this point, all these rays are in phase (no shift high to low η). 3r reflects back as 4 within polymer, its phase then changes relative to 2t. 3t + 4 = resultant, constructive + or destructive - depends on the λ. So to solve this for max. constructive transmitted interference, we take: OPL (3r + 4) must equal 0 λ or 1 λ or 2 λ OPL (3r + 4) = 2(thickness of polymer x η polymer) so.... 0 λ or 1 λ or 2 λ or 3 λ = 2(thickness of polymer x η polymer) These integer values (1, 2, 3, etc.) for wavelengths are called 'orders' . As we can see, we lose energy with each reflection so that the most important orders (with regard to amplitude) are usually the lowest order effects. single semi-silvered surfaces reflect 50% and transmit 50% of light (all λ ) η - hi η - air η - hi This diagram may help you solve the extra credit question on the midterm exam. for phase shifts on reflection: low to high, shift in π high to low, no shift in π air = white glass = blue light rays = black semi-silvered surfaces = grey waves/rays = orange resultant http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/hframe.html They won’t let you use their calculator for normal (90 degree) incidence so to try their calculator use a 30 degree angle (answers are close to those for 90). WOW! Murphy 2001 out of phase by π,3π ,5π , etc. resources.yesican-science.ca www.jasondoucette.com/ graphics/interfrs.gif Note that energy is neither destroyed nor created during interference. Laser design inc. Phase change of 180 deg (pi) when reflection is rare (low refractive index) to dense (high refractive index), no phase change when reflection is dense to rare as in TIR or total internal reflection. Oil on water AR coating Georgia State U. http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/hph.html