* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Understand the meaning of “perpendicular” such
Duality (projective geometry) wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Riemannian connection on a surface wikipedia , lookup
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Perspective (graphical) wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
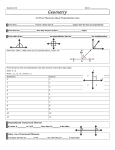
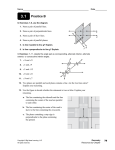
Geometry Chapter 3 Test STUDY GUIDE SOL G.2 (Parallel/Perpendicular Lines) Mrs. Grieser Name: _____________________________ Date: _______________ Block: _________ Geometry Chapter 3 Test STUDY GUIDE SOLs: G.2 Textbook Sections: All of chapter 3 Study Resources: Notes distributed in class, flipchart PDFs (on my web site under “Class Summary”), checkpoints, homework, textbook (chapter review pp. 202-205, chapter test p. 206, extra practice pp. 900-901), and textbook website (classzone.com; click link on my web page). How to Study: Review notes, checkpoints, and textbook chapters for each section, as well as reviewing the summaries written here. Don’t limit study to the questions in this study guide!! See textbook pages: 201-206, 900-901 for extra problems. Quizlet flashcards can be found here: http://quizlet.com/7099704/geometry-chapter-3-parallel-perpendicular-lines-flashcards/ Things to Know: Identify corresponding, alternate interior, alternate exterior, corresponding interior, and vertical angles formed when a transversal crosses two lines (parallel or not). Know congruence/supplementary postulate/theorems for these angles if the transversal crosses parallel lines; find missing angle values based on these theorems. Apply the converse theorems of above: be able to find missing angle values that would make lines parallel. Be able to identify whether lines are parallel or perpendicular, given the lines themselves or two points on a line. Be able to graph linear equations and write a linear equation given a line. Be able to write a linear equation that is parallel or perpendicular to a given line that passes through a point not on the line. Understand the meaning of “perpendicular” such that missing angle measures can be found given a set of perpendicular lines. Be able to find the distance, using the distance formula, between two parallel lines. Practice questions: 1) Classify the angle pair as corresponding, alternate interior, alternate exterior, consecutive interior, or vertical angles: a) 6 and 2 b) 7 and 2 c) 5 and 3 d) 4 and 5 e) 1 and 5 f) 5 and 8 1 Geometry Chapter 3 Test STUDY GUIDE SOL G.2 (Parallel/Perpendicular Lines) Mrs. Grieser 2) Find the value of x. a) b) 3) Find the value of x and y. a) b) 4) Find the value of x that makes m||n. a) b) 5) Tell whether the lines through the given points are parallel, perpendicular, or neither. a) Line 1: (7, 4), (10, 5); Line 2: (2, 3), (8, 5) b) Line 1: (-6, 0), (8, 7); Line 2: (1, 4), (2, 2) 6) Write an equation of the line that passes through point P and is parallel to the given line: a) P(1, -2); y = -2x + 6 b) P(-7, 3); y = x + 3 7) Write an equation of the line that passes through point P and is perpendicular to the given line: a) P(3, -1); y = 6x – 4 b) P(-1, 1); 3y – 7x = 30 8a) Write an equation of the line shown: b) Graph the equation: 2x + 4y = 3 9) Find the m ADB: a) 10) Use the distance formula to find the distance between the parallel lines (put answer in simplest radical form): b) 2