* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson 15. Grammar material: Prepositions. Text: “Transformers
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
War of the currents wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Single-wire earth return wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Ignition system wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
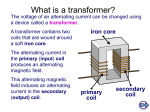
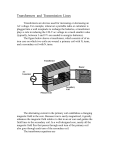
Lesson 15. Topic “TRANSFORMERS”. Grammar material: Prepositions. Text: “Transformers” One of the great advantages in the use of the alternating current is the ease with which the voltage may be changed by means of a relatively simple device known as a transformer. Although there are many different types of transformers and a great variety of different applications, the principles of action are the same in each case. The transformer is a device for changing the electric current from one voltage to another. It is used for increasing or decreasing voltage. So the function of a transformer is to change voltage and current of an alternating system to meet requirements of the equipment used. It is known to be simple in elementary principle, and in construction that is it involves no moving parts. Transformers change voltage through electromagnetic induction. The principle parts of a transformer are: an iron core and, usually, two coils of insulated windings. One of them is called primary, another is called the secondary. The primary coil is connected to the source of power. The secondary coil is connected to the load. Thus, the primary is the coil to which poweris supplied. The secondary is the coil from which power is taken. In scientific terms to produce an alternating magnetic flux in the iron core an alternating current must be passed through the primary coil. This flux is considered to induce electromotive force in both primary and secondary coils. The secondary coil is open – circuited. Current flows in the secondary coil when the latter is connected to the external circuit or load. The flow of current in the secondary coil tends to reduce the flux in the core. Transformers are placed inside a steel tank usually with oil to improve the insulation and also to cool the device. II. Guess the meaning of the following international words: 1) transformer; 2) type; 3) principle; 4) electric; 5) function; 6) elementary; 7) construction; 8) induction. III. Translate into Russian the words and expressions from the text: 1) advantage; 2) voltage; 3) relatively simple; 4) application; 5) increase; 6) to decrease; 7) to meet requirements; 8) moving parts; 9) iron core; 10) insulated windings; 11) load; 12) electromotive force; 13) to induce. IV. Give the English equivalents to the words below: 1) ; 2) ; 3) ; 5) ; 8) ; 6) ; 9) ( ( ); 4) ) ; 10) V. State questions to the underlined words: 1. Voltage may be changed by a transformer. (General Question). 2. Transformers change voltage through electromagnetic induction. (How ...) 3. Transformer is used for increasing or decreasing voltage. 4. The primary winding is connected to the source of power. (...or...) 5. Transformers are placed inside a steel tank. (Question-tag) VI. Answer the questions: 1. What kind of device is a transformer? 2. What are the functions of a transformer? 3. What are the principle parts of a transformer? 4. What is the primary coil connected to? 5. What is the secondary coil connected to? 6. What are the principles of action of a transformer? 7. Where are transformers usually placed? VI. Topics for discussion: 1. Transformer as an electric device; 2. Main parts and principles of a transformer action. TEST . TRANSFORMERS I. Connect the word combinations: Induction sets ; 7) . Moving flux Little quantity Iron line Primary coil Step-up line Negligible importance Transmission parts Radio winding Great transformer Magnetic maintenance II.Find the correct variant: 1. A transformer is used a) to store charge. b) to prevent the change of energy. c) to transfer energy. d) to change the voltage and current value in the circuit. 2. A transformer consists of a) cores only b) the primary and the secondary windings. c) a core and the primary and the secondary windings. 3. The transformer is called ‘one-to-one’ transformer when: a) the number of turns of wire on the secondary is greater than those on the primary. b) the number of turns of wire on the primary is greater than those on the secondary. c) when the number of turns of wire on the secondary is the same as the number on the primary. 4. A step-up transformer is used a) to step down or to decrease the secondary voltage. b)to step up or to increase the primary voltage. III. Complete the sentences with be going to and a verb or expression from the box: Crash, snow, be sick, jump, be late, move, have a job, interview 1. Look at the man on the bridge! I think … 2. I don’t feel well. I think … 3. It’s so cold and look at those clouds! I think it… 4. That man’s driving too fast. He … 5. Sally’s wearing her best clothes. She … 6. Hurry up! It’s nearly ten o’clock! You… 7. Sarah and Pete’s flat is too small. They … IV. Complete the sentences with have to, has to, don’t have to, or doesn’t have to: 1. At this store you can’t use a credit card. You … use cash. 2. You can’t wear jeans to the interview. You … wear a suit. 3. This ticket is good anytime. You … use it today. 4. We … do any homework tonight. Tomorrow’s holiday. 5. He’d like to stay out later, but he … be home before midnight. 6. She … buy the book. She can borrow it from the library. 7. They … pay their rent before the first of the month. Otherwise, they pay a penalty. 8. He doesn’t need much sleep. Grammar. I. Complete the exercise with the correct prepositions. 1. Uluru is located … central Australia. 2. The large sandstone rock formation is also known … Ayers Rock … honour … Sir Henry Ayers, who was a Premier … South Australia … 1873. 3. Uluru is listed … a World Heritage Area … both its natural and cultural values. 4. It is sacred … the Aboriginal people … the area. 5. … different times … the day, Uluru seems to change colour. 6. The sandstone is infused … minerals that reflect the red light … sunrise and sunset. II. Exercise on Prepositions – Place . Complete the exercise according to the picture. . 1. … the picture, I can see Santa Claus and a girl. 2. Santa is sitting … a chair. 3. The girl is standing … Santa. 4. Santa and the girl are looking … each other. 5. The girl has a present … her hands. 6. … the girl, there is a Christmas tree. 7. There are more presents … the tree. 8. Santa's big bag is lying … the floor.