* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Math 362 - Section 001 Fall 2006 Practice Test 1
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Perspective (graphical) wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Projective plane wikipedia , lookup
Lie sphere geometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Cartesian coordinate system wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Geometrization conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Duality (projective geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Hyperbolic geometry wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Name:
Math 362 - Section 001
Fall 2006
Practice Test 1
Closed Book / Closed Note. Write your answers on the test itself.
Part I: Circle T if the statement is true, and F if the statement is false.
1.
Euclid’s work is important mainly because he discovered many new
geometrical facts.
T
F
2.
David Hilbert developed an axiom system for geometry that filled in
many of the “holes” in Euclid’s system.
T
F
3.
So called “synthetic” geometry does not rely on other mathematical
systems such as real numbers.
T
F
4.
The undefined terms in our axiom system include point, line, plane,
lies on, and distance.
T
F
5.
The Postulate of Pasch in equivalent to the Plane Separation
Postulate.
T
F
6.
The Ruler Postulate establishes a single coordinate function that
works for every line.
T
F
7.
If a statement and its negation can both be proved within an axiom
system, that statement is said to be independent.
T
F
8.
Any statement that is proveable within an axiom system is true in
every model of that system.
T
F
9.
In the early 1900's a group of European mathematicians who
published under the name of Nicolas Bourbaki standardized the
axioms of geometry so that now every textbook uses the same axiom
system.
T
F
10.
The Protractor Postulate establishes a one-to-one correspondence
between non-negative real numbers less than 180, and a set of
angles.
T
F
Section II: Matching
Match the Postulate on the left with the description on the right by writing the letter of the
correct description in the blank after each statement.
11.
Postulate of Pasch
A.
Establishes how lines and points interact
with one another.
12.
Crossbar Theorem
B.
Establishes a metric or distance
function.
13.
Ruler Postulate
C.
Guarantees that your geometry is not
empty.
14.
Incidence Postulate
D.
Is equivalent to the Plane Separation
Postulate.
15.
Linear Pair Theorem
E.
Guarantees that a ray between
will intersect
point.
16.
Existence Postulate
F.
and
at an interior
Establishes the relationship between
linear pairs and supplementary angles.
Section III: Short answer.
17.
A model for Incidence Geometry has points S = {1, 2, 3, 4} and lines {1, 2}, {1, 3},
{1, 4}, and {2, 3} (among others). What sets must the remaining lines be?
18.
Consider the model: Points: S= { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; Lines: {1, 2, 3, 4}, {1, 5}, {2, 5}, {3,4},
{3, 5}, {4, 5}. Is this a model for Incidence Geometry? Explain briefly.
19.
Suppose that K, L, and W are three points lying on a line, with ruler coordinates 3, 5, and
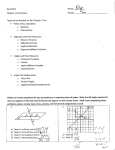
x, respectively. If KW =5 and LW = 7, what are the possible values for x?
20.
Rays on one side of
form angles with measures of pCBF, pDBC, and pEBD as
indicated in the figure. Ray
is opposite ray
the betweeness relations evident in the figure, find
a.
mpABG
b.
mpGBD
, and
is opposite
. Using
21.
pQMN and pQMP are a linear pair of angles. Rays
pQMP, respectively. Find: µpQMX + µpQMY.
22.
Two lines
meet at a point M, with A-M-B and C-M-D. Identify the shaded
region in the figure in terms of half-planes, with unions and/or intersections as
appropriate.
and
bisect pQMN and
23.
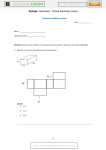
Use the language of angle interiors (along with unions and intersections) to describe the
shaded region in the figure.
24.
Consider the following relationships among three angles: p1 is complementary to p2, p1
is supplementary to p3, and the sum of the measures of p2 and p3 equals 120. Find
mp2.
25.
Point B lies on
the ray opposite ray
and you are given that µpABC = 40 and µpABE = 160. In addition,
bisects pABC. What values are possible for µpDBE?