* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Science Journals * 3-18-13
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Standard solar model wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
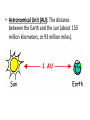
March 24, 2014 • Remember…. • What is the smallest particle of matter that still retains all of the properties of that matter? • What is in the center of the smallest particle of matter? • What surrounds the center? • Do you remember that the atom is mostly empty space? • What did we explore Friday that is mostly empty space? TEK 8.8B • Recognize that the Sun is a medium-sized star near the edge of a disc-shaped galaxy of stars and that the Sun is many thousands of times closer to the earth than any other star. • Star - a large ball of gas that generates its own energy by fusing hydrogen atoms to make helium. It is held together by its own gravity. This process emits a tremendous amount of energy, and some of the energy is in the form of light. • Astronomical Unit (AU): The distance between the Earth and the sun (about 150 million kilometers, or 93 million miles). Where’s The Sun? (where’s waldo?) 1. Where is our solar system located in the Milky Way galaxy? 2. How does the Sun’s mass compare with other stars in the galactic neighborhood? 3. How does the distance of the Sun from Earth compare to the distances of other stars from Earth? 4. How long does it take for light from the Sun to reach Earth’s surface? Your Galactic Address • • • • • • • • • North Ridge Middle School 7332 Douglas Lane North Richland Hills, Tx USA, North America Planet Earth Solar System Milky Way Galaxy Virgo Supercluster Universe Artistic rendering of the possible shape of the known universe. http://scienceblogs.com/startswithabang/upl oad/2010/12/whats_in_the_uni verse/WMAP.jpeg Virgo Supercluster SUN’S MASS • The Sun’s mass is 199 with 28 zeros after it in kg, and it’s a medium sized star. • There are billions and billions of stars in the galaxy. • To make writing the mass of these stars easier, the Sun is the frame of reference and the Sun is equal to one solar mass. • Smaller stars < one solar mass • Larger stars> one solar mass How Long Does it Take for the Light of our Sun to reach us? http://www.universetoday.com/15021/howlong-does-it-take-sunlight-to-reach-the-earth/ The LIGHT-YEAR • A light-year is a measure of distance. It is not a measure of time. • A light-year is the distance that light travels in one year. • It is equal to about 6 trillion miles. • 6,000,000,000,000 miles. Science Journals – 3-25-14 • The light from Alpha Centauri A takes 4.3 years to reach Earth. The light from Ross 154 takes 9.7 years to reach Earth. The light from Luyten 726-8A takes 8.7 years to reach Earth. The light from Procyon A takes 11.4 years to reach Earth. The light from Sirius B takes 8.1 years to reach Earth. 1. What is the order of the following stars from the closest to Earth to the farthest from Earth? Massive Stars • OUR SUN IS JUST AN AVERAGE SIZED STAR! • There are stars out there much, much bigger… Note down this definition - Our Sun →