* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download (Expressions and Equations).
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Big O notation wikipedia , lookup
Functional decomposition wikipedia , lookup
Recurrence relation wikipedia , lookup
Law of large numbers wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Elementary algebra wikipedia , lookup
7 Math Vocabulary # 2 (Expressions and Equations).notebook
7th Grade Math Vocabulary
Ahrens
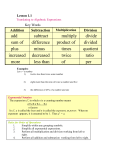
Operation
A calculation by a mathematical process.
Expressions and Equations
calculators perform operations
Expressions and Equations Glossary
x
exponents are operations too
Operation
Operation
Order of Operations
A mathematical process.
The rules of which calculation comes first in an expression. Addition
Subtraction
Multiplication
Division
+
3
y = y y y
Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication or Division, Addition or Subtraction
+
_
x
÷
÷
21 3 = 7
7x = 21
11 = 3y + 2
4 x 5 = 20
5 + x = 5 Please Excuse My Dear Aunt Sally
sign
11 1 = 3b + 1
Operation
Order of Operations
Order of Operations
Expression
The rules of which calculation comes first in an expression.
Numbers, symbols and operations grouped together that show the value of something.
Parentheses Exponents
Multiplication
Division
Addition
Subtraction
"Please Excuse
My
Dear
Aunt
Sally"
Order of Operations
7 + (6 x 52 3) 7 + (6 x 25 3) 7 + (150 3) 7 + (147) 150
2
3 2 + 1
An expression is one side of an equation.
2 x 3 = 6
Expressions DO NOT have equals signs.
Expression
1
7 Math Vocabulary # 2 (Expressions and Equations).notebook
Ahrens
Algebraic Expression
Expression
An expression that consists of one or more: numbers, variables, and operations.
Numbers, symbols and operators (such as + and ×) grouped together that show the value of something.
7x
2 9b
0.5a
7 x 6
4x
Remember!
3y + 2
7x 7x = 21
"7 times x"
"7 divided by x"
11 = 3y + 2
3 + 2 = y
x
2
number: operation: variable:
number: operation: variable:
number: operation: variable:
11 1 = 3z + 1
Expressions
equals sign:
Algebraic Expression
Evaluate
Inverse Operations
To find the value/amount of something.
Operations that "undo" each other. They are opposites.
You cannot "evaluate" an algebraic expression if you do not know the value of the variable.
If x=3, then 2x is 2 times 3; so 2x = 6
Addition reverses subtraction
+
+
Subtraction reverses addition
Evaluate
The operation that reverses the effect of another operation.
Addition
_
Subtraction
Multiplication
x
÷
Division
5 + x = 5 + 5
+ 5
x = 10
Inverse Operation
x
x
Multiplication reverses division 9
32
9
Square roots reverses squaring Inverse Operations
Inverse Operation
+
Division reverses multiplication
Squaring 32
reverses square roots
11 = 3y + 2
2
2
9 = 3y
÷ 3 ÷ 3
3 = y
Variable
A letter or symbol that represents a changeable or unknown value.
4x + 2
x x
variable
x = ?
2x = 6
Variable
2
7 Math Vocabulary # 2 (Expressions and Equations).notebook
Ahrens
Isolate the Variable
Variable
To move the variable to one side of the equation, and all of the numbers to the other side.
A symbol for a number that is unknown. any letter towards end of alphabet!
x
y
u
z
v
*Sometimes Greek!
Inverse x
operation 7x = 21
Expression 1: Only the variable
2y = 12
11 = 3y + 2
2
2
To isolate the variable, use inverse operations & properties of numbers.
y = 6
11 1 = 3z + 1
Expression 2: Everything else
Variable
Isolate the Variable
Solution
Solution Set
A value you can put in place of a variable that would make the statement true.
A set of values that can make a statement true.
x + 4 = 9
Solution: x = 5
3y 6 Solution: y 2
The answer to a math problem.
The #s in a solution set are written in curly brackets.
{ }
Constant
A fixed value, a number on its own, whose value does not change. A constant may either be positive or negative.
constant
3y
constant
Constant
y={4,5,6,7}
Solution Set
Constant
11m 7
y2 = 16
y = {4,4}
Solution
2 + 4x 3 < y < 7
There is no constant.
A number that is on
its own within an
expression or equation. 4
Tricky!
69
110
π
1/2
0.45 7
8
A fixed value. 7x
These are not constants. These are coefficients! 7x = 21
3z
11 = 3y + 2
3y
11 1 = 3z + 1
Constant
3
7 Math Vocabulary # 2 (Expressions and Equations).notebook
Ahrens
Term
Coefficient
A number multiplied by the variable. 4x + 2
x4
coefficient
Coefficients are in front of the variable.
4 x
= x+x+x+x
A single number or variable, or a variable with a coefficient.
4x
4x + y
1 term
Term
Like Terms Like Terms
Terms that have the same variable raised to the same power
Like terms
4x + y
different variables
3 terms
2 terms
Coefficient
4x2 + x2 4x + y 1
4x + x2 different powers
Terms whose variables (and their exponents) are the same.
3x x 1/2x
15.7x 5x
2.3x
Like Terms
5x3
5
x3 27x3
2x3
1/4x3
5x3
2.7x3
NOT 5x2
LIKE TERMS! 5x
Like Terms
Equation
Equation
Two expressions that are equivalent to each other. Equivalence is shown with an equal sign.
A mathematical statement, in symbols, where two things are exactly the same (or equivalent).
4x= 8
equivalent expressions
4 = x3
5x4
x3
no equivalence
1 + 2 = 3
22 = 20 + 2
7x = 21
(where x = 3)
4 + 9 = 13
= 11
3y + 2 (where y = 3)
equivalent expressions
11 1 = 3z + 1
Equation
Equation
7 + 4 = 90
5 = 3 + 10
3x + 6 = 11
(where x = 3)
(where z = 3)
4
7 Math Vocabulary # 2 (Expressions and Equations).notebook
Distributive Property
Equivalent
Equal; the same amount or value.
3+3=3x2
=
For all real numbers a, b, c, a(b+c) = ab + ac and a(b c) = ab ac. a(b + c) = ab + ac
Formula
To find all numbers or variables that divide into all of the parts of an expression.
=
13x + 8z
2x + 4y =
7(x + 5)
2 • x + 2 • 2 • y
cannot be factored
(terms have nothing in common). A special type of equation that shows the relationship between different variables.
Numbers and symbols that show how to work something out.
Distance Formula:
distance = rate x time
d = r x t
PRIME
=
=
7 • x + 7 • 5
3(x + 4) = 48 (3)(x) + (3)(4) = 48 3x + 12 = 48 3x = 36 x = 12 Distributive Property
Factoring 7x + 35 3(2 + 4) = (3)(2) + (3)(4) =
6 + 12 = 18
3(2 4) = (3)(2) (3)(4) =
6 12 = 6
a(b c) = ab ac
Equivalent
The distributive property in reverse. Ahrens
Area of a circle Formula:
Celsius to Fahrenheit Formula:
5 C = (F 32)
9
Area = π(radius)2
A = πr2
2(x + 2y) Factoring Formula
Addition Property
Subtraction Property
If a=b, then a+c=b+c for all real numbers a, b, and c. The same number can be added to each side of the
equation without changing the solution of the equation. If a=b, then ac=bc for all real numbers a, b, and c. The same number can be subtracted from each side of the equation without changing the solution of the equation. a = 2
b = 2
c = 4
a = b
a + 4 = b + 4
2 + 4 = 2 + 4
6 = 6
a = b
x 3 = 5
+ 3 + 3
x = 8
Addition Property
z 14 = 6
+ 14 + 14
z = 20
a = 2
b = 2
c = 4
a = b
a 4 = b 4
2 4 = 2 4
2 = 2
a = b
x + 3 = 5
3
3
x = 2
z + 7 = 20 7 7
z = 13
Subtraction Property
5
7 Math Vocabulary # 2 (Expressions and Equations).notebook
Ahrens
Multiplication Property
Division Property
If a=b, then ac=bc for all real numbers a, b, and c. Each side of an equation can be multiplied by the same
number without changing the solution of the equation. If a=b, and c=0, then a/c=b/c for all real numbers a, b, and c.
Each side of an equation can be divided by the same nonzero number without changing the solution of the equation. a = 2
b = 2
c = 4
a = b
a x 4 = b x 4
2 x 4 = 2 x 4
8 = 8
z ÷ 2 = 10
x 2
x 2
z = 20
a = b
x ÷ 3 = 5
x 3
x 3
x = 15
a = 2
b = 2
c = 4
a = b
a = b
x x 3 = 5
÷ 3 ÷ 3
x = 5/3
a ÷ 4 = b ÷ 4
2 ÷ 4 = 2 ÷ 4
.5 = .5
Multiplication Property
Minimum
The lowest or least amount or value.
Greater than or equal to
smaller
larger
larger
A comparison of two numbers that are not, or may not, be equal.
smaller
z = 20
Division Property
Inequality
Greater than
z x 2 = 10
÷ 2 ÷ 2
Less than or equal to
You must drive at least 40 mph.
Less than
Inequality Minimum includes the smallest possible value.
You must be at least this tall to ride.
It means ____ or more.
Minimum
Maximum
Dependent Variable
The highest or greatest amount or value.
The variable whose value varies based on the value of another variable.
Maximum includes the highest value.
It means ____ or less.
Maximum
Equations
Graphing
y = x
The dependent variable is always along the y axis.
2
The value of y is determined by the value of x.
Function Tables
The (x) (y)
dependent 1
1
variable is 4
always the 2
9
3
output (y).
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Dependent Variable
6
7 Math Vocabulary # 2 (Expressions and Equations).notebook
Ahrens
Function Table
Rule
Organizes the special relationship between x and y values. Each of its input values gives back exactly one output value.
Defines the relationship between the input and the output, using an algebraic equation. It says what happens to the input in a function.
(x) (y)
1
1
2
4
3
9
The output (y) depends on the input (x).
x is the independent variable, on the left,
and y is the dependent variable, on the right.
3
Rule: In
pu
t
y = 4x+2
ut
p
ut
O
9
Rule:
y = x2
Function Table
Rule: (x) (y)
y = 3x
(x) (y)
1
3
2
6
3
9
1
6
2
10
3
14
Rule
Input
Output
The input is the independent variable in a function (x).
The output is the dependent variable in a function (y).
In
The (x) (y)
output (y) 1
1
depends 4
2
on the input (x). 3 9
3 put
y = x
2
Input
The value of y is determined by the value of x.
Input
ut
tp
Ou
9
Rule
y = x2
The (x) (y)
output (y) 1
1
depends 4
2
on the input (x). 3 9
y = x
3
In
pu
t
t
pu
2
Output
The value of y is determined by the value of x.
t
Ou
9
Rule
y = x2
Output
7