* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download In The Name of God
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
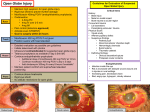
In The Name of God Infectious Endophthalmitis Symptoms ,Signs, Differential Diagnosis MR.Ansari MD Infectious endophthalmitis is a condition in which the internal structures of the eye are invaded by replicating microorganisms . Exogenous endophthalmitis occurs when the outer wall of the eye sustains a break as a result of surgery or trauma. Exogenous endophthalmitis is the most common subtype. 90% of all cases are caused by bacteria. In certain clinical settings ,there is an increased likelihood of infection by certain groups of bacteria . Endophthalmits following cataract surgery is most often caused by staphylococcus epidermidis. Injured eyes → Gram-positive Bacillus spp. Allen reviewed 30000 ICCE from 1964 to 1977 and found an incidence of endophthalmitis of 0.057% . Review of 23625 cases of ECCE in Bascom Palmer Eye Institute revealed an incidence of 0.072% Phaco →incidence of 0.03% to 0.04% In Sweden & Norway →0.1% to 0.16% Following open globe injuries→4.2% to 7% . Symptoms of Acute Endophthalmitis ( within 6 weeks ) Sudden increase in pain 1-7 days after surgery . ↓VA Redness and conjunctival injection. Lid swelling In EVS 98% with acute endophthalmitis presented with one or more of the four classic symptoms. ↓VA ( 93% ) Conjunctival injection ( 81% ) Pain ( 75% ) Lid swelling ( 33% ) Signs of acute endophthalmitis In fulminant cases conjunctival chemosis and increased injection often with a significant amount of yellowish exudates in the conjunctival cul - de - sac Edematous lids often difficult to open Corneal edema ( variable degrees ) Pigmented cells may accumulate on its posterior surface of cornea. Surgical wound may show signs of dehiscens and in advanced cases exudates can stream from the wound. AC reaction ( heavy flare and cells ) Hypopyon ( mixed with a tinge of red blood ) Fibrin membrane is usually present over both surfaces. Heavy cellular debris is present in the vitreous . Focal accumulations of whitish material or sheets of opacification within the vitreous . IOP → low , normal or high . Pupil often dilates poorly . Retinal prephlebitis has been reported an early sign but in most cases the retinal vessels are seen poorly . Red reflex ? Notice to risk factors Leakage of wound Rupture of posterior capsule Vitreous wick Time of operation Diabetes mellitus Cutting of sutures too early A case – control study demonstrated a threefold greater risk of endophthalmitis with clear corneal incisions than with scleral tunnel incisions . Continuation Temporal incisions were noted to have a higher incidence of infection than superior incision . Transcleral suture fixation of posterior – chamber IOL . Polypropylene haptics Preoperative eyelid abnormalities and blepharomeibomitis . Re – entry of the eye through a previous wound . Differential Diagnosis Postoperative inflammation Retained lens material →respond to corticosteroids. Chronic , low grade endophthalmitis may occur secondary to coagulase – negative Gram – positive organisms such as s.epidermidis and also result from infections with the anaerobic species Propionibacterium acnes . ( 40% of cases ) Propionibacterium can present with mild iritis and pigmented KP . Continuation On examination , the most common findings are vitritis , white plaques on the posterior capsule or the IOL , beaded fibrin strands , hypopyon ?,granulomatous KP . TASS Toxic substance enters the anterior chamber Causes Acute sterile postoperative inflammation Photophobia , ↓VA , corneal edema and marked anterior chamber reaction with hypopyon TASS presents within hours of surgery Pathologic changes limited to AC Pain is much less than that of endophthalmitis ↑IOP Tainted BSS , reusable double cannula , se of preserved solution , subconjunctival injection near the wound . Thank you for your attention