* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Animals, including humans: The Circulatory System
Blood transfusion wikipedia , lookup
Autotransfusion wikipedia , lookup
Schmerber v. California wikipedia , lookup
Blood donation wikipedia , lookup
Jehovah's Witnesses and blood transfusions wikipedia , lookup
Plateletpheresis wikipedia , lookup
Men who have sex with men blood donor controversy wikipedia , lookup
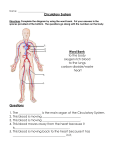
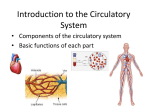
Animals, including humans: The Circulatory System Objectives Identify and name the main parts of the human circulatory system and describe the function of the heart, blood vessels and blood. Describe how water and nutrients are transported within the body. Plenary Pupils should look at the worksheet and decide which statements are true (colour in green) and which are false (colour in red). True: heart beats faster when you exercise, heart is found in the upper chest, heart is a muscle, heart pumps blood around the body. All about the heart Pupils should place their clenched fists in the centre of their upper chests. This is the size and position of the heart. Which part of the skeleton protects it? (The ribs.) Show the pupils a photograph or diagram of a heart; it is not remotely ‘heart-shaped’. Ask the pupils for ideas about what the purpose of the heart might be. They may already know that it acts as a pump. Can the pupils find their own pulse? The easiest place to feel is on the wrist: pupils should take two fingers and draw them down the thumb and further until they reach the wrist, where a pulse can be felt. Other good places to feel the pulse include the side of the neck and behind the clavicle (place your fingers on top of the collar bone and gently press down). How many beats can pupils count in a minute? Write this down. It is normal to count 60-100 beats per minute when a young person rests. A normal heart beats more than 100,000 times every day. You can feel your heart beating all over your body because the heart is pumping blood all around the body. The system which carries blood around your body is called the circulatory system. Pupils must note: The heart is a vital organ which pumps blood around the body. The circulatory system The circulatory system (cardiovascular system) includes the heart, blood and blood vessels and is responsible for transportation. Blood is very important. In blood, we find water, nutrients and air. These need to be carried to every part of the body. Blood travels through special tubes in our bodies. These tubes are called blood vessels and include veins, arteries and capillaries. Whenever our heart beats, it © Education Umbrella 2015 pumps blood through the blood vessels, which go all over the body. Therefore, water, nutrients and air (specifically oxygen) are carried all over the body. Pupils must note: The circulatory system is made up of heart, blood and blood vessels. Blood contains water, air and nutrients and is carried around the body in blood vessels. When you put an elastic band on your finger and it starts going purple and numb, this is because the blood vessels are blocked and so the heart cannot pump blood to the end of your finger. When you donate blood, a nurse needs to find a blood vessel to remove blood from. A simple model could be made of the circulatory system with a rubber pump, clear tubing and water (with red food dye). Ask a pupil to squeeze the pump in time with their pulse. Making your heart work hard (non-statutory) The heart is always beating to keep water, nutrients and air moving around your body. However, sometimes it is necessary for the heart to work faster because your body needs more of these things. An example of this is when you are exercising. Pupils have already written down their resting heart beats. Ask for some volunteers (multiple volunteers are necessary as some will struggle to find their pulse). These volunteers should undergo 2-3 minutes of very intense exercise. This could include running on the spot, jumping jacks, lunges, step-ups or whatever else is safe in a classroom environment. Afterwards, volunteers should measure their pulse for another minute and compare it with their resting pulse. They should all find that it is higher. This is because the heart needs to work harder to get air around the body. Pupils may note: The heart beats faster when you exercise. Possible extra-curricular questions Why do people say your heart makes you fall in love? Thousands of years ago, the heart was described as the ‘centre’ of the body and the centre of intelligence and emotion. In Europe during the Middle Ages, people started to draw the heart as ‘heart-shaped’ and connect it with loyalty, bravery and love. The heart ‘races’ when a person is in love because at times of excitement, the heart works harder to provide the body with air (could be excitement due to fear, anticipation, joy or sexual arousal, many of which are combined when a person experiences love). Do all animals have circulatory systems? All vertebrates have similar circulatory systems to humans; these circulatory systems are described as ‘closed’. Invertebrates have different circulatory systems; some have ‘open’ © Education Umbrella 2015 systems. An ‘open’ system has little structure and the organs are bathed in nutrient-rich fluid rather than having blood pumped to them. Some animals, including flatworms, have no circulatory system at all. How fast do hearts beat in other animals? Pulses are quicker in small animals because the heart has to make up for its small size by working faster. A mouse heart beats at 670bpm, a cat or dog at 60-120bpm (same as a human), a horse at 40bpm and a blue whale at 6bpm. What is blood made out of? Blood is made out of various blood cells, floating in plasma. The blood cells are red blood cells (carry oxygen), white blood cells (protect the body from disease) and platelets (form scabs). Why don’t you die when a nurse takes blood? To die of blood loss, you need to lose about 40% of your blood – this is a lot! When you donate blood, a tiny hole is punctured in your body to take blood. When the needle is removed, the platelets in your blood go to the hole to form a scab and stop you from losing any more blood. Can anybody give blood? Most people of the age of 17 and older can donate blood several times a year. Why are veins blue? Veins are not really blue. They look blue because the skin filters out the reddish colours of light, making it appear that the veins are more of a blueish colour (can also appear greenish or violet). © Education Umbrella 2015