* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pacemaker Emergencies - Calgary Emergency Medicine
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
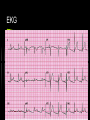
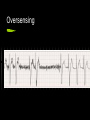
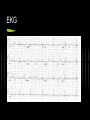
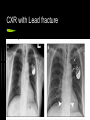
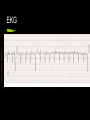
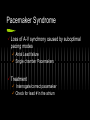
Pacemaker Emergencies Arun Abbi MD Jan 21, 2010 Overview Initial approach Pocket Complications Acute complications with placement Nonarrythmic complications Pacemaker function issues Initial Approach ABC’s - make sure your patient is stable and on a monitor Pacemaker Information pacemaker type, model, number and manufacturer Patient will often have a card with the info Initial Approach EKG Should be a LBBB pattern for the QRS Meds Cardiac meds, anti seizure meds (dilantin) Lytes Check K+,Mg+,Ca+ Initial Approach If patient is stable and is complaining of palpitations, near syncope, light headedness Get the pacemaker nurse to interrogate the pacemaker Pocket Complications Hematomas Occur after implantation-venous or arterial bleeder (check for anticoagulation) If the size of your palm - needs surgery Infection Acute infection - staph aureus Chronic/late infection - staph epidermidis Case 1 76 yr old male presents with chest pain for 2 days Pain worse with lying down and better with sitting up No diaphoresis/orthopnea/SOB Pt had a pacemaker inserted 3 weeks earlier V/S and physical were normal EKG Management? What do you want to do? Any concerns? Complications with Placement Pneumothorax/hemothorax Typically present in the first 48 hrs. Treat as most pneumothoraces DVT Upper extremity DVT’s can occur soon after placement or in a delayed fashion. Secondary to endothelial disruption Infection Can get endocarditis (right sided) Can present with chronic infection wasting/malaise/thromocytopenia/anemia Complications with Placement Acute dislodgement Patient may have an ASD/VSD and pacemaker lead may migrate across the heart or may migrate into a coronary sinus. Myocardial Perforation Can present as acute pericarditis Can present with hiccups secondary to diaphragmatic innervation Failure to Pace 1.Oversensing Secondary to the pacemaker sensing P or T waves of muscle fasciculations Careful with succinylcholine Higher incidence with unipolar sensing (VVI) as the antennae is larger Treatment - reduce the sensitivity Oversensing Oversensing Failure to Pace 2. Failure to capture When the impulse is insufficient to cause myocardial depolarization Causes Lead Fracture Battery failure Pacemaker failure Local inflammatory response post insertion Electrolyte imbalance leading to prolonged Q-T Medications Case 2. 62 yr old female presents to emergency with increasing lethargy and confusion Pt has had a few falls PMHx Pt has hx of complete heart block and has a VVI pacemaker EKG Failure to Pace Management 1. Make sure pacemaker rate is faster than intrinsic heart rate (to see if it paces) Will see change in QRS morphology (LBBB) 2. CXR (look for lead fracture) 3. Check Lytes 4. Check Meds CXR with Lead fracture Case 3 54 yr old male presents to the ER with palpitations and feeling light headed. No chest pain/SOB EKG Failure to Sense When the pacemaker fails to detect native cardiac activity Secondary to ischemia, infarct, pvc’s Lead dislodgement/fracture Failure to Sense Management CXR Lytes Meds Will need pacemaker interrogated for malfunction Pacemaker Mediated Tachycardia 1. Endless Loop Tachycardia Re-entry dysrhythmia that occurs with dual chamber pacemakers PVC - initiating factor Retrograde P-waves that are sensed by the atrial lead - leading to subsequent ventricular paced beat Treatment - apply magnet over the patient’s pacemaker to break the cycle Have pacemaker nurse reset parameters of pacemaker Pacemaker Mediated Tachycardia Pacemaker Mediated Tachycardia 2. Tracking of Native Atrial Tachyarrythmia Atrial Flutter/Atrial Fib. Management Cardiovert the patient if < 48 hrs or pt is therapeutically anticoagulated Slow the ventricular response rate Pacemaker Syndrome Loss of A-V synchrony caused by suboptimal pacing modes Atrial Lead failure Single chamber Pacemakers Treatment Interrogate/correct pacemaker Check for lead # in the atrium Runaway Pacemaker When you see rapid tachycardia > 300 beats/minute True emergency -may lead to VT/VF Due to pacemaker damage Management Place the magnet over the patient’s pacemaker It will default to asynch mode at a rate of 70 Pacemaker and MI’s Treat as per patient with LBBB Concordant ST changes > 1mm ST depression > 1mm in the anterior leads V1 - V3 Discordant ST changes > 5 mm in the anterior leads Can also slow the pacemaker rate down and see what the underlying ST changes are (would need pacemaker nurse to come in If concerned - refractory pain not amenable to medical Tx - send to the cath lab. ICD’s Placed in patient with class IV chf Ventricular arrthymias HOCUM ICD’s Pt’s with V-fib ICD will shock immediately and every 5-10 seconds thereafter After 15 shocks it will time out for 10 - 15minutes Pt’s with V-tach ICD will try to overdrive pace for 15-20 seconds before initiating a shock It will give repeated shocks and then time out after 15-20 shocks to prevent battery fatigue ICD’s If the patient has had ICD shocks; the patient should be seen by cardiology/ICD nurse to have the device interrogated Check EKG - ischemia Check lytes Refractory V-tach If wanting to turn off ICD – place magnet over the ICD Place defib pads Anterior – Posterior Shock as per normal