* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson 24 - Understanding Economics in US History
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
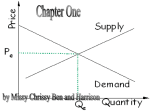
LESSON 24 INDUSTRIAL ENTREPRENEURS OR ROBBER BARONS? VISUAL 24.1 TRAITS OF ENTREPRENEURS Economically speaking, an entrepreneur is a productive resource — a special sort of human resource. Entrepreneurs have several characteristics: • They organize resources and manage them in innovative ways to increase output or produce new goods and services — or both. • They look for new ways to produce goods and services. • They are willing to take risks. Seeking success, they risk failure. • They are willing to face stiff competition. • They are willing to take advantage of legal ways to limit the competition they face — by using patents and copyrights, for example. • They take steps to earn as much profit as possible. 276 FOCUS: UNDERSTANDING ECONOMICS IN UNITED STATES HISTORY ©NATIONAL COUNCIL ON ECONOMIC EDUCATION, NEW YORK, NY INDUSTRIAL ENTREPRENEURS OR ROBBER BARONS? LESSON 24 VISUAL 24.2 ENTREPRENEURSHIP DURING LATE NINETEENTH CENTURY Entrepreneurial Activity (Causes) Mass production THE Definition Involves the production of large quantities of similar goods using large-scale operations, especially mass production in factories employing many workers. Examples include breakthroughs in producing steel, clothing, shoes, cans and so forth. Division of labor and specialization Laborers (productive resources) can usually produce more goods and services per hour if their work tasks are divided among different workers. This is division of labor. Division of labor allows laborers working repetitively on the same tasks to specialize in the production process. As time passes and laborers become skilled at specific tasks, output rises and labor costs fall. Vertical integration Vertical integration occurs when firms manufacturing goods or providing resources along the same production chain merge. Gustavus Swift in meat packing and Andrew Carnegie in steel are among those who used vertical integration. Horizontal integration Horizontal integration occurs when business competitors in the same industry merge; it occurs when a company in one sector of an industry acquires or gains control over other companies in that sector. For example, a production company may expand by purchasing other production firms. John D. Rockefeller is the best example an industrialist who used horizontal mergers. FOCUS: UNDERSTANDING ECONOMICS IN Effects • More output can be achieved at a lower cost. Supply increases. • The number of people employed increases because the demand for labor rises. • Improves efficiency: output per labor hour rises. Supply increases. • Production costs fall. Supply increases. • Vertically integrated firms may restrict output and increase prices. Supply decreases. • Production costs fall if economies of scale are realized. Supply increases. • Horizontally integrated firms may restrict output and increase prices. Supply decreases. UNITED STATES HISTORY ©NATIONAL COUNCIL ON ECONOMIC EDUCATION, NEW YORK, NY 277 LESSON 24 INDUSTRIAL ENTREPRENEURS OR ROBBER BARONS? VISUAL 24.3 MASS PRODUCTION AND NEW TECHNIQUES: CHANGE IN SUPPLY S1 PRICE S2 P1 P2 D Q1 Q2 OUTPUT 278 FOCUS: UNDERSTANDING ECONOMICS IN UNITED STATES HISTORY ©NATIONAL COUNCIL ON ECONOMIC EDUCATION, NEW YORK, NY