* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Angiography - WordPress.com
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
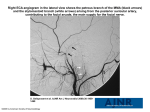
Angiography is a specialized test which is used to examine the state and functioning of the arteries in our heart. The arteries are the important blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood from the heart to the various parts of the body. When a person suffers from a chest pain, which is also known as angina, it becomes necessary to get an angiography done. Angiographies are done in order to study the biology of blood vessels like the arteries and the veins. In short, it is the inspection of the condition inside the 'tubular structures' in the body. This technique was first developed in the year 1927 by a Portuguese physician and neurologist Egas Moniz. He came up with this technique to provide contrasted x-ray cerebral angiography which will help in diagnosing several kinds of nervous diseases, such as tumors, artery disease and arteriovenous malformations. He is recognized as one of the pioneers in this field. Moniz performed the first cerebral angiogram in Lisbon in 1927, and Reynaldo Cid dos Santos performed the first aortogram in the same city in 1929. The Seldinger technique or the insertion of radio opaque material was introduced in 1953. The technique is named after Dr. Sven-Ivar Seldinger, a Swedish radiologist who introduced the procedure in 1953. This technique made angiography a safe method as no sharp introductory devices needed to remain inside the body. Till date, different types of angiography are used to determine different ailments. Angiography has become a widely used technique and is considered as a boon to the medical industry. The process of angiography involves a fluorescent dye and an x-ray examination. Basically, in this procedure the x-rays of the chest are taken. But soft tissues or the 'inside' area of arteries are not clear in a regular x-ray and hence the help of a fluorescent dye or the contrast agent is taken. The dye or contrast is a fluorescein sodium is a highly fluorescent chemical compound that absorbs blue light with fluorescence. It is commonly referred as fluorescein, or fluorescein sodium, the sodium salt of fluorescein. A radio opaque material is first inserted in the blood stream with the help of a device called as the catheter which is a thin, narrow, tube-like structure. Once the dye has entered the blood vessels, the x-ray machine will capture visual descriptions called fluoroscopy. In case of any blockage in the heart, the dye will not reach and the doctor will understand that there is a blockage present in the heart. A coronary angiogram is a procedure that uses X-ray imaging to see the inside of your heart's blood vessels. Coronary angiograms are part of a general group of procedures known as cardiac catheterization. Catheterization refers to any procedure in which a long, thin, flexible plastic tube (catheter) is inserted into your body. A cerebral angiogram (also known as an arteriogram) is a diagnostic procedure that provides images of the blood vessels in the brain and/or head. The test is performed to find blocked or leaking blood vessels. This test can help to diagnose such conditions as the presence of a blood clot, fatty plaque that increases the patient's risk of stroke, cerebral aneurysm or other vascular malformations like AVM’s. Carotid angiography, also called carotid angio or an arteriogram, is an invasive xray procedure used to find narrowing or blockage (atherosclerosis) in the carotid arteries. Carotid angiography may be performed when carotid artery disease is suspected, based on the results of other tests, such as a carotid duplex ultrasound, computed tomography angiogram (CTA) or magnetic resonance angiogram (MRA). Peripheral angiograms test the arteries which supply the blood to the head and neck or those to the abdomen and legs. An aortogram is an invasive diagnostic test that uses a catheter to inject dye into the aorta. X-rays are taken of the dye as it travels within the aorta, allowing a clear view of your blood flow. This way, any structural abnormalities of the aorta can be seen accurately. What is CT angiogram? A computerized tomography (CT) angiogram is an imaging test for various types of heart disease. Unlike a traditional coronary angiogram, CT angiograms don't use a catheter threaded through your veins to your heart. Instead, a CT angiogram relies on a powerful X-ray machine to produce images of your heart and heart vessels. CT angiograms require less recovery time than traditional angiograms and are becoming an increasingly popular option for people who have a moderate risk of blocked or narrowed arteries. A CT angiogram can determine the location and severity of artery narrowing of blockages caused by: -PAD in the legs -Kidney and artery disease - Aortic disease - During a CT scan, a beam of x-rays is sent towards your body in a 360-degree circle. Detectors pick up the x-rays after they have passed through your body, creating digital images in thin “slices” of your body. A computer assembles these slices into a complete 3 dimensional picture of the arteries and surrounding tissues. A pulmonary angiogram is an angiogram of the blood vessels of the lungs. A pulmonary angiogram may be used to assess the blood flow to the lungs. One of the primary indications for the procedure is the diagnosis of a clot. It may also be used to deliver medication into the lungs to treat cancer or hemorrhage. Female conjoined twins, of 15 month of age, were evaluated for evaluated for the possibility of separation. They were joined below the xiphoid process at an angle of approximately 90 degrees. The twins shared a single pelvis, and each child exhibited a normal anterior lower limb and a conjugated posterior lower one. One of the twins was visibly bigger than the other. Pre-operative testing included: Bone structure- plain radiography and helical CT scan Cardiovascular system- plain radiography, echocardium and helical CT Urogenital System- intravenous pyelogram and helical CT. Gastrointestinal System- contrasted radiological study of digestive system. Liver and spleen- abdomen ultrasound and helical CT. An Angiographic study was performed under general anesthesia. The procedure was carried out in the angiography suite through the femoral arteries of both children using a JV1 catheter and hydrophilic guide wire. Celiac and mesenteric angiographic study demonstrated a normal hepatic arterial supply for the smaller twin. The study confirmed agenesis of the IVC in the smaller twin but also showed that the hepatic parenchyma drained into her right atrium though small hepatic veins, which allows the twins to be successfully separated. CASE STUDY The use of the angiography in the procedure of the conjoined twins was to accurately define the hepatic arterial and venous vascular anatomy, allowing the hepatic section without complications. The test allowed for surgical separation of the children. Despite being an invasive method, angiographic study should be indicated as a preoperative diagnostic complementation in cases in which the vital anatomic vascular structures are not identified by other tests. Traditional diagnosis for various vascular diseases should be done using a catheter angiography as the gold standard of reference. New techniques such as an MRI angiography are useful for diagnosing atherosclerotic renovascular disease. The images produced by a CT angiogram allow doctors to detect narrowing or blockages in your blood vessels caused by PAD. The CT angiogram is an accurate and reliable test for diagnosing and investigating PAD. A large analysis of 12 studies that included 436 PAD patients (24% were women) found that CT angiography was about 92% accurate at diagnosing PAD in aorta, abdomen, and legs. CT angiogram technology continues to improve and the latest studies find the test can be 98% accurate. CT angiograms can be used safely on patients who can not have an MRI test because of metal implants like pacemakers or defibrillators All available methods of diagnosing have advantages and disadvantages Based on our findings physicians might consider using the ultrasound test as an initial screen. Contrast-enhanced MRI angiography and CT angiography overcome the major limitations of duplex http://www.humantouchofchemistry.com/ angiography-a-boon-for-people.htm http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?pid=S18 0759322006000200013&script=sci_arttext