* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Wireless power for mobile phones
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Loudspeaker wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Crystal radio wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Loading coil wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
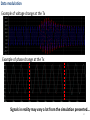
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
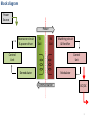
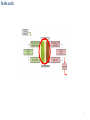
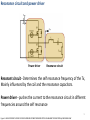
Wireless power for mobile phones System overview Nov 25, 2012 V1.1 1 System overview Rx Tx • Embedded in mobile device • After market case/dongle connected through the power connector • Add-on connected through dedicated WLC pins • Embedded in furniture/car/infrastructure • After market mat 2 Block diagram Power Source Power Resonance circuit & power driver TX Coil RX Coil Matching circuit & Rectifier Control Unit Control Unit Demodulator Modulator Communication DC/DC 3 Tx-Rx coils 4 Tx-Rx coils – Magnetic induction basics Electric current flowing in a wire gives rise to a magnetic field around it. Alternating the current will alternate the magnetic field Shaping the wire as a loop will band that field in a “lung” shape. 5 Figures: http://ipodphysics.com/magnets-loop-or-coil.phpt Tx-Rx coils – Magnetic induction basics Energy coupling means that an energy source has a mean of transferring its energy to a second object. Transformers may use iron core to deliver the magnetic flux Wireless power system is an air core transformer between planar coils one on top of the other. Figure 1: http://www.electrical4u.com/what-is-transformer-definition-working-principle-of-transformer/ Figure 2: http://makezine.com/2013/11/04/component-of-the-monthtransformer/ Figure 3: http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/media/1355/Magnetic-field-B-of-two-current-loops-with-currents-in 6 Tx-Rx coils – Coil designs Single coil– Most common design Pros – chip and easy solution / Cons – difficult alignment Large Tx coil – Common in loosely coupled systems Pros – easy alignment / Cons – difficult design and tune Array of small Tx coil – One or more coils provide power simultaneously Pros – easy alignment / Cons – Cost of coils and drivers 3 coil array – Only one coil provides power at a time Pros – easy alignment / Cons – Cost of coils and drivers 7 Fig1:http://www.qitah.com/blog.htmlFig2:http://phys.org/news203691107.htmlFig3:http://patentimages.storage.googleapis.com/US20130119773A1/US20130119773A1-20130516-D00015.png Resonance circuit and power driver 8 Resonance circuit and power driver Power driver Resonance circuit Resonant circuit - Determines the self resonance frequency of the Tx, Mainly influenced by the coil and the resonance capacitors. Power driver - pushes the current to the resonance circuit in different frequencies around the self resonance 9 Figure 1: HIGH EFFICIENCY LOOSELY COUPLED WIRELESS POWER TRANSFER SYSTEM VIA MAGNETIC INDUCTION By ZHEN NING LOW Resonance circuit • The overall impedance the driver “sees” when modeled as a series RLC circuit • At the resonance frequency the capacitive and inductive impedance equals Amplitude The driver then sees resistive only minimum overall impedance and the power delivery to the Rx is maximal Frequency • The resonance curve changes with each different : Rx design (EE & ME) Phone material Misalignment from the center Variation during manufacturing Load drawn Figure 1: http://perlgeek.de/blog-en/perl-6/rakudo-memory-leaks.html 10 Driving the power Amplitude Frequency control – the driver changes the frequency along the resonance curve Control becomes difficult when Q is high & at resonance control is unstable Frequency range shall be dynamic due to curve changes Passing to the second side of the peak may reverse the control rules Frequency Other methods of control: Voltage control – increasing the input voltage will increase the current through the coil and the transmitted power Pulse width control – increasing the on time of the signal will increase the transmitted power 11 Data modulation 12 Data modulation Power driver Modulator Matching circuit & Rectifier Demodulator load modulation • Rx modulates the operational frequency by short circuiting the coil to a secondary load • The secondary load changes both the load of the Tx and the resonance curve • The demodulator sense the change in voltage, current or phase between them on the operational frequency 13 Data modulation Example of voltage change at the Tx Example of phase change at the Tx Signals in reality may vary a lot from the simulation presented…. 14 Questions? Comments? Remarks? It’s called wireless power, it’s the future Thanks, Rotem Shraga ([email protected] ; 052-6443944) Figure: http://www.fodrizzle.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/02/funny-birds-wire-drawing.jpg 15