* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Notes
Plane of rotation wikipedia , lookup
Rotation matrix wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Rotation formalisms in three dimensions wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Rotation group SO(3) wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
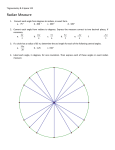
Lesson #1: Rotations and Angles Algebra II with Trigonometry CC Unit 9: Trigonometry Recall from Geometry: Trigonometry istherelationship betweenthelengthsofsidesand anglesinatriangle. This year: Trigonometricfunctions arebased onthegeometryofthecircleand rotationsarounditscenter. Lesson #1 Rotations and Angles Unit 9: Trigonometry 1 Lesson #1: Rotations and Angles Algebra II with Trigonometry CC An angle is in standard position is when the initial side is the positive x-axis and the vertex is at the origin. The ray on the x-axis, is called the intial side of the angle, and the ray at which the rotation ends is the terminal side of the angle. Unit 9: Trigonometry 2 Lesson #1: Rotations and Angles Algebra II with Trigonometry CC An angle formed by a counterclockwise rotation has a positive angle measure. An angle formed by a clockwise rotation has a negative angle measure. Terminal Angles w/ Quadrants Quadrantal Angles – angle in standard position whose terminal side lies on one of the axes. ex) 0°, 90°, 180°, 270°, 360° Unit 9: Trigonometry 3 Lesson #1: Rotations and Angles Algebra II with Trigonometry CC Examples Determine the quadrant in which an angle of the given measure lies. 1. 140° II 2. -168° III 3. 500° II 4. -34° IV Coterminal Angles Angles in standard position having the same terminal side. Unit 9: Trigonometry 4 Lesson #1: Rotations and Angles Algebra II with Trigonometry CC If two angles are coterminal, the difference in their measures is 360° or a multiple of 360° Examples: Find the angle of smallest positive measure coterminal with an angle of the given measure. 1. 400° 40° 2. -110° 250° 3. 790° 70° Reference Angles Associated with every angle drawn in the standard position (exceptquadrantal angles)there is another angle called the reference angle. The reference angle is the positive acute angle formed by the terminal side of the given angle and the x-axis. Reference angles may appear in all four quadrants. Angles in quadrant I are their own reference angles. Remember! The reference angle is measured from the terminal side to the x-axis. (NOT THE Y‐AXIS!) Unit 9: Trigonometry 5 Lesson #1: Rotations and Angles Algebra II with Trigonometry CC Remember: The reference angle is measured from the terminal side to the x-axis. (NOT THE Y‐AXIS!) Remember: The reference angle is measured from the terminal side to the x-axis. (NOT THE Y‐AXIS!) Unit 9: Trigonometry 6 Lesson #1: Rotations and Angles Algebra II with Trigonometry CC Remember: The reference angle is measured from the terminal side to the x-axis. (NOT THE Y‐AXIS!) Remember: The reference angle is measured from the terminal side to the x-axis. (NOT THE Y‐AXIS!) Unit 9: Trigonometry 7 Lesson #1: Rotations and Angles Algebra II with Trigonometry CC Examples:Draweachangleinstandard positionandidentifythereferenceangle. 2. 120° 1. ° 330° ° Examples:Draweachangleinstandard positionandidentifythereferenceangle. Unit 9: Trigonometry 4. 225° 3. ° 45° ° 8