* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy Lesson
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
Efficient energy use wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Gibbs free energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
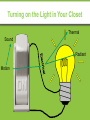
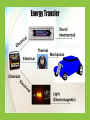
Who’s doing work? Work is only done by a force on an object if the force causes the object to move in the direction of the force. Objects that are at rest may have many forces acting on them, but no work is done if there is no movement. Work, the product of the force exerted on an object and the distance the object moves in the direction of the force. W = F·d Power, by definition, is the time rate of doing work; or the time rate transfer of energy. P=W/t Power, My friend, has been so stressed. His boss keeps making him work over time. P=W/t Energy click on energy for a short video Energy: Forms and Changes Nature of Energy • Energy is all around you! – You can hear energy as sound. – You can see energy as light. – And you can feel it as wind. Nature of Energy • You use energy when you: – hit a softball. – lift your book bag. – compress a spring. Nature of Energy Living organisms need energy for growth and movement. Nature of Energy • Energy is involved when: – – – – a bird flies. a bomb explodes. rain falls from the sky. electricity flows in a wire. Energy the ability to do work Energy comes in many forms: mechanical, electrical , magnetic, solar, thermal, chemical, etc... The SI unit of energy is the Joule. Energy Energy Potential Energy Stored energy and the energy of position Kinetic Energy Motion of waves, electrons, atoms, molecules, and substances Potential Energy Stored energy and the energy of position Chemical Energy Energy stored in the bonds of atoms and molecules Nuclear Energy Energy stored in the nucleus of an atom – the energy that holds the nucleus together Potential Energy Stored energy and the energy of position Gravitational Energy Energy of place or position Elastic Energy Energy stored in objects by the application of force. Kinetic Energy Motion of waves, electrons, atoms, molecules, and substances Radiant Energy Thermal Energy Electromagnetic energy that travels in transverse waves Internal energy in substances – vibration or movement of atoms and molecules in substances a.k.a. “heat” Kinetic Energy Sound Energy Movement of energy through substances in longitudinal waves Motion of waves, electrons, atoms, molecules, and substances Mechanical Motion Movement of substance from one place to another Electrical Energy Movement of electrons Potential Energy Stored Energy gravitational potential energy GPE = mgh m - mass of object in kg g - acceleration of gravity in m/s2 h - height of object, in m GPE – gravitational potential energy in J Kinetic Energy energy of motion All moving objects that have mass have kinetic energy. KE = 1/2 2 mv m - mass of the object in kg v - speed of the object in m/s KE - the kinetic energy in J Different Types of Energy. Kinetic Energy Anything that moves has kinetic energy. Gravitational Potential Energy (GPE) Anything above the ground has gravitational potential energy i.e. anything that can fall, like ski jumpers, aeroplanes and climbers. Nuclear Energy Released only from nuclear reactions The sun and all of the stars. Hydrogen bomb (Fusion) Nuclear power plants Sound Energy Anything noisy gives off sound energy like vocal chords, speakers and instruments. Chemical Energy Anything with stored energy which can be released by a chemical reaction has chemical energy, things like food fuels and batteries. Radiant Energy also called electromagnetic energy All life on Earth depends upon radiant energy from the sun Examples: radio waves, microwaves, Xrays, Heat/Thermal Energy Anything with a temperature above absolute zero (-273°C) has heat energy. That means everything has some thermal energy. Light Energy Anything luminous gives off light energy, like the sun, light bulbs , candles and glow worms. Electrical Energy Electrical energy is very useful, because its easily converted into other forms – wherever there's a current flowing there's electrical energy. Elastic Energy Anything stretched, has elastic energy – things like rubber bands, springs, knickers, elastic etc Different types of energy click on link above for a video : thermal light sound elastic gravitational kinetic electrical chemical nuclear Can you think of examples of each type of energy? Energy transfer Energy can be changed from one form to another. For example: Chemical energy in food is converted to thermal energy and kinetic energy by our bodies. Gravitational energy in a ball is converted to kinetic energy when it falls to the ground. What other energy transfers can you think of? Energy the ability to do work Energy comes in many forms: mechanical, electrical , magnetic, solar, thermal, chemical, etc... The SI unit of energy is the Joule. Energy Energy Potential Energy Stored energy and the energy of position Kinetic Energy Motion of waves, electrons, atoms, molecules, and substances Potential Energy Stored energy and the energy of position Chemical Energy Energy stored in the bonds of atoms and molecules Nuclear Energy Energy stored in the nucleus of an atom – the energy that holds the nucleus together Potential Energy Stored energy and the energy of position Gravitational Energy Energy of place or position Elastic Energy Energy stored in objects by the application of force. Kinetic Energy Motion of waves, electrons, atoms, molecules, and substances Radiant Energy Thermal Energy Electromagnetic energy that travels in transverse waves Internal energy in substances – vibration or movement of atoms and molecules in substances a.k.a. “heat” Kinetic Energy Sound Energy Movement of energy through substances in longitudinal waves Motion of waves, electrons, atoms, molecules, and substances Mechanical Motion Movement of substance from one place to another Electrical Energy Movement of electrons What impacts an object’s GPE? Who has more energy? Who has more energy? Potential Energy Stored Energy gravitational potential energy GPE = Wh W – Weight of object in N h - height of object, in m, GPE – gravitational potential energy in J Roller Coaster Conversions The NEED Project Law of Conservation of Energy “Energy can be neither created nor destroyed. It may only change forms.” energy before the event = energy after the event Examples: •A dropped object loses gravitational PE as it gains KE. •A block slides across the floor and comes to a stop. •A compressed spring shoots a ball into the air. Law of Conservation of Energy Watch the video and take notes on the law of conservation of energy Turning on the Light in Your Closet Thermal Sound Radiant Motion Describe energy transfer in each device burning match portable torch microphone radio television catapult mobile phone car Describe energy transfer in each device burning match microphone radio television car chemical to thermal and light sound to electrical electrical to sound and thermal electrical to sound and light and thermal chemical to kinetic and sound and thermal In all these transfers the energy is not lost, it is conserved. Energy cannot be destroyed or created. Energy poker Look at the scenes on the slides that follow. Make a bid for the number of energy transfers that you can see. The person with the highest bid has to explain where they are. If they fail to find that number they lose. Can you win at energy poker? Let’s look at an example first… First Example… Energy poker score: 1 Sunlight energy converted into heat to boil the water for tea