* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Stars - Sun
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Equation of time wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
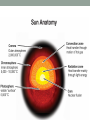
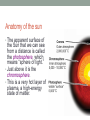
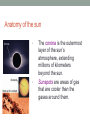
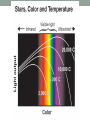
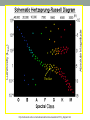
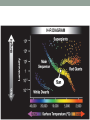
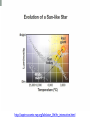
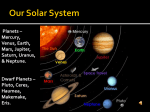
The Sun • The Sun is a giant, hot ball of gas held together by gravity. • The Sun is a medium-sized compared with other stars in the universe. • Main sequence star Approximately 1 million planet Earths could fit inside the Sun! The Sun • Gravity squeezes the density of a star so tightly in the core that the electrons are stripped away and the bare nuclei of atoms almost touch each other. • Nuclear fusion occurs. The Sun • In the process, huge amounts of energy are given off. • Because of its mass, the Sun’s gravitational force is strong enough to hold the entire solar system in orbit. Anatomy of the sun • The apparent surface of the Sun that we can see from a distance is called the photosphere, which means “sphere of light.” • Just above it is the chromosphere. • This is a very hot layer of plasma, a high-energy state of matter. Anatomy of the sun • • The corona is the outermost layer of the sun’s atmosphere, extending millions of kilometers beyond the sun. Sunspots are areas of gas that are cooler than the gases around them. Features of the sun • Occasionally, large “loops” of gas called prominences can be seen jumping up from groups of sunspots. Features of the sun • Solar wind is an electrically charged mixture of protons and electrons that cause magnetic storms. • Auroras, called the northern lights, occur when layers of our atmosphere are energized by solar winds. Solar energy • Solar energy is a term that refers to radiant energy from the Sun. • The radiant energy of the Sun reaches Earth in the form of electromagnetic waves. • We can use solar energy to heat buildings and generate electricity. More about the Sun’s energy • In 1905, Albert Einstein proposed that matter can be converted into energy. • His famous equation shows how huge amounts of energy can be created from a smaller mass. 27.2 Temperature and color • If you look closely at the stars on a clear night, you might see a slight reddish or bluish tint to some stars. • This is because their surface temperatures are different. 27.2 Temperature and color • The color of light is related to its energy. • White light is a mixture of all colors at equal brightness. More about the Sun’s energy • The amount of this energy from the Sun that reaches the outer edge of Earth’s atmosphere is known as the solar constant. • The accepted value is 1,386 watts per square meter (W/m2), or about thirteen 100-watt light bulbs per square meter of surface. Brightness and luminosity • For a distant source of light like a star, the brightness decreases as the inverse square of the distance. The Sun http://astrosun2.astro.cornell.edu/academics/courses/astro201/hr_diagram.htm http://aspire.cosmic-ray.org/labs/star_life/hr_interactive.html