* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetics problems supplemental_KEY
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Inbreeding avoidance wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
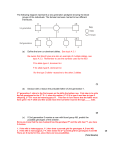
Biology 101: Additional practice genetics problems ------ KEY These will not be collected In the fruit fly Drosophila, normal wings (W) are dominant to vestigial (w), and normal ocelli (N) are dominant to white ocelli (n). Note: vestigial means shrunken and nonfunctional; “ocelli” are the tiny single-facet eyes located between their two large compound eyes. 1. If a male fruit fly with vestigial wings mates with a female heterozygous normal fly: A. What are the genotypes of the gametes each of the parents can produce? Dad: _w_ Mom: __W or w__ B. What percentage of their offspring can fly? ___1/2___ 2. A male, vestigial winged fly with normal ocelli mates with a female, normal winged fly with white ocelli and among their offspring are approximately equal numbers of normal and vestigial young, all with normal ocelli. A. What are the genotypes of the parents and the offspring? Dad: ____wwNN____ Mom: ____Wwnn____ Offspring with Normal wings : _ WwNn _ Vestigial wings: _ wwNn __ B. What are the genotypes of the gametes the parents produced? Dad: __wN ___ Mom: ___Wn, wn_____ C. Draw a Punnett square that shows the observed result. wN Wn wn WwNn wwNn 3. In radishes, the enlarged root is the edible part of the plant. Root shape determined by incompletely dominate alleles elongated (E) and round (e). Root color is determined by the codominant alleles red (R) and white (r). A. Since the shape alleles are incompletely dominant, which one of these root phenotypes is likely to occur for an Ee plant? 1) highly irregular knobby and bumpy roots; 2) oval-shaped roots, or 3) un-enlarged roots. Explain. The heterozygous phenotype is intermediate between the homozygous dominant and homozygous recessive phenotypes B. Since the root color alleles are codominant, would a heterozygote with pink or brown roots be most likely? Explain. The heterozygote with brown roots is more likely because the red and white alleles contribute to a distinctive phenotype. C. Assume that plants heterozygous for both traits are crossed. Using the product rule, calculate the percentage of the offspring that will be ‘Eerr’. 1/8 Chance of Ee = ½ Chance of rr = ¼ ½ x ¼ = 1/8 4. Assume that height in humans is determined by 2 polygenic genes (T and S). A. If the dominant alleles for each gene have an additive effect upon tallness, what would be the genotype of tallest and shortest individuals? Tallest: ___TTSS___ Shortest: ___ttss___ B. What is the possible number of different phenotypes? 5 C. If a mating occurred between persons heterozygous for each gene, what fraction of the children would be expected to be the same height as their parents? 6/16 = 3/8 Parents (TtSs) have 2 dominant alleles; 6/16 of possible offspring would also have 2. TS TTSS TTSs TtSS TtSs TS Ts tS ts Ts TTSs TTss TtSs Ttss tS TtSS TtSs ttSS ttSs ts TtSs Ttss ttSs ttss 5. Mary has type A blood, and her mother has type B. Bob has type B blood, and his mother was type A. A. Draw a pedigree that shows the genotypes (as well as can be determined) of Mary and Bob and their parents. B. What are the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the fathers of Bob and Mary? Bob’s father: ___ B (IBi or IB IB ) or AB (IA IB ) ___ Mary’s Father: ____ A (IA IA or IA i) or AB (IA IB) ___ C. Draw a Punnett Square that predicts the possible genotypes and phenotypes among Bob and Mary’s children? B I i IA I I AB IA i A A B i B I i B ii O In humans, assume that brown eyes (B) are dominant over blue eyes (b); and that righthandedness (R) is dominant over left-handedness (r). Pseudohypertrophic muscular dystrophy, a sex-linked disorder, causes progressive deterioration of muscles and is usually fatal in the early teenage years. The alleles are designated as XN (normal) and Xn (pseudohypertrophic). 6. A right-handed, blue-eyed man marries a right-handed brown-eyed woman. They have two children, one left-handed and brown-eyed, the other right-handed and blue eyed. By a later marriage, to a woman who is also right-handed and brown-eyed, this man has nine children, all of whom are right-handed and brown eyed. Determine the probable genotypes for all individuals mentioned. Write “ ? ” where an allele cannot be determined exactly. Man: __Rrbb____ First wife: __RrBb___ Second wife: __RRBB___ Child 1: _rrBb___ Child 2: ___R?bb___ 9 children: ___RrBb or RRBb____ 7. Suppose a blue-eyed female carrier for PDM marries a normal male heterozygous for brown eyes. A. What are the genotypes of the gametes each parent will produce? Mom: _____bbXN Xn _____ Dad: ____Bb XNY____ B. What are the genotypes of the gametes each parent will produce? Mom: _____bXN or bXn _____ Dad: ____ BXN, bXN , BY, or bY ____ C. When their children reach adulthood, what is the expected frequency of blue-eyed males and blue-eyed females? 1/3 blue-eyed females 1/6 blue-eyed male BXN BY bXN bY bXN Bb XN XN Bb XNY bbXN XN bb XNY bXn Bb XN Xn Bb XnY --die bbXN Xn bb XnY - die