* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Warmup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Cavity magnetron wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
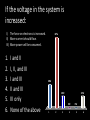
Warmup 100,000 J of energy are added to a 10g block of ice starting at -5*C. What temperature does it end up at? Q = m C ∆T Q=mL Cs = 2.11 J/g K Cl = 4.18 J/g K Cg = 2.08 J/g K Lf = 334 J/g Lv = 2260 J/g MARCH 30TH, 2012 Electromagnetism Basics Essential Standard Students can solve problems to determine characteristics of circuits involving voltage sources, resistors, and capacitors using Ohm’s Law and the Power Law. Students can draw and interpret field diagrams and relate them to the force on a charged particle. Students understand how a transistor operates and how it is used in technology. Students understand the link between electricity and magnetism and can identify the orientation of a current or magnetic field using the Right Hand Rule. Vocabulary Concept Variable Unit Label Definition Voltage V Volts (V) How hard the electrical field is pushing electrons Current I Amps (A) (coloumbs/s) How many electrons flow per second Resistance R Ohms (Ω) How easily the material allows the electrons to move Power P Watts (W) (coloumbs * volts/ s) Work done per second Charge q Coloumbs (C) 6.24×1018 electrons or protons Inductance L Henries (H) How much a current affects (and stores potential energy) in magnetic fields Capacitance C Farads (F) (coloumbs/volt) How much charge can be built up as a result of a voltage Circuit Diagram Symbols Voltage Source Wire Meter Resistor Capacitor Inductor Switch (closed) Switch (open) Ground Practice Diagrams Equations V=I*R P=I*V xt = x 1 + x 2 + x 3 … 1/xt = 1/x1 + 1/x2 + 1/x3… Ohm’s Law Power Law Serial resistors or parallel capacitors Parallel resistors or serial capacitors Practice Problems (Ohm’s and Power Laws) If the voltage in the system is increased: I) The force on electrons is increased. II) More current should flow. III) More power will be consumed. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. I and II I, II, and III I and III II and III III only None of the above 60% 20% 10% 1 2 3 10% 0% 0% 4 5 6 Batteries store: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Charge Current Voltage Inductance Capacitance Power 25% 17% 17% 17% 17% 8% 1 2 3 4 5 6 If you lower the voltage on a charged capacitor: 1. Current will flow forward to increase the charge. 2. The power of the system decreases. 3. Current will flow backwards to decrease the charge. 4. Inductance will store lost energy in a magnetic field. 5. None of the above. 67% 25% 8% 1 2 3 0% 0% 4 5 A circuit has a resistance of 4 Ohms and a voltage of 3 Volts. What current flows through it? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 4/3 Amps ¾ Amps 1 Amp 12 Amps 4/3 Farads ¾ Farads 1 Farad 12 Farads 57% 21% 14% 7% 1 2 3 0% 0% 0% 0% 4 5 6 7 8