* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 11
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
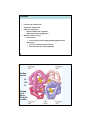
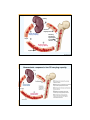
Chapter 11 The Blood and Body Defenses Blood • • • Represents about 8% of total body weight Average volume – 5 liters in women – 5.5 liters in men Consists of 3 types of specialized cellular elements suspended in plasma (liquid portion of blood) – Erythrocytes ◊ – ◊ – Red blood cells for O2 & CO2 transport Leukocytes White blood cells ◘ Immune system’s mobile defense units Platelets ◊ Cell fragments ◘ Important in hemostasis ♦ the process of keeping blood within a damaged blood vessel (the opposite of hemostasis is hemorrhage) Plasma 55% of whole blood Packed cell volume, or hematocrit Buffy coat: platelets and leukocytes (<1% of whole blood) Erythrocytes (45% of whole Blood) Platelets Leukocytes (white blood cells) Erythrocytes (red blood cells) Fig. 11-1, p. 298 Plasma • Plasma proteins – Compose 6% to 8% of plasma’s total weight – 3 groups of plasma proteins ◊ Albumins ◘ Most abundant plasma proteins (60%, 3.5‐5g/dl) ♦ Osmotic pressure (oncotic pressure) ♦ Transport of hormone, bile salts, bilirubin, fatty acids, calcium, transferrin, etc ♦ Tranport of many drugs – competition = drug interactions ◊ Globulins (2‐3.5g/dl) ◘ 3 subclasses ♦ Alpha1, Alpha2 (α) transport ♦ Beta (β) transport ♦ Gamma (γ) immune ◊ Fibrinogen ◘ Key factor in blood clotting Erythrocytes • Red blood cells (RBCs) – 2‐3 x 1013 ◊ 4‐5million per cc female ◊ 5‐6million per cc male – 120 day life span ….. 2 million new RBC/sec – Contain no nucleus, organelles, or ribosomes – Structure is well suited to main function of O2 transport in blood – Biconcave discs ◊ Provides larger surface area for diffusion of O2 across the membrane ◊ Thinness = short diffusion distance from exterior to innermost regions of the cell – Flexible membrane ◊ Allows RBCs to travel through narrow capillaries without rupturing in the process Hemoglobin • Found only in red blood cells • 15g/dl male 13g/dl female • Pigment containing iron – Appears reddish when oxygenated – Appears bluish when deoxygenated • Molecule consists of 2 parts – Globin portion ◊ Protein composed of four highly folded polypeptide chains – Heme groups ◊ Four iron‐containing nonprotein groups ◊ Each is bound to one of the polypeptides •Binding sites for O2 CO2 H+ •Binding of one effects affinity for the other Hemoglobin • Primary role is to carry O2 • Also combines with – Carbon dioxide – Acidic hydrogen‐ion portion (H+) of ionized carbonic acid – Carbon monoxide – Nitric oxide Erythropoiesis • • • • • Erythrocyte production RBCs survive about 120 days Spleen removes most of old erythrocytes from circulation Must be replaced at rate of 2 million to 3 million cells/second Erythropoiesis occurs in bone marrow – Pluripotent stem cells in red bone marrow differentiate into the different types of blood cells Kidney 2 1 Normal Erythropoietin 3 normal oxygencarrying capacity keeps Normally Developing erythrocytes in red bone marrow 5 4 Normal oxygencarrying capacity Erythrocytes Fig. 11-3, p. 301 Homeostasis: response to low O2 carrying capacity