* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Test Review Sheet
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Equivalence principle wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
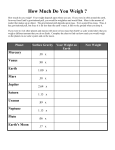
Test Review Sheet ‘Gravitational force’ There will be a TEST next class( A day 4/28 or B day 4/29). The test will be based on ‘Gravitational InteractionI, II’ and ‘FluidsI, II’ True or False 1. If Earth had its present mass but twice the radius, the acceleration due to gravity would increase (True False) 2. The Sun pulls harder on Earth’s ocean than the moon (True False) 3. Ocean tides are caused by differences in the gravitational pull between the moon and the opposite sides of Earth (True False) 4. If the distance between two objects doubles, then the gravitational force acting between them would be one half the original force (True False) 5. Pressure at the bottom of a lake depends on the density of the lake and on the volume of the lake (True False) 6. The strength of the buoyant force that will act on an object depends on the mass of the object (True False) 7. As a solid object sinks deeper into the water, the pressure will increase (True False) 8. As a solid object sinks deeper into the water, the buoyant force will increase (True False) 9. The strength of the buoyant force that will act on an object depends on the volume of the object (True False) 10. As a solid object sinks deeper into the water, the buoyant force stays the same (True False) Multiple Choice 1. Two objects move toward each other because of gravitational interaction. As the objects gets closer and closer, the force between them a) increase b) decrease c) remain constant d) increase and then decrease 2. Suppose the gravitational force between two massive spheres is 10N. If the distance between them the spheres is cut in half, what is the force between the masses? a) 40N b) 20N c) 10N d) 5N e) 2.5N 3. Why did Newton think there was a force acting on the moon? a) Because the moon always keeps one side toward Earth b) Because the moon moves in a curved path c) Because there is no air on the moon d) Because the moon is moving 4. The factor most directly responsible for making a black hole invisible is its a) size b) mass c) color d) escape velocity 5. Two friends say they cannot feel the gravitational attraction between them. The reason for that is because a) gravitational force does not exist between living things b) the friend’s masses are too small for the gravitational force between them to be significant c) gravity only acts at large distance; they are too close together d) there is too much friction between their chairs and the floor 6. The mass of an object at the surface of the Earth compared to the mass of the same object at a distance of two Earth radii from the surface of the Earth is: a) the same b) one half c) one quarter d) one ninth 7. Which of the following graphs best represents the gravitational force between two masses as the distance between the masses change is: a) Fg b) Fg r c) Fg r d) Fg r r 8. A 90kg astronaut weighs 1/6 as much on the moon as on Earth because: a) the moon is made of denser rock than the Earth b) the astronaut is closer to the center of the mass when standing on the moon’s surface c) the mass of the Earth also pulls on the astronaut d) the mass of the moon is substantially less than the mass of the Earth 9. If the distance between two objects were doubled, the force of gravitational attraction between the object would be: a) the same b) double the original force c) one half the original force d) one quarter the original force 10. The force of gravitational attraction between two objects is 20N. If the mass of one of the object were doubled, the gravitational force between the objects would be: a) 5.0N b) 10N c) 40N d) 80N 11. The force of gravitational attraction between two objects is 20N. If the mass of both objects were doubled, the gravitational force between the objects would be: a) 5.0N b) 10N c) 40N d) 80N 12. Two stars are bound together by gravity. The larger star has four times the mass of the smaller star. Which diagram best illustrates the orbital motion of the two stars? a) b) c) d) 13. The reason a life jacket help people float is that a) jacket and the person together will have less weight than the person alone b) the jacket has the same density as an average person c) the jacket repels the water and exerts a buoyant force on the person 14. When first put in water, a plastic toy boat will sink until a) it displaces a volume of water equal to its own volume b) it displaces a weight of water equal to its own weight c) the water density equals the density of the boat d) the buoyant force equals the volume of the boat 15. In a vacuum on earth, an object has no a) buoyant force b) mass c) heat d) weight 16. As a whale swims deeper into the ocean, increasing water pressure squeezes its volume, making the whale smaller. As the whale swims deeper and deeper, the buoyant force on it a) decreases b) increases c) remains the same d) doubles Additional Questions 1. An object’s mass is 2kg. If the buoyant force acting on the object is 20N, would the object float, sink or stay still? Justify your answer~ 2. An object’s mass is 4kg. If the buoyant force acting on the object is 20N, would the object float, sink or stay still? Justify your answer~ The information below will be needed to solve questions 3 ~ 4 A 1-liter container filled with water has a mass of 1kg and weighs 9.8N. A 1-liter container filled with mercury. A 1-liter container filled with mercury has a mass of 13.6kg and weighs 133N. Weight Wg=mg ,where g=9.8m/s2. 3. i) If you fill up 1liter container with sand, and immerse into a pool of liquid mercury, how much buoyant force will act on the object? ii) You weigh the sand-filled container and discover it weighs 17.64N. Will the container sink or float? Justify your answer~ iii) If you take that same sand-filled container and immerse into water, what is the buoyant force and explain whether the container will sink or float. 4. i) What is the buoyant force acting on an empty 1-liter container when completely submerged into water? Will it float, sink or stay still in the water? Justify your answer~! ii) What is the buoyant force acting on an empty 1-liter container when submerged halfway into water? That is, half a liter is submerged into water. Justify your answer~! The weight of objects under water is called apparent weight(Wa) and can be expressed as Wa = Wg - Fb, where Fb is the buoyant force. Answer question 13 using the concept above. Fb Wg 5. A 0.6kg rock suspended above water weighs 5.88N. When suspended beneath the surface of the water, its apparent weight is 3.9N. What is the buoyant force on the rock? 5.88N 3.9N scale