* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Let`s Hear it for Almigal
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
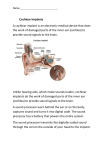
A Study of the Ear, Sound Transfer, and Cochlear Implants to compliment Let’s Hear it for Almigal Written by Wendy Kupfer Illustrated by Tammie Lyon Published by Handfinger Press Guide Created by Debbie Gonzales 2 A Study of the Ear, Sound Transfer, and Cochlear Implants The intention for this packet is to identify the parts of the ear, demonstrate how sound is transferred through to the brain, and to illustrate how cochlear implants serve the same purpose. The lessons and manipulative activities in this packet may be done independently or in a group setting. Through the understanding of the parts and functions of the ear, the mysteries of cochlear implants seem less daunting and more marvelously miraculous! Table of Contents Parts of the Ear – Coloring Sheet……………………………………………………………………………………………3 The Parts of the Ear- A Matching Game………………………………….………………………………………………6 The Parts of the Cochlear Implant-A Matching Game……………………………………………………………15 CCSSI Annotations…………………………………………………………..……………………………………………………24 Acknowledgments………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..25 www.debbiegonzales.com www.almigal.com 3 Parts of the Ear – Coloring Sheet Objective: To present and identify the parts of the ear directly affected by the use of cochlear implants. Materials: Print out pages 4 and 5 Markers, colored pencils, or crayons Procedure: Study page 4. o Note the color-coding for the various parts of the ear. o Note the colors labeled in the circular spaces on the key below the drawing. o Take some time to associate the various parts of the ear and their designated color-code. Using page 5 and markers, colored pencils, or crayons, color-code the parts of the ear. Follow the code established on page 4 or create your own! www.debbiegonzales.com www.almigal.com 4 Parts of the Ear – Coloring Sheet pinna auditory nerve auditory canal cochlea ear drum oval window hammer anvil stirrup www.debbiegonzales.com www.almigal.com 5 Parts of the Ear – Coloring Sheet pinna auditory nerve auditory canal cochlea ear drum oval window hammer anvil stirrup www.debbiegonzales.com www.almigal.com 6 The Parts of the Ear – A Matching Game Objective: To guide the understanding of the transfer of sound, from the outer ear to the brain, through a manipulative game. Materials: Cardstock Scissors Four part printouts o Parts of the Ear – Master Copy (pages 7 to 8) o Parts of the Ear – Label Matching (pages 9 to 10) o Parts of the Ear – Picture Matching (pages 11 to 12) o Parts of the Ear – Label Cut Outs (pages 13 to 14) Procedure: Print pages 7 to 14 on cardstock. Parts of the Ear – Master Copy (pages 7 to 8) is intended to serve as a guide for correct matching of picture and labels. Print these pages to be used as a reference throughout the game. Use scissors to cut out Parts of the Ear – Label Cut Outs (pages 13 to 14). These labels are to be used as manipulatives to be matched and placed in the appropriate blank spaces on the Parts of the Ear – Label Matching (pages 9 to 10) and the Parts of the Ear – Picture Matching (pages 11 to 12) grids. Read the manipulative cut out labels and place them in the appropriate blank space on the Parts of the Ear – Label Matching (pages 9 to 10) Using the Parts of the Ear – Picture Matching (pages 11 to 12), match the appropriate picture cut out next to its descriptive label. Mix up the cut out labels and start all over again! www.debbiegonzales.com www.almigal.com 7 Parts of the Ear – Master Copy The pinna is part of the outer ear. The pinna is curved, circular ridged cartilage that captures and directs sound into the auditory canal. The auditory canal is part of the outer ear. The auditory canal transfers sound toward the inner ear. The ear drum is part in the middle ear. The ear drum is air tight and transfers sound to the tympanic cavity, where there are three bones called ossicles. The hammer is an ossicle found in the tympanic cavity. The hammer shifts position because of vibrations created by the ear drum. The anvil is an ossicle found in the tympanic cavity. The anvil is set in motion by the movement of the hammer. www.debbiegonzales.com www.almigal.com 8 The stirrup is an ossicle found in the tympanic cavity. The stirrup amplifies sound by thumping against another air tight seal called the oval window. The oval window is part of the inner ear. The oval window amplifies sound vibrations through a chamber filled with fluid called perilymph. The cochlea is part of the inner ear. Inside the cochlea is the organ of corti which is lined with special hairs that respond to frequencies, sending signals as sound to the auditory nerve. The auditory nerve is part of the inner ear. The auditory nerve sends signals as sound to the brain. www.debbiegonzales.com www.almigal.com 9 Parts of the Ear – Label Matching www.debbiegonzales.com www.almigal.com 10 www.debbiegonzales.com www.almigal.com 11 Parts of the Ear – Picture Matching The pinna is part of the outer ear. The pinna is curved, circular ridged cartilage that captures and directs sound into the auditory canal. The auditory canal is part of the outer ear. The auditory canal transfers sound toward the inner ear. The ear drum is part in the middle ear. The ear drum is air tight and transfers sound to the tympanic cavity, where there are three bones called ossicles. The hammer is an ossicle found in the tympanic cavity. The hammer shifts position because of vibrations created by the ear drum. The anvil is an ossicle found in the tympanic cavity. The anvil is set in motion by the movement of the hammer. www.debbiegonzales.com www.almigal.com 12 The stirrup is an ossicle found in the tympanic cavity. The stirrup amplifies sound by thumping against another air tight seal called the oval window. The oval window is part of the inner ear. The oval window amplifies sound vibrations through a chamber filled with fluid called perilymph. The cochlea is part of the inner ear. Inside the cochlea is the organ of corti which is lined with special hairs that respond to frequencies, sending signals as sound to the auditory nerve. The auditory nerve is part of the inner ear. The auditory nerve sends signals as sound to the brain. www.debbiegonzales.com www.almigal.com 13 Parts of the Ear – Label Cut Outs The pinna is part of the outer ear. The pinna is curved, circular ridged cartilage that captures and directs sound into the auditory canal. The auditory canal is part of the outer ear. The auditory canal transfers sound toward the inner ear. The ear drum is part in the middle ear. The ear drum is air tight and transfers sound to the tympanic cavity, where there are three bones called ossicles. The hammer is an ossicle found in the tympanic cavity. The hammer shifts position because of vibrations created by the ear drum. The anvil is an ossicle found in the tympanic cavity. The anvil is set in motion by the movement of the hammer. www.debbiegonzales.com www.almigal.com 14 The stirrup is an ossicle found in the tympanic cavity. The stirrup amplifies sound by thumping against another air tight seal called the oval window. The oval window is part of the inner ear. The oval window amplifies sound vibrations through a chamber filled with fluid called perilymph. The cochlea is part of the inner ear. Inside the cochlea is the organ of corti which is lined with special hairs that respond to frequencies, sending signals as sound to the auditory nerve. The auditory nerve is part of the inner ear. The auditory nerve sends signals as sound to the brain. www.debbiegonzales.com www.almigal.com 15 The Parts of the Cochlear Implant – A Matching Game Objective: To demonstrate how cochlear implants work by use of a manipulative game. Materials: Cardstock Scissors Four part printouts o Parts of the Cochlear Implant – Master Copy (pages 16 to 17) o Parts of the Cochlear Implant – Label Matching (pages 18 to 19) o Parts of the Cochlear Implant – Picture Matching (pages 20 to 21) o Parts of the Cochlear Implant – Label Cut Outs (pages 22 to 23) Procedure: Print pages 16 to 23 on cardstock. Parts of the Cochlear Implant – Master Copy (pages 16 to 17) is intended to serve as a guide for correct matching of picture and labels. Print these pages to be used as a reference throughout the game. Use scissors to cut out Parts of the Cochlear Implant – Label Cut Outs (pages 22 to 23). These labels are to be used as manipulatives to be matched and placed in the appropriate blank spaces on the Parts of the Cochlear Implant – Label Matching (pages 18 to 19) and the Parts of the Cochlear Implant – Picture Matching (pages 20 to 21) grids. Read the manipulative cut out labels and place them in the appropriate blank space on the Parts of the Cochlear Implant – Label Matching (pages 18 to 19) Using the Parts of the Cochlear Implant – Picture Matching (pages 20 to 21), match the appropriate picture cut out next to its descriptive label. Mix up the cut out labels and start all over again! www.debbiegonzales.com www.almigal.com 16 Parts of the Cochlear Implant – Master Copy The microphone is found on the external part of the cochlear implant, worn on the back of the pinna. The microphone picks up sound. The speech processor is found on the external part of the cochlear implant. The speech processor filters, analyzes, and digitizes sound into coded signals. The transmitting coil and transmitter are found on the external part of the cochlear implant. These send coded radio signals to the receiver imbedded under the skin. The receiver is an internal part of the cochlear implant. The receiver takes coded electrical signals and delivers them to electrodes that have been surgically inserted in the cochlea. The electrodes are an internal part of the cochlear implant. Electrodes stimulate the remaining auditory nerve fibers in the cochlea. www.debbiegonzales.com www.almigal.com 17 Lastly, electrical sound information is sent through the auditory canal for interpretation by the brain. www.debbiegonzales.com www.almigal.com 18 Parts of the Cochlear Implant – Label Matching www.debbiegonzales.com www.almigal.com 19 www.debbiegonzales.com www.almigal.com 20 Parts of the Cochlear Implant – Picture Matching The microphone is found on the external part of the cochlear implant, worn on the back of the pinna. The microphone picks up sound. The speech processor is found on the external part of the cochlear implant. The speech processor filters, analyzes, and digitizes sound into coded signals. The transmitting coil and transmitter are found on the external part of the cochlear implant. These send coded radio signals to the receiver imbedded under the skin. The receiver is an internal part of the cochlear implant. The receiver takes coded electrical signals and delivers them to electrodes that have been surgically inserted in the cochlea. The electrodes are an internal part of the cochlear implant. Electrodes stimulate the remaining auditory nerve fibers in the cochlea. www.debbiegonzales.com www.almigal.com 21 Lastly, electrical sound information is sent through the auditory canal for interpretation by the brain. www.debbiegonzales.com www.almigal.com 22 Parts of the Cochlear Implant – Label Cut Outs The microphone is found on the external part of the cochlear implant, worn on the back of the pinna. The microphone picks up sound. The speech processor is found on the external part of the cochlear implant. The speech processor filters, analyzes, and digitizes sound into coded signals. The transmitting coil and transmitter are found on the external part of the cochlear implant. These send coded radio signals to the receiver imbedded under the skin. The receiver is an internal part of the cochlear implant. The receiver takes coded electrical signals and delivers them to electrodes that have been surgically inserted in the cochlea. The electrodes are an internal part of the cochlear implant. Electrodes stimulate the remaining auditory nerve fibers in the cochlea. www.debbiegonzales.com www.almigal.com 23 Lastly, electrical sound information is sent through the auditory canal for interpretation by the brain. www.debbiegonzales.com www.almigal.com 24 Common Core State Standards Annotation Comprehension and Collaboration SL.K.1: Participate in collaborative conversations with diverse partners about kindergarten topics and texts with peers and adults in small and larger groups. SL.1.1: Participate in collaborative conversations with diverse partners about grade 1 topics and texts with peers and adults in small and larger groups. SL.2.1: Participate in collaborative conversations with diverse partners about grade 2 topics and texts with peers and adults in small and larger groups. SL.3.1: Engage effectively in a range of collaborative discussions (one-on-one, in groups, and teacher led) with diverse partners on grade 3 topics and texts, building on others’ ideas and expressing their own clearly. SL.4.1: Engage effectively in a range of collaborative discussions (one-on-one, in groups, and teacher led) with diverse partners on grade 4 topics and texts, building on others’ ideas and expressing their own clearly. SL.5.1: Engage effectively in a range of collaborative discussions (one-on-one, in groups, and teacher led) with diverse partners on grade 5 topics and texts, building on others’ ideas and expressing their own clearly. SL.3.2: Determine the main ideas and supporting details of a text read aloud or information presented in diverse media and formats, including visually, quantitatively, and orally. SL.4.2: Paraphrase portions of a text read aloud or information presented in diverse media and formats, including visually, quantitatively, and orally. Sl.5.2: Summarize a written text read aloud or information presented in diverse media and formats, including visually, quantitatively, and orally. Presentation of Knowledge and Ideas SL.K.4: Describe familiar people, places, things, and events and, with prompting and support, provide additional detail. SL.1.4: Describe people, places, things, and events with relevant details, expressing ideas and feelings clearly. SL.K.5: Add drawings or other visual displays to descriptions as desired to provide additional detail. SL.1.5: Add drawings or other visual displays to descriptions when appropriate to clarify ideas, thoughts, and feelings. www.debbiegonzales.com www.almigal.com 25 Acknowledgements Author Wendy Kupfer www.almigal.com Illustrator Tammie Lyon http://www.childrensillustrators.com/tammielyon Guide Creator Debbie Gonzales www.debbiegonzales.com Healthy Hearing - http://www.healthyhearing.com The University of Miami School of Medicine – Cochlear Implants eHow – How Does and Ear Work? – http://www.ehow.com iStock Photos – www.istock.com www.debbiegonzales.com www.almigal.com