* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Noise-induce hearing loss Ototoxicity
Survey
Document related concepts
Lip reading wikipedia , lookup
Soundscape ecology wikipedia , lookup
Olivocochlear system wikipedia , lookup
Hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Auditory system wikipedia , lookup
Audiology and hearing health professionals in developed and developing countries wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
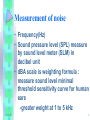
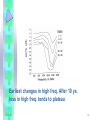
Noise-induce hearing loss & Ototoxicity โดย พญ.ปาริ ชาต บุณะสุ วรรณ อาจารย์ที่ปรึ กษา อ.ขวัญชนก ยิม้ แต้ 11/01/50 1 Noise - induce hearing loss • Pure tone : one frequency (ex. Tuning fork ,piano) • Complex tone : multi frequency ( ex. Talking ,music) • Noise : undesirable & loud sound to harm hearing 11/01/50 2 Measurement of noise • Frequency(Hz) • Sound pressure level (SPL) measure by sound level meter (SLM) in decibel unit • dBA scale is weighting formula : measure sound level minimal threshold sensitivity curve for human ears -greater weight at 1 to 5 kHz 11/01/50 3 • Pathogenesis • Rupture mb of outer hair cell Inc.glutamate,NO,produce ROS & free radical Dec. Mg , inc. Ca in intracellular 11/01/50 4 PATHOGENESIS • Temporary threshold shift (TTS) : exposure moderately intense sounds and lead to elevate thresholds for higher mid frequency (3000-6000 Hz) • TTS can occur minute to hr & day and it can recovery in 16 hr (24 hr) • If TTS is not recovery & reexposed to noise , it change to PTS • Longer expose > increase TTS but interrupt expose >less TTS ( recovery within the rest interval) 11/01/50 5 ข้ อเท็จจริงเกีย่ วกับ Temporary threshold shift • ได้ แก่ - Temporary threshold shift จากได้ ยนิ เสี ยงทีด่ ังมากกว่ า 100 เดซิ เบล ในหนึ่งวัน อาจแตกต่ างกันในแต่ ละบุคคลได้ ต้งั แต่ ไม่ มีการ เปลีย่ นแปลงจนถึงมีการได้ ยนิ เสี ยไป 40 เดซิเบล - ลักษณะเฉพาะการสู ญเสี ยการได้ ยนิ จากการทางานในโรงงาน อุตสาหกรรมคือ มีการเปลีย่ นแปลงของการได้ ยนิ มากทีส่ ุ ดที่บริเวณ การรับเสี ยงทีค่ วามถี่ระหว่ าง 4000-6000 Hz - ส่ วนใหญ่ ของการเกิด TTS มักเกิดขึน้ ภายใน 2 ชั่วโมง ของการได้ ยนิ เสี ยงทีม่ ีความดัง 11/01/50 6 ข้ อเท็จจริงเกีย่ วกับ Temporary threshold shift - ปริ มาณของการสู ญเสี ยการได้ยนิ แบบชัว่ คราวที่มีความถี่ใดจะ แปรผกผันกันปริ มาณของการสู ญเสี ยแบบถาวรที่ความถี่น้ นั หมายความว่าถ้าผูป้ ่ วยมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงของระดับการได้ยนิ ที่ ความถี่ใดมากเป็ นแบบถาวรแล้ว ผูป้ ่ วยจะมีโอกาสเปลี่ยนแปลง ระดับการได้ยนิ แบบชัว่ คราวหลังจากการได้ยนิ เสี ยงที่ความถี่น้ นั น้อย 11/01/50 7 ข้ อเท็จจริงเกีย่ วกับ Temporary threshold shift - การฟื้ นตัวของการสู ญเสี ยการได้ยนิ แบบชัว่ คราวมักเกิดขึ้นยายใน 1 หรื อ 2 ชัว่ โมง แรกหลังจากที่เสี ยงนั้นหยุด - เสี ยงที่ไม่ทาให้เกิดการสู ญเสี ยการได้ยนิ แบบชัว่ คราวจะไม่สามารถ ทาให้เกิดการสู ญเสี ยการได้ยนิ แบบถาวรได้เช่นกัน - ลักษณะของ Audiogram ที่พบในการสู ญเสี ยการได้ยนิ แบบ ชัว่ คราวจะเหมือนกับที่วดั ได้เมื่อเกิดการสู ญเสี ยการได้ยนิ แบบถาวร 11/01/50 8 Permanent threshold shift (PTS) • Permanent threshold shift (PTS) : elevated threshold is irreversible because cochlea is damaged • Protective against NIPTS • 1. expose intermittency • 2. acoustic reflex • 3. efferent innervation of OHC ( strong resistance to NIHL) -The precise relationship between the TTS and PTS stages of hearing loss due to noise exposure is unknown - Recent studies : unrelated 11/01/50 9 Earliest changes in high freq. After 10 ys. loss in high freq. tends to plateau 11/01/50 10 Pathology • TTS : stereocillia of OHC are floppy&disarray may recover function again • PTS : fusion & loss stereocilia , primary side inj. at rootlets(connection of stereocilia with top of hair cell) 11/01/50 11 • • • • 11/01/50 PTS has been seperated to 2 Dz : Acoustic trauma : singer & short lasting exposure to intense sound , & painful direct damage middle & inner ear(organ of Corti, tearing Mb, rupturing cell, peri&endolymph to mix), not proceeded by TTs • NIHL : • chronic exposure to less intense sound , result hearing loss ,damage inner ear ( gradual loss of stereocilia & hair cell),proceeded by TTs • usually attributed to metabolic process 12 Acoustic trauma VS NIHL ลักษณะเฉพาะ Acoustic trauma ประวัติของการสัมผัส การสัมผัสเสี ยงที่มีความดังมากเกินใน การสัมผัสเสี ยงที่มีความดังปานกลาง ระยะเวลาอันสั้นและสัมผัสเพียงครั้งเดียว จนถึงดังมากเป็ นประจา อาการและการแสดง ปวดหูและการได้ยนิ เสื่ อมอย่างเฉียบพลัน การได้ยนิ เสื่ อมอย่างค่อยเป็ นค่อยไปและ พบมีอาการเวียนศีรษะร่ วมด้วย มีเสี ยงรบกวนในหู ไม่ค่อยพบอาการเวียน ศีรษะ หูขา้ งที่มีพยาธิสยาพ ส่ วนใหญ่เป็ นข้างเดียวโดยเฉพาะข้างที่อยู่ มักเป็ นทั้งสองข้างเท่าๆกัน ใกล้แหล่งกาเนิดเสี ยง ชนิดของการได้ยนิ เสื่ อม พบได้ท้ งั แบบการนาเสี ยงเสี ย และแบบ ประสาทหูเสื่ อม 11/01/50 Noise – induced hearing loss มักพบเป็ นแบบประสาทหูเสื่ อม 13 Symp & Obj finding in NIHL • • • • • • 11/01/50 Permanent SNHL with damage cochlear hair cell & primarily OHCS Hx long term expose to dangerous noise level(i.e., 90 dBA for 8 hour/day) Gradual loss of hearing over 5-10 yr of exposure Hearing loss that stabilizes once the noise exposure is terminated Speech recognition score that are consistent with audiometric loss Hearing loss involve initially higher frequency 3-8 kHz before including <= 2kHz 14 Symp & Obj finding in NIHL • symptom : difficulty in hearing and understanding ordinary speech • Profile of noise - induced threshold hearing is usually symmetric for both ears. • Other forms of noxious sound, such as the gunfire associated with sport shooting cause an asymmetric pattern of hearing loss • Length of time of exposure to loud noise increases, hearing loss becomes greater and begins to affect adjacent higher and lower frequencies 11/01/50 15 Anatomic mechanisms underlying noise damage • • • • • • 11/01/50 Classical audiometric pattern NIHL 4 kHz notch explained by resonator fx of EAC The other mech.: Severe motion basilar mb Metabolic exhaustion of activated cell Activity induce vv narrowing isch. Ionic damage 16 New knowledge about cellular/Molecular Mechanisms of Noise-Induced hearing Loss • Hair Cell Regeneration and Repair -In human : noise – induced hair cell loss irreversible -In animal : Hair Cell Regeneration and Repair • Protection from Conditioning the Cochlear – Efferent System – Both TTS&PTS : amount of threshold shift can be reduced by prior exposure “ toughening” or “conditioning” – Efferent func. Of OHC related resistance to NIHL 11/01/50 17 New knowledge about cellular/Molecular Mechanisms of Noise-Induced hearing Loss • Pharmacologic Protection from Noise – Induced Hearing Loss • Hypoxia is a major pathogenic factor in NIHL – Noise-induced oxidative stress leading to cochlear injury was related to (1) impaired mitochondrial function (2) glutamate excitotoxicity (3) depletion of glutathione (GSH) 11/01/50 18 pharmacologic agent : • acetyl-L-carnitine:help maintain mb of mitochondria • Carbamathione is glutamate antagonist • Allopurinol,xanthine oxidase blocker,N-Lacetylcysteine,GSHperoxidase,superoxide dismutate : combat cellular oxidative stress 11/01/50 19 New knowledge about cellular/Molecular Mechanisms of Noise-Induced hearing Loss • Susceptibility – Some ears are more easily damaged by noise than others. – Genetically cochlea (e.g., stiffness of the cochlear partition), or cochlear ultrastructure (e.g., density of hair cells). • Most exciting in current experimental research : genetic origin. 11/01/50 20 Interaction • Age : relate elevate SPL in adult (expose to noise) but not relate in elderly : HL =sum of threshold shift from aging & from noise 11/01/50 21 Interaction • • • 11/01/50 Vibration : relate elevate SPL in pt (expose to noise) Drug & chemical :ototoxic drug: aminoglycoside,Platinum anti tumor,Loop diuretic, salicylate : chemical (CO , hydrogen cyanide , toluene) relate elevate SPL in pt (expose to noise) Individual susceptibility 22 Other Adverse Effects Caused By Noise • Damage to the vestibular system because – balance receptors are coupled with the auditory receptors. – Great similarity cochlear and vestibular hair cell ultrastructure. – Common arterial blood supply. – Complaints of disequilibrium. 11/01/50 23 Other Adverse Effects Caused By Noise • Nonauditory problems : biologic stressor • prolonged activation of the autonomic nervous system, the pituitary-adrenal complex, resulting in general health impairment. • Circulatory problem, such as hypertension • Disorders involving gastrointestinal motility, such as peptic ulcers • Emotional unrest 11/01/50 24 Evaluate & diagnosis • Hx + PE • PTA : pure tone average asymmetries> 15dB →another etiology or asymmetric exposure( rifles and shotguns) • NIHL is devided 2 type: • Nonoccupational exposure • occupational exposure ( table : diag. occupational NIHL) 11/01/50 25 table : diag. occupational NIHL 11/01/50 26 Early detection of NIHL • Detecting small acoustically induced injuries to the organ of Corti (i.e., the beginning stages of NIHL) • OAEs is ideal for assesing cochlea fx , it well recognized sensitivity to detect OHC class of receptor cell which involved in initial stage • OAE 2 type • DPOAE • TEOAE 11/01/50 27 Treatment • Terminate noise at least 48 hr • if TTS is recovery in 16 hr • if HL > 60 dB recovery 48 hr – 20d • Anti noise elixir : pharmacologic agent , antioxidants and related compounds 11/01/50 28 Handicap & compensation • Hearing handicap : sufficient to affect the individual’s efficiency in the activity living ,interfere with speech communication • Typical pt. can hear speech – without difficulty in vowel sound – difficulty discriminating among consonant sound (high frequency ,low intensity sound) 11/01/50 29 Hearing conservation program( HCP) • Essential components of HCP • 1. Noise measurement -Assessment of noise levels OSHA (occupational safety & health administration) Regulations • 5dB rule • Allowable levels – – – – – 11/01/50 – 90dBA for 8 hours 95dBA for 4 hours 100dBA for 2 hours 105dBA for 1 hour 110dBA for 30 minutes 115dBA for 15 minutes 30 Hearing conservation program( HCP) • 2. Engineering or administrative control to reduce exposure: improve machine for dec. sound & vibration • 3. Periodic audiometry & f/u : Serial audiograms , exam before start working and then exam every 6 mo 11/01/50 31 4. Use of personal hearing protection devices(HPDs) Earplugs 11/01/50 Earmuffs 32 • ค่าเฉลี่ยของความสามารถในการ ป้องกันเสี ยงของปลัก๊ อุดหู และที่ ครอบหู เมื่อใส่ แยกกัน และเมื่อใส่ รวมกัน 5. Education,motivation,counseling 11/01/50 33 Evaluation of hearing handicap in thailand • ตามประกาศกระทรวงมหาดไทย 12 กย 2537 • ข้อ 1 กรณี ลูกจ้างต้องสู ญเสี ยอวัยวะส่ วนของรางกาย ตามมาตรา 18(2)ให้ มีระยะเวลาจ่ายเงินทดแทนดังนี้ (5) หูหนวกทั้งสองข้าง ห้าปี สิ บเดือน (6) หูหนวกหนึ่งข้าง สองปี แปดเดือน • หากค่าเฉลี่ยของระดับการได้ยนิ 500 1000 2000 3000 Hz >25dB • ถือว่ามีการสู ญเสี ยการได้ยนิ สาหรับหูขา้ งเดียวในแต่ละเดซิเบลมีค่า เท่ากับร้อยละ1.5 11/01/50 34 Evaluation of hearing handicap in thailand • • • • หากการได้ ยนิ หูสองข้ างยังเหลือคานวณดังนี้ ระดับการได้ ยนิ มากกว่ า 100 dB คิดเป็ น 100 dB ระดับการได้ ยนิ ดีกว่ า 0 dB คิดเป็ น 0dB รวมค่ าระดับการได้ ยนิ แต่ ละข้ างทีค่ วามถี่ 500 1000 2000 3000 Hz • นาค่ าทีไ่ ด้ ไปดูในตาราง • นาค่ ามาคานวณการจ่ ายทดแทน เช่ น คานวณได้ 20%ได้ ค่า ทดแทน 70*20/100=14 เดือน 11/01/50 35 Ototoxicity • Introduction • Ototoxicity : tendency of a drug or chemical agent to cause inner ear dysfunction, producing symptoms of hearing loss, dizziness, or both. 11/01/50 36 Aminoglycoside Antibiotics • Vestibular toxicity 15% ขึ้นกับจานวน methylamine gr., Cochlear toxicity 20% ขึ้นกับจานวน free amino gr. - Vestibular toxicity : streptomycin, Gentamicin, Tobramycin, kanamycin, dmikacin, neomycin, netilmycin, sisomycin - Cochlear toxicity : neomycin, amikacin, kanamycin, tobramycin, Gentamycin, streptomycin, netilmycin, sisomycin 11/01/50 37 • Pharmacokinetics • ยาในกลุ่มนี้จะเข้าสู่ หูช้ นั ในทางเส้นเลือด เข้าสู่ perilymph ทาง spiral ligament และ stria vascularis หลังจากนั้นจึงเข้าสู่ endolymph และorgan of Corti ตามลาดับ • Histopathology • Cochlear and/or vestibular hair cells serve as primary targets for injury. • In the organ of Corti, OHC of basal turn are first damaged. • IHC more resistant. • Progressive destruction of spiral ganglion cells. • The stria vascularis become thinner. 11/01/50 38 • Mechanisms of ototoxicity Ototoxicity complex reactive oxygen species (ROS) : react with various cell components, phospholipids, proteins, DNA cell death. • Clinical Manifestations • High-frequency hearing loss,tinnitus • Continued exposure hearing loss progresses to lower frequencies. • Vestibular ototoxicity : imbalance, ataxia, dramatically worsened by motion, with relative freedom from symptoms during periods of complete immobility. 11/01/50 39 • Some clinical improvement (beginning 2 months after onset of symptoms) it is rarely complete irreversible HL • Various risk factors : Bactermia, fever, hepatic and renal dysfunction, combinations of another ototoxicity drug 11/01/50 40 Suggested guidelines for monitoring • (1) In patients with normal kidney function, the peak level ( first day or two of treatment), the trough level (1 week) and both peak and trough levels (every week after ) • (2) In patients with impaired but stable renal function, the peak level ( within the first 2 days of treatment), the trough and peak level within 1 week, then both peak and trough levels ( twice weekly thereafter) • (3) In the presence of impaired and unstable kidney function, peak and trough levels ( within the first 2 days), Serum levels may need to be measured as frequently as every day as long as renal function is unstable. • (4) After any changes in dosage, peak and trough levels are determined within the next 2 days. 11/01/50 41 • Prevention • มีการใช้ ยา fosfomycin, glutathione, poly-L-aspartic acid (PLAA) , • 4-methylcatechol อาจช่ วยลดการได้ ยนิ เสื่ อมจากยา aminoglycoside ได้ • Iron chelation (iron +aminoglycosides > free radicals) 11/01/50 42 Antineoplastic Agents : Cisplatin • Potent antineoplastic agent. • Side effects include nausea and vomiting, neurotoxicity, ototoxicity, and nephrotoxicity. • Pharmacokinetics • adenylate cyclase ,lateral wall of stria vascularisendolymph,endocochlear potential • ขบวนการขนส่ งในเซลล์ ปริมาณ ca ในเซลล์ ลดลง 11/01/50 43 • Histopathology • Degeneration of outer hair cells in the lower turns of the cochlea, spiral ganglia, and cochlear nerve. • Fusion of stereocilia of the outer hair cells, with damage to the cuticular plate. • Stria vascularis was atrophic. 11/01/50 44 • Mechanisms of Ototoxicity • Production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) : superoxide anion, hydrogen peroxide , reactive nitrogen species (RNS) : nitric oxide cell damage. • OHC in the basal turn( most susceptible) : low stores of glutathione. • In vitro, evidence that cisplatin ototoxicity : mediated by the cell death pathways. 11/01/50 45 • Clinical Ototoxicity • Hearing loss : highly related to dose, age of the patient, and other factors, such as noise exposure, other ototoxicity drugs, depleted nutritional state, cranial irradiation, Children. • Symptoms : hearing loss ( irreversible) , ear pain, or tinnitus( 2% to 36% , may be transient or permanent) >50% of patients who received cisplatin in dose >400 mg/ m2 cumulative dose had permanent hearing loss. 11/01/50 46 • Prevention • sodium thiosulfate หลังจากให้ ยา Cisplatinum ไปแล้ ว 4 ชั่วโมงจะช่ วยลดและป้องกันการได้ ยนิ เสื่ อม • D- Methionine, Fosfomycin , free oxygen radical scavengers เช่ น glutathione, gingko biloba extract • Caspase inhibitors (inhibitor of cell death cascade) 11/01/50 47 • • • • • 11/01/50 Carboplatin Newer platinum compound. Less nephrotoxic, Less ototoxicity than cisplatin. High dose carboplatin (2 g/m2 total dose) hearing loss. Mechanisms of ototoxicity : production of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species 48 Loop Diuretics Pharmacokinetics & Clinical findings • Furosemide : average half – life of 29.5 minutes may be as long as 10 to 20 hours. : Cause temporary and some permanent of hearing loss tinnitus and vertigo. • Bumetanide : more potent sulfonamide loop diuretic. : Smaller incidence of hearing loss than furosemide. • Piretanide : no patients were found to have hearing loss. • Torsemide : a new loop diuretic , No evidence . 11/01/50 49 Histopathology & Mechanisms of Ototoxicity • Primary target : stria vascularis (extensive edema) loss of auditory function. The Na/2Cl/K transporter (SLG12A2) o Biochemical interaction b/w aminoglycosides & loop diuretics: aminogly. promotes penetration of loop diuretics to inner ear 11/01/50 50 • Prevention • Ototoxicity of furosemide may be reduced by infusing rates of less than 15 mg./minute. • No combinations of another ototoxicity drug 11/01/50 51 Salicylates • Pharmacokinetics. • เข้ าสู่ หูช้ันในทางเลือด ตรวจพบยาที่ stia vascularis และ spiral ligament • ยับยั้ง เอนไซม์ cyclooxygenase : prostaglandins ในเซลล์ลดลง leukotrienes เพิม่ ขึน้ ทาให้ หลอดเลือดหดตัวมากขึน้ • Histopathology : not show 11/01/50 52 • Mechanisms of Ototoxicity • Effects on the cochlea : by changes in blood flow , by changes in the stiffness the lateral membrane of the outer hair cells. • Clinical Ototoxicity • Hearing loss ( reversible) related to concentration in blood. • 20 to 50 mg/dL can have hearing losses 30 dB. • 11 mg/dL : hearing loss was 12 dB. 11/01/50 53 • Prevention • จากการศึกษาใน chinchilla ให้ dexamethasone ผ่ าน round window membrane สามารถป้องกันการได้ ยนิ เสื่ อม ได้ บางส่ วน ยากลุ่ม adrenergic blockers และ zinc อ่ าน ป้ องกันและลดภาวะเป็ นพิษต่ อหู 11/01/50 54 Quinine and Related Drug • Pharmacokinetics • Block Ca –K channel cell edema,dec.blood,abnormal OHC func. • Clinical findings • Quinine toxicity syndrome (cinchonism) : Deafness, vertigo, tinnitus, headache, visual loss and nausea. • prolonged courses of treatment : 20% high frequency hearing loss (reversible) , 4-kHz notch, speech discrimination score may be less than 30% • Prevention • effect blocked by nimodipine, a calcium channel blocker 11/01/50 55 Erythromycin and Related Macrolide Antibiotics • Pharmacokinetics รบกวนการส่ งกระแสประสาทรับเสี ยงที่บริ เวณก้านสมอง • Clinical findings • Erythromycin ototoxicity : bilateral sensorineural hearing loss, “blowing” tinnitus, some cases vertigo , confusion, fear, psychiatric disturbances. • Most hearing loss and tinnitus : transient (reversible), Recovery within 1 to 2 weeks after stopping. 11/01/50 56 • Audiometric : flat type of sensorineural hearing loss. High frequency loss. • Auditory brain stem response absence of waves I to III. Normalized after cessation of erythromycin. • Related : Elderly, liver or kidney disease, high dose erythromycin. 11/01/50 57 • Prevention • (1) Pretretment audiograms in elderly patients , impaired liver or kidney function • (2) Caution should be used in combining erythromycin with other potentially ototoxic drugs. • (3) If the serum creatinine ins >1.8 , the daily dose of erythromycin should not be > 1.5 g. 11/01/50 58 • Azithromycin • Clinical findings : hearing loss -audiograms : mild to moderate sensorineural hearing loss. -Resolved within 2 to 4 weeks after cessation of treatment ( reversible ) • mechanisms of ototoxicity : not know. 11/01/50 59 • Vancomycin • Vancomycin have a low probability of causing permanent ototoxicity if it is not given in combination with another ototoxic agent or high doses (>200mg/kg/d), or liver or kidney failure. • Not know temporary or permanent. 11/01/50 60 Topical ototopic agent o ส่ วนประกอบในยาหยอดหูทที่ าให้ เกิดพิษต่ อหู ได้ แก่ o ยาantibiotics เช่ น aminoglycosides , chloramphenicol , polymyxin B เป็ นต้ น o สาร antiseptics เช่ น acetic acid, alcohol, chlorhexidine , cresylate, povidone – iodine, potassium iodide เป็ นต้ น o สารละลาย เช่ น propylene glycol,polyethylene glycol เป็ นต้ น 11/01/50 61 o Ototoxicity : several factors 1.Status of middle ear ในผูป้ ่ วยที่มีอาการอักเสบของหูช้ นั กลางจากการติดเชื้อมักจะมี middle ear effusion และ inflammatory changes ของ middle ear mucosa ทาให้ toxic agent จากยาหยอดหูมีความเข้มข้นลดลง และเข้าถึง round window membrane ได้ยาก 2. Size of TM defect : large TM defect > agent to ME 3. ET tube function : ability to open affect duration of exposure 11/01/50 62 • 4. Status of round window membrane : ยาวะเป็ นพิษต่อหูจากยาหยอดหูในมนุษย์นอ้ ยกว่าในสัตว์ ได้แก่ 1) round window membrane ของมนุษย์ จะมี false membrane ทีเ่ ป็ น cuboidal epithelium คลุม 2) round window membrane ของมนุษย์มกั จะหนากว่าในสัตว์ 3) round window membrane ของมนุษย์มี densely structured intermediate layer • 5. Concentration of agent used & duration of exposure Prevention • Avoid prolong use esp.TM defect • Avoid use in healthy ear 11/01/50 63 Chemicals • Oraganic solvents :Trichlorethylene, Xylene , Styrene , Hexane , Carbon disulfide , Toluene • Gas : Carbon monoxide • Heavy metals : Arsenic ,Mercury , Tin, Lead 11/01/50 64 DIAGNOSIS • Cochleotoxicity 1.Audiometry แนะนาให้ตรวจการได้ยนิ เฉพาะผูป้ ่ วยที่มีปัจจัย เสี่ ยง หากใช้ high frequency audiometry จะมี ความไวในตรวจวัดการเกิด ototoxicity ในระยะเริ่ มต้นได้ • Limit by : not perform at bedside,require pt.participation &concentration 2. Electrocochleography ไวในการตรวจวัดการเกิด ototoxicity ในระยะเริ่ มต้น แต่ ราคาแพง สิ้ นเปลืองเวลา และบุคลากรมาก 11/01/50 65 3. Otoacoustic emission • Adv. : rapid bedside testing, Specific toward OHC , no pt. participation requirement • Disadv. : cannot be used in all pt.( ME fluid) 4. Auditory brainstem response ไวสู ง แต่ใช้เวลา ในการตรวจนานและเครื่ องมือราคาแพง 11/01/50 66 o Vestibulotoxicity : 1.Electronystagmography 2.Rotation test 3.Dynamic posturography impractical, often impossible to detect early changes 11/01/50 67 TREATMENT 1.การวินิจฉัยยาวะเป็ นพิษต่อหูจากยาและสารเคมีต้ งั แต่แรกเริ่ มมี อาการ 2.หยุดยาที่ทาให้เกิดพิษต่อหู 3.ให้ยาหรื อสารที่ป้องกันและลดอาการยาวะเป็ นพิษต่อหู 4.การฟื้ นฟูสมรรถยาพ • การได้ยนิ เสื่ อม : ใช้เครื่ องช่วยฟัง , Cochlear implant • เสี ยงดังรบกวนในหู : อธิบายสาเหตุและแนะนา • อาการเวียนศีรษะและเสี ยสมดุล : แนะนาให้ผปู ้ ่ วยทากายบริ หาร เพื่อรักษาอาการเวียนศีรษะ 11/01/50 68 11/01/50 69