* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Early Childhood Caries Redux, Part II
Focal infection theory wikipedia , lookup
Dentistry throughout the world wikipedia , lookup
Water fluoridation wikipedia , lookup
Periodontal disease wikipedia , lookup
Dental hygienist wikipedia , lookup
Water fluoridation in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Fluoride therapy wikipedia , lookup
Dental degree wikipedia , lookup
Special needs dentistry wikipedia , lookup
Dental emergency wikipedia , lookup
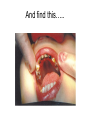
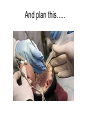
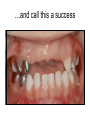
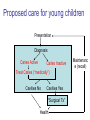
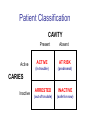
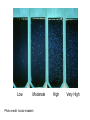
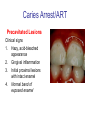
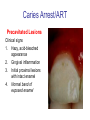
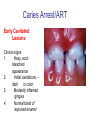
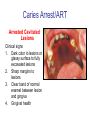
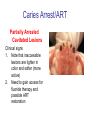
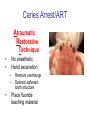
Early Childhood Caries Redux, Part II Burton L. Edelstein DDS MPH Chair, Social & Behavioral Sciences Columbia University School of Dental and Oral Surgery Founding Director, Children’s Dental Health Project When dentists see these… And find this….. They often think this…. And plan this….. …and call this a success And it would be a success…. If it worked to stop disease progression (But it generally doesn’t) Alternative Dental Office Management of ECC Alternative Dental Office Management of ECC • New Techniques 1. 2. 3. 4. Changed Terminology with Parents & Staff Caries Risk Assessment Primary Prevention & Anticipatory Guidance Caries Arrest/ART 1. Changed Terminology and Resultant Opportunities New Terminology • Premise: Can’t treat what you can’t name • Terminology: – – – – Caries: The pathologic decay process White Spots: An initial-stage sign of caries damage Cavities: A late-stage sign of caries damage* Tooth Decay: A global term for caries and cavities • Conclusion: Terminology allows caries treatment at various levels *GV Black 110 years ago, “Cavities of decay” Cavities are the result of failed caries management Current care for young children Presentation Diagnosis Cavities Yes Surgical Treatment Cavities No No Treatment Health Maintenance (Recall) Proposed care for young children Presentation Diagnosis Caries Active Caries Inactive Treat Caries (“medically”) Cavities No Cavities Yes “Surgical Tx” Health Maintenanc e (recall) Patient Classification CAVITY Present Active Absent ACTIVE AT RISK (in trouble) (prodromal) ARRESTED INACTIVE (out of trouble) (safe for now) CARIES Inactive New opportunities emanating from new terminology • Opportunities – to assess • caries activity as well as cavity status • level of individual risk for future disease – to engage in • true primary prevention • anticipatory guidance • disease suppression – To treat active, at risk, arrested, and inactive patients through four different approaches Differential Treatment Approaches • Active – Suppress caries activity before repairing any teeth – If necessary, treat sufficiently to stop pain/infection • Arrested – Minimal repair: Restore only those teeth essential to esthetics and function – Maintain arrest • At Risk – Aggressively treat caries process to prevent cavitation – Watch for “white spot lesions” & manage aggressively • Inactive – Initiate “anticipatory guidance” and monitor 2. Caries Risk Assessment Caries Risk Assessment “NIH Consensus Development Conference on Diagnosis and Management of Dental Caries Throughout Life” March 2001 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Part III: Indicators of Risk Socioeconomic and Behavioral Sugar Consumption Low Birth Weight Microbiologic Factors Inheritance Metal Ion Exposure Caries Risk Assessment 1. 2. 3. American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Caries-Risk Assessment Tool (CAT) Risk Factors Clinical Conditions Caries evidence, Hygiene/gingivitis, Appliances, Hypoplasia, Mutans levels Environmental Characteristics Fluoride exposure, Sugar exposure/frequency, Socioeconomic status, Use of dental care General Health Conditions Saliva impairment, Special needs children Caries Risk Assessment The Most Useful Tautology “Past Caries Experience is the Best Predictor of Future Caries Experience” CAT includes: – – – White spots Radiographic evidence of early decay Past caries experience in last 12-24 months These are not risk factors for caries but are evidence of existing caries activity Caries Risk Assessment Mutans Streptococci • • • • • • Necessary but not sufficient for caries initiation Acquired by children, typically from mothers Transferred by salivary contact First evident in youngest children as voluminous plaque on anterior teeth Associated with inception, prevalence, and incidence of caries (also extent and severity) Readily cultured at chairside Caries Risk Assessment Mutans Streptococci • • • Useful measure of current caries activity Maternal suppression delays transmission and subsequent caries in children High specificity but low sensitivity (Kids who lack cavities have little mutans but kids with cavities may or may not have high mutans) • Highly responsive to diet control and fluoride exposure Caries Risk Assessment 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Mutans Culture Collect saliva on sterile tongue blade from dorsum of tongue Impress onto selective medium Provide low Oxygen environment Incubate 2 days Read using chart as zero, low, mod, high, or very high Low Moderate Photo credit: Ivoclar vivadent High Very High Caries Risk Assessment Mutans Conference Report • • • • • • • Colonize only after first teeth appear Highest concentration over lesions Increased in volume with sugar ingestion Synthesize macromolecules to attach to teeth Rapidly produce acid and are acid tolerant Always recovered on initial & advanced lesions Virulence associated with sugar consumption 3. Primary Prevention and Anticipatory Guidance Prevention/Guidance 1. 2. 3. 4. True “primary prevention” “Anticipatory guidance” “Dental Home” “Age one dental visit” Prevention/Guidance True Primary Prevention • • By definition, prevents disease occurrence by avoiding disease determinants For caries, must target mutans implantation by – – – • Reducing source availability Reducing transfer opportunities Increasing receptor resistance Intervention in saliva transfer only appropriate for “high-risk” mothers – those who have had high caries experience Prevention/Guidance True Primary Prevention • Reduce source: – • Xylitol chewing gum, Stannous Fluoride, Chlorhexidine (dental repair) Reduce transmission – – • Spoon sharing, Pacifier cleaning, Hand-in-mouth Frequency, timing, amount Reduce implantation – Fluoride varnish Prevention/Guidance Anticipatory Guidance • Pediatricians’ Concept: – • Classic Example: – • Providing information and guiding health behaviors in anticipation of normal development or onset of risk Informing parents of child’s impending ability to roll over and instructing on fall prevention Application to dentistry: – Informing parents of the conditions that create caries & cavities; its natural progression; and its prevention Prevention/Guidance Dental Home (AAPD Policy2001) • • Built on concept of “Medical Home” – AAP “Child’s first visit establishes dental home” – – – Opportunity for prevention Goal is to reduce risk of preventable disease Provides risk assessment; tailored counseling; anticipatory guidance; emergency plan; access to comprehensive dental care, including any necessary referrals Prevention/Guidance Age One Dental Visit • • • Accepted policy by ADA, Pediatric Dentists, Pediatricians, and Public Health Association Intended to allow for true primary prevention, establishment of dental home, and ongoing anticipatory guidance Consists of history, risk assessment, examination, tailored anticipatory guidance, and counselling 4. Caries Arrest and ART Caries Arrest/ART Precavitated Lesions Clinical signs 1. Hazy, acid-bleached appearance 2. Gingival inflammation 3. Initial proximal lesions with intact enamel 4. Normal band of exposed enamel Caries Arrest/ART Precavitated Lesions Clinical signs 1. Hazy, acid-bleached appearance 2. Gingival inflammation 3. Initial proximal lesions with intact enamel 4. Normal band of exposed enamel Caries Arrest/ART Early Cavitated Lesions Clinical signs 1. Hazy, acidbleached appearance 2. Initial cavitations – dark in color 3. Modestly inflamed gingiva 4. Normal band of exposed enamel Caries Arrest/ART Arrested Cavitated Lesions Clinical signs 1. Dark color to lesions or glassy surface to fully excavated lesions 2. Sharp margins to lesions 3. Clear band of normal enamel between lesion and gingiva 4. Gingival health Caries Arrest/ART Partially Arrested Cavitated Lesions Clinical signs 1. Note that inaccessible lesions are lighter in color and softer (more active) 2. Need to gain access for fluoride therapy and possible ART restoration Caries Arrest/ART • Attaining Caries Arrest – Intensive diet control to reduce frequency of attack – Intensive fluoride control to increase resistance and remineralize – Sequential excavation to prevent pain and build trust – Intensive follow-up visits with sequential cultures to monitor compliance Caries Arrest/ART Atraumatic Restorative Technique • • No anesthetic Hand excavation – – • Remove overhangs Debreid softened tooth structure Place fluoride leaching material Warning about change & its uncertainty: “Yesterday, we stood at the brink of the future. Today, we take a giant step forward.” President of the Ukraine on declaring independence